
Apollo 4, also known as SA-501, was the uncrewed first test flight of the Saturn V launch vehicle, the rocket that eventually took astronauts to the Moon. The space vehicle was assembled in the Vehicle Assembly Building, and was the first to be launched from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida, ascending from Launch Complex 39, where facilities built specially for the Saturn V had been constructed.

Apollo 5, also known as AS-204, was the uncrewed first flight of the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) that would later carry astronauts to the surface of the Moon. The Saturn IB rocket bearing the LM lifted off from Cape Kennedy on January 22, 1968. The mission was successful, though due to programming problems an alternate mission to that originally planned was executed.

The S-IVB was the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB launch vehicles. Built by the Douglas Aircraft Company, it had one J-2 rocket engine. For lunar missions it was fired twice: first for Earth orbit insertion after second stage cutoff, and then for translunar injection (TLI).

AS-201, flown February 26, 1966, was the first uncrewed test flight of an entire production Block I Apollo command and service module and the Saturn IB launch vehicle. The spacecraft consisted of the second Block I command module and the first Block I service module. The suborbital flight was a partially successful demonstration of the service propulsion system and the reaction control systems of both modules, and successfully demonstrated the capability of the command module's heat shield to survive re-entry from low Earth orbit.

AS-203 was an uncrewed flight of the Saturn IB rocket on July 5, 1966. It carried no command and service module, as its purpose was to verify the design of the S-IVB rocket stage restart capability that would later be used in the Apollo program to boost astronauts from Earth orbit to a trajectory towards the Moon. It achieved its objectives, but the stage was inadvertently destroyed after four orbits.

AS-202 was the second uncrewed, suborbital test flight of a production Block I Apollo command and service module launched with the Saturn IB launch vehicle. It was launched on August 25, 1966, and was the first flight which included the spacecraft guidance, navigation control system and fuel cells. The success of this flight enabled the Apollo program to judge the Block I spacecraft and Saturn IB ready to carry men into orbit on the next mission, AS-204.

The Saturn family of American rockets was developed by a team of former German rocket engineers and scientists led by Wernher von Braun to launch heavy payloads to Earth orbit and beyond. The Saturn family used liquid hydrogen as fuel in the upper stages. Originally proposed as a military satellite launcher, they were adopted as the launch vehicles for the Apollo Moon program. Three versions were built and flown: the medium-lift Saturn I, the heavy-lift Saturn IB, and the super heavy-lift Saturn V.

The Saturn IB was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the Apollo program. It uprated the Saturn I by replacing the S-IV second stage, with the S-IVB. The S-IB first stage also increased the S-I baseline's thrust from 1,500,000 pounds-force (6,700,000 N) to 1,600,000 pounds-force (7,100,000 N) and propellant load by 3.1%. This increased the Saturn I's low Earth orbit payload capability from 20,000 pounds (9,100 kg) to 46,000 pounds (21,000 kg), enough for early flight tests of a half-fueled Apollo command and service module (CSM) or a fully fueled Apollo Lunar Module (LM), before the larger Saturn V needed for lunar flight was ready.
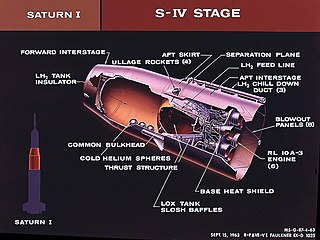
The S-IV was the second stage of the Saturn I rocket used by NASA for early flights in the Apollo program.

The S-IB stage was the first stage of the Saturn IB launch vehicle, which was used for Earth orbital missions. It was an upgraded version of the S-I stage used on the earlier Saturn I rocket and was composed of nine propellant containers, eight fins, a thrust structure assembly, eight H-1 rocket engines, and many other components. It also contained the ODOP transponder. The propellant containers consisted of eight Redstone-derived tanks clustered around a Jupiter rocket-derived tank containing LOX. The four outboard engines gimballed to steer the rocket in flight, which required a few more engine components. The S-IB burned for nearly 2.5 minutes before separating at an altitude of 42 miles (68 km).
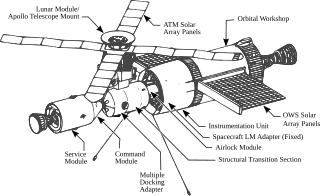
A wet workshop is a space station made from a spent liquid-propellant rocket stage. Such a rocket stage contains two large, airtight propellant tanks; it was realized that the larger tank could be retrofitted into the living quarters of a space station, while the smaller one could be used for the storage of waste. A large rocket stage would reach a low Earth orbit and undergo later modification. This would make for a cost-effective reuse of hardware that would otherwise have no further purpose, but the in-orbit modification of the rocket stage could prove difficult and expensive. As of April 2023, no wet-workshop space station has been built or flown.
Several planned missions of the Apollo crewed Moon landing program of the 1960s and 1970s were canceled, for reasons which included changes in technical direction, the Apollo 1 fire, hardware delays, and budget limitations. After the landing by Apollo 12, Apollo 20, which would have been the final crewed mission to the Moon, was canceled to allow Skylab to launch as a "dry workshop". The next two missions, Apollos 18 and 19, were later canceled after the Apollo 13 incident and further budget cuts. Two Skylab missions also ended up being canceled. Two complete Saturn V rockets remained unused and were put on display in the United States.

The Saturn INT-20 was a proposed intermediate-payload follow-on from the Apollo Saturn V launch vehicle. A conical-form interstage would be fitted on top of the S-IC stage to support the S-IVB stage, so it could be considered either a retrofitted Saturn IB with a more powerful first stage, or a stubby, cut-down Saturn V without the S-II second stage.

The Saturn II was a series of American expendable launch vehicles, studied by North American Aviation under a NASA contract in 1966, derived from the Saturn V rocket used for the Apollo lunar program. The intent of the study was to eliminate production of the Saturn IB, and create a lower-cost heavy launch vehicle based on Saturn V hardware. North American studied three versions with the S-IC first stage removed: the INT-17, a two-stage vehicle with a low Earth orbit payload capability of 47,000 pounds (21,000 kg); the INT-18, which added Titan UA1204 or UA1207 strap-on solid rocket boosters, with payloads ranging from 47,000 pounds (21,000 kg) to 146,400 pounds (66,400 kg); and the INT-19, using solid boosters derived from the Minuteman missile first stage.
The Saturn IB-CE rocket was a proposed variant of the Saturn IB rocket. However unlike the Saturn IB the Saturn IB-CE was to be a three-stage rocket. The IB-CE used the same configuration as the Saturn IB for the first two stages however with the addition of a Centaur D/E rocket as the third stage. It was to be capable of delivering 22,000 kg to low Earth orbit and 5,590 kg into a translunar trajectory. Although this version never flew, a similar rocket, the Titan IIIE, built primarily for the U.S. Air Force, but launching a few NASA payloads, including the Viking and Voyager spacecraft, had the same equivalent thrust as the Saturn IB-CE.
The proposed Saturn IB-B was to be essentially an uprated Saturn IB using the new MS-IVB-2 upper stage, using the HG-3 engine, developed from the S-IVB and an uprated S-IB-A first stage.

The Saturn C-4 was the fourth rocket in the Saturn C series studied from 1959 to 1962. The C-4 design was proposed in 1960 for a three-stage launch vehicle that could launch 99,000 kg (218,000 lb) to low Earth orbit and send 32,000 kg (70,000 lb) to the Moon via trans-lunar injection. It met the initial requirements for a lunar orbit rendezvous and lunar landing mission.
Studied in 1965, the same year that Project Gemini started, the Saturn IB-C was simply designed as an orbital launch vehicle like the original Saturn IB. The booster would consist of an ordinary Saturn IB with four Minuteman first stages used as strap-on boosters. The Saturn IB core booster did fly from 1966 until 1975, but never with its Minuteman strap-on boosters.

Skylab B was a proposed second US space station similar to Skylab that was planned to be launched by NASA for different purposes, mostly involving the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project, but was canceled due to lack of funding. Two Skylab modules were built in 1970 by McDonnell Douglas for the Skylab program, originally the Apollo Applications Program. The first was launched in 1973 and the other put in storage, while NASA considered how to use the remaining assets from Apollo.

The Saturn V dynamic test vehicle, designated SA-500D, is a prototype Saturn V rocket used by NASA to test the performance of the rocket when vibrated to simulate the shaking which subsequent rockets would experience during launch. It was the first full-scale Saturn V completed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Though SA-500D never flew, it was instrumental in the development of the Saturn V rocket which propelled the first men to the Moon as part of the Apollo program. Built under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, it served as the test vehicle for all of the Saturn support facilities at MSFC.
















