| Submandibular lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
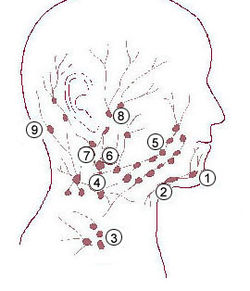 1: Submental lymph nodes 2: Submandibular lymph nodes 3: Supraclavicular lymph nodes 4: Retropharyngeal lymph nodes 5: Buccinator lymph node 6: Superficial cervical lymph nodes 7: Jugular lymph nodes 8: Parotid lymph nodes 9: Retroauricular lymph nodes and occipital lymph nodes | |
 Superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of head and neck. (Submaxillary glands labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Source | Mandibular lymph node |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodi lymphoidei submandibulares |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The submandibular lymph nodes (submaxillary glands in older texts), are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible. [1]
