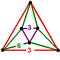
The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb, alternated cubic honeycomb is a quasiregular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of alternating regular octahedra and tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:2.

In eight-dimensional geometry, an eight-dimensional polytope or 8-polytope is a polytope contained by 7-polytope facets. Each 6-polytope ridge being shared by exactly two 7-polytope facets.

In seven-dimensional geometry, a 7-polytope is a polytope contained by 6-polytope facets. Each 5-polytope ridge being shared by exactly two 6-polytope facets.

In nine-dimensional geometry, a nine-dimensional polytope or 9-polytope is a polytope contained by 8-polytope facets. Each 7-polytope ridge being shared by exactly two 8-polytope facets.

In six-dimensional geometry, a uniform 6-polytope is a six-dimensional uniform polytope. A uniform polypeton is vertex-transitive, and all facets are uniform 5-polytopes.

In four-dimensional euclidean geometry, the tesseractic honeycomb is one of the three regular space-filling tessellations, represented by Schläfli symbol {4,3,3,4}, and constructed by a 4-dimensional packing of tesseract facets.
In geometry, a hypercubic honeycomb is a family of regular honeycombs (tessellations) in n-dimensional spaces with the Schläfli symbols {4,3...3,4} and containing the symmetry of Coxeter group Rn for n ≥ 3.
The 8-cubic honeycomb or octeractic honeycomb is the only regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 8-space.

In geometry, the alternated hypercube honeycomb is a dimensional infinite series of honeycombs, based on the hypercube honeycomb with an alternation operation. It is given a Schläfli symbol h{4,3...3,4} representing the regular form with half the vertices removed and containing the symmetry of Coxeter group for n ≥ 4. A lower symmetry form can be created by removing another mirror on an order-4 peak.
In five-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 5-simplex honeycomb or hexateric honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation. Each vertex is shared by 12 5-simplexes, 30 rectified 5-simplexes, and 20 birectified 5-simplexes. These facet types occur in proportions of 2:2:1 respectively in the whole honeycomb.
In geometry an omnitruncated simplectic honeycomb or omnitruncated n-simplex honeycomb is an n-dimensional uniform tessellation, based on the symmetry of the affine Coxeter group. Each is composed of omnitruncated simplex facets. The vertex figure for each is an irregular n-simplex.
In six-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 6-simplex honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation. The tessellation fills space by 6-simplex, rectified 6-simplex, and birectified 6-simplex facets. These facet types occur in proportions of 1:1:1 respectively in the whole honeycomb.

In geometry, the simplectic honeycomb is a dimensional infinite series of honeycombs, based on the affine Coxeter group symmetry. It is represented by a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram as a cyclic graph of n + 1 nodes with one node ringed. It is composed of n-simplex facets, along with all rectified n-simplices. It can be thought of as an n-dimensional hypercubic honeycomb that has been subdivided along all hyperplanes , then stretched along its main diagonal until the simplices on the ends of the hypercubes become regular. The vertex figure of an n-simplex honeycomb is an expanded n-simplex.

In geometry, the cyclotruncated simplectic honeycomb is a dimensional infinite series of honeycombs, based on the symmetry of the affine Coxeter group. It is given a Schläfli symbol t0,1{3[n+1]}, and is represented by a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram as a cyclic graph of n+1 nodes with two adjacent nodes ringed. It is composed of n-simplex facets, along with all truncated n-simplices.
In seven-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 7-simplex honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation. The tessellation fills space by 7-simplex, rectified 7-simplex, birectified 7-simplex, and trirectified 7-simplex facets. These facet types occur in proportions of 2:2:2:1 respectively in the whole honeycomb.
In eighth-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 8-simplex honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation. The tessellation fills space by 8-simplex, rectified 8-simplex, birectified 8-simplex, and trirectified 8-simplex facets. These facet types occur in proportions of 1:1:1:1 respectively in the whole honeycomb.
In six-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the omnitruncated 6-simplex honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation. It is composed entirely of omnitruncated 6-simplex facets.
In five-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the quarter 5-cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation. It has half the vertices of the 5-demicubic honeycomb, and a quarter of the vertices of a 5-cube honeycomb. Its facets are 5-demicubes and runcinated 5-demicubes.
In seven-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the quarter 7-cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation. It has half the vertices of the 7-demicubic honeycomb, and a quarter of the vertices of a 7-cube honeycomb. Its facets are 7-demicubes, pentellated 7-demicubes, and {31,1,1}×{3,3} duoprisms.
In six-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the quarter 6-cubic honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation. It has half the vertices of the 6-demicubic honeycomb, and a quarter of the vertices of a 6-cube honeycomb. Its facets are 6-demicubes, stericated 6-demicubes, and {3,3}×{3,3} duoprisms.