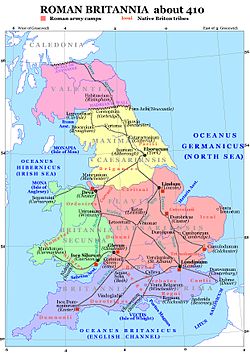
This is a list of cities in Great Britain during the period of Roman occupation from 43 AD to the 5th century.
Roman cities were known as civitas in Latin. They were mostly fortified settlements where native tribal peoples lived, governed by the Roman officials. The majority of the cities (civitates) listed are either former Iron Age tribal capitals, strategic settlements on Roman roads, trading posts between tribal groups or, occasionally, ports, although the latter two were more usually not defined as civitas. A small number of these cities were settlements of Roman origin, the most famous of which is Aquae Sulis, modern day Bath. At least 26 of the current 63 cities in England and Wales were fortified civitates during the Roman era, the most famous being Camulodunum, modern day Colchester, the first capital of the Roman province of Britannia, and Londinium, modern day London, the later capital of the province and current capital of both England and the United Kingdom today.
This list covers cities throughout Great Britain but does not include Cornwall or Scotland where the Romans had less influence. The list shows the modern (Anglo-Saxon) settlement names as well as the native Brythonic and Roman names for the settlement. Civitates were prefixed with Caer in Brythonic which roughly equates to the same word in modern Welsh, meaning "stronghold", "fortress", or "citadel", usually written in Anglo-Saxon as -caster, -cester, and -chester. The eighth century Welsh monastic author of the Historia Brittonum , Nennius, recorded 28 civitates, which together make up a large proportion of the cities in this list (26 out of the 28 are listed with their likely locations, but several are by no means certain). However, "Caer Custoeint" and "Caer Brithon" are not included, the former having an unknown location and the latter being in Scotland and unlikely to actually have been a Roman civitas. [2] Many of the Roman civitates transitioned into Anglo-Saxon settlements during the Dark Ages, remaining as cities or large towns today. Others, however, fell into disrepair and little but ruins remain, often close to small villages.

























































![Remains of Roman wall ([?]200 D.C.) - panoramio.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4d/Remains_of_Roman_wall_%28%E2%89%88200_D.C.%29_-_panoramio.jpg/250px-Remains_of_Roman_wall_%28%E2%89%88200_D.C.%29_-_panoramio.jpg)












