
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation (strain) in the rocks, and ultimately, to understand the stress field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. This understanding of the dynamics of the stress field can be linked to important events in the geologic past; a common goal is to understand the structural evolution of a particular area with respect to regionally widespread patterns of rock deformation due to plate tectonics.

Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized silicate grains, cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.

Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than 150 to 200 °C and, often, elevated pressure of 100 megapascals (1,000 bar) or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock.

Chert is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a chemical precipitate or a diagenetic replacement, as in petrified wood.
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, silt, and clay, and the processes that result in their formation, transport, deposition and diagenesis. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures.

Quartzite is a hard, non-foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone. Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals.

The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain size, and composition. Lithology may refer to either a detailed description of these characteristics, or a summary of the gross physical character of a rock. Examples of lithologies in the second sense include sandstone, slate, basalt, or limestone.

Skarns or tactites are coarse-grained metamorphic rocks that form by replacement of carbonate-bearing rocks during regional or contact metamorphism and metasomatism. Skarns may form by metamorphic recrystallization of impure carbonate protoliths, bimetasomatic reaction of different lithologies, and infiltration metasomatism by magmatic-hydrothermal fluids. Skarns tend to be rich in calcium-magnesium-iron-manganese-aluminium silicate minerals, which are also referred to as calc-silicate minerals. These minerals form as a result of alteration which occurs when hydrothermal fluids interact with a protolith of either igneous or sedimentary origin. In many cases, skarns are associated with the intrusion of a granitic pluton found in and around faults or shear zones that commonly intrude into a carbonate layer composed of either dolomite or limestone. Skarns can form by regional or contact metamorphism and therefore form in relatively high temperature environments. The hydrothermal fluids associated with the metasomatic processes can originate from a variety of sources; magmatic, metamorphic, meteoric, marine, or even a mix of these. The resulting skarn may consist of a variety of different minerals which are highly dependent on both the original composition of the hydrothermal fluid and the original composition of the protolith.

Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.

In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.

Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.

The rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that describes transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. Each rock type is altered when it is forced out of its equilibrium conditions. For example, an igneous rock such as basalt may break down and dissolve when exposed to the atmosphere, or melt as it is subducted under a continent. Due to the driving forces of the rock cycle, plate tectonics and the water cycle, rocks do not remain in equilibrium and change as they encounter new environments. The rock cycle explains how the three rock types are related to each other, and how processes change from one type to another over time. This cyclical aspect makes rock change a geologic cycle and, on planets containing life, a biogeochemical cycle.

In geology, cross-bedding, also known as cross-stratification, is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. The original depositional layering is tilted, such tilting not being the result of post-depositional deformation. Cross-beds or "sets" are the groups of inclined layers, which are known as cross-strata.

In geology, texture or rock microstructure refers to the relationship between the materials of which a rock is composed. The broadest textural classes are crystalline, fragmental, aphanitic, and glassy. The geometric aspects and relations amongst the component particles or crystals are referred to as the crystallographic texture or preferred orientation. Textures can be quantified in many ways. The most common parameter is the crystal size distribution. This creates the physical appearance or character of a rock, such as grain size, shape, arrangement, and other properties, at both the visible and microscopic scale.
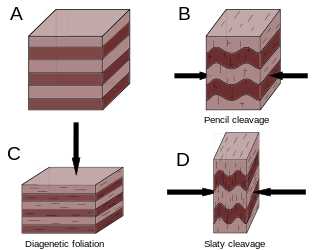
Cleavage, in structural geology and petrology, describes a type of planar rock feature that develops as a result of deformation and metamorphism. The degree of deformation and metamorphism along with rock type determines the kind of cleavage feature that develops. Generally, these structures are formed in fine grained rocks composed of minerals affected by pressure solution.
Neomorphism refers to the wet metamorphic process in which diagenetic alterations systematically transform minerals into either polymorphs or crystalline structures that are structurally identical to the rock(s) from which they developed.
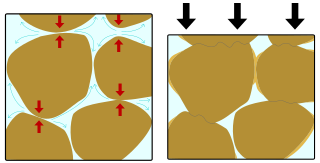
In structural geology and diagenesis, pressure solution or pressure dissolution is a deformation mechanism that involves the dissolution of minerals at grain-to-grain contacts into an aqueous pore fluid in areas of relatively high stress and either deposition in regions of relatively low stress within the same rock or their complete removal from the rock within the fluid. It is an example of diffusive mass transfer.
This glossary of geology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to geology, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For other terms related to the Earth sciences, see Glossary of geography terms.
Robert "Bob" Louis "Luigi" Folk was an American geologist and petrologist, specializing in sedimentology, sandstone petrology, and carbonate petrology. He is known for the 1959 eponymous Folk classification of sedimentary rocks, which, with some minor modifications, is still in use today. He is one of the founders of what is sometimes called "Soft Rock Geology".



















