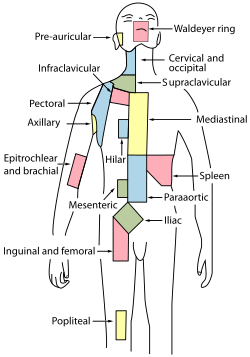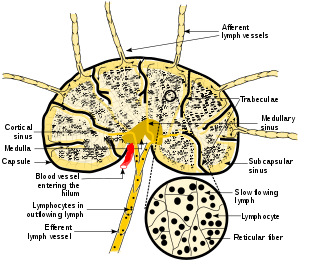
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function.
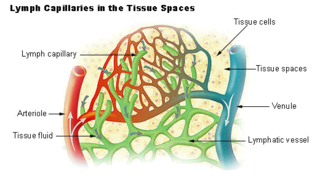
Lymph is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood.

The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels.

The pararectal lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are in contact with the muscular coat of the rectum.

The preaortic lymph nodes lie in front of the aorta, and may be divided into celiac lymph nodes, superior mesenteric lymph nodes, and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes groups, arranged around the origins of the corresponding arteries.

The inferior mesenteric lymph nodes consist of:

The internal iliac lymph nodes surround the internal iliac artery and its branches, and receive the lymphatics corresponding to the distribution of the branches of it, i. e., they receive lymphatics from all the pelvic viscera, from the deeper parts of the perineum, including the membranous and cavernous portions of the urethra, and from the buttock and back of the thigh. The internal iliac lymph nodes also drain the superior half of the rectum, above the pectinate line.

The mastoid lymph nodes are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear, on the mastoid insertion of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, beneath the posterior auricular muscle.

One or two supratrochlear lymph nodes are placed above the medial epicondyle of the humerus, medial to the basilic vein.

The deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes in the neck that form a chain along the internal jugular vein within the carotid sheath.

The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes are one of the two groups of the deep cervical lymph nodes.

The superior deep cervical lymph nodes are the deep cervical lymph nodes that are situated adjacent to the superior portion of the internal jugular vein. They drain either to the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes or into the jugular trunk.

The submental lymph nodes are 2-3 lymph nodes situated in the submental triangle, between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone.

Supraclavicular lymph nodes are lymph nodes found above the clavicle, that can be felt in the supraclavicular fossa. The supraclavicular lymph nodes on the left side are called Virchow's nodes. It leads to an appreciable mass that can be recognized clinically, called Troisier sign.

The superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.

The submandibular lymph nodes, are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible.

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:
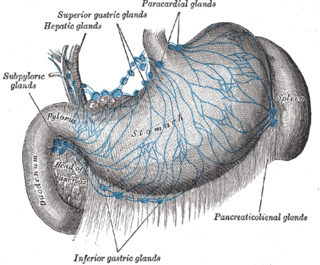
The celiac lymph nodes are associated with the branches of the celiac artery. Other lymph nodes in the abdomen are associated with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries. The celiac lymph nodes are grouped into three sets: the gastric, hepatic and splenic lymph nodes. They receive lymph from the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, spleen, liver, and gall bladder.

The splenic lymph nodes are found at the splenic hilum and in relation to the tail of the pancreas.

The gastric lymph nodes are lymph nodes which drain the stomach and consist of two sets, superior and inferior: