The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as parotid gland secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal adult human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27 mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3 mm.

The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.
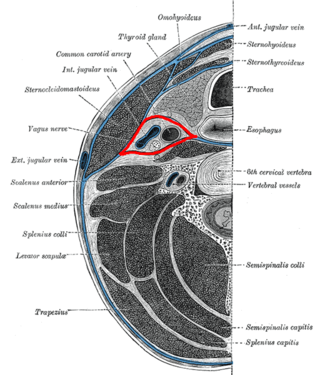
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve, and ansa cervicalis. The carotid sheath helps protects the structures contained therein.

The tarsi or tarsal plates are two comparatively thick, elongated plates of dense connective tissue, about 10 mm (0.39 in) in length for the upper eyelid and 5 mm for the lower eyelid; one is found in each eyelid, and contributes to its form and support. They are located directly above the lid margins. The tarsus has a lower and upper part making up the palpebrae.

The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels.

The retroaortic lymph nodes are placed below the cisterna chyli, on the bodies of the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae.

The common iliac lymph nodes, four to six in number, are grouped behind and on the sides of the common iliac artery, one or two being placed below the bifurcation of the aorta, in front of the fifth lumbar vertebra.
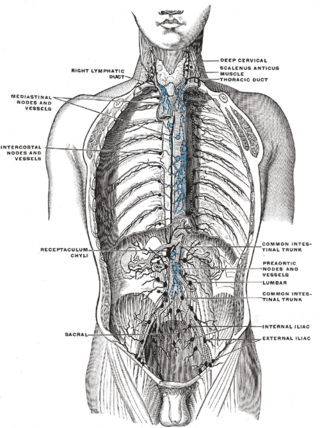
The lumbar trunks are formed by the union of the efferent vessels from the lateral aortic lymph nodes.

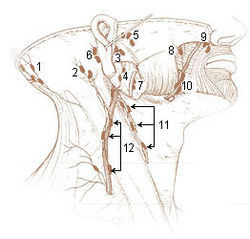
The mastoid lymph nodes are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear, on the mastoid insertion of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, beneath the posterior auricular muscle.
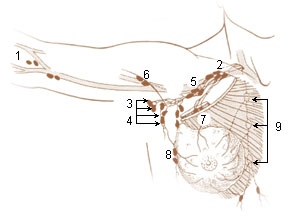
A brachial lymph nodes are group of four to six lymph nodes which lies in relation to the medial and posterior aspects of the axillary vein; the afferents of these glands drain the whole arm with the exception of that portion whose vessels accompany the cephalic vein.

An anterior or pectoral group consists of four or five glands along the lower border of the Pectoralis minor, in relation with the lateral thoracic artery.

The submandibular lymph nodes, are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible.

The deep parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found below the parotid gland.

The intercostal lymph nodes occupy the posterior parts of the intercostal spaces, in relation to the intercostal vessels.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.

The superficial parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes anterior to the ear.
Auricular glands can refer to: