
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.
Articles related to anatomy include:

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm, is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle.

The intercostal muscles comprise many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity.

The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest.
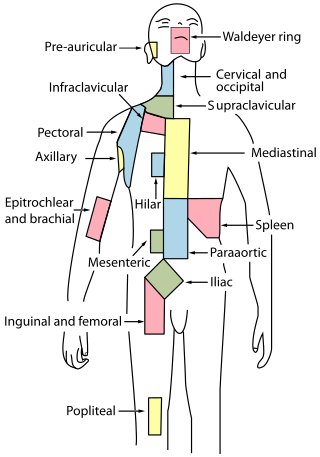
The periaortic lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs.
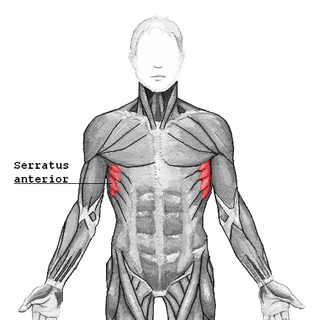
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thoracic nerve from the brachial plexus. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax.

The intertransversarii are small muscles placed between the transverse processes of the vertebrae.

The superior thoracic aperture, also known as the thoracic outlet, or thoracic inlet refers to the opening at the top of the thoracic cavity. It is also clinically referred to as the thoracic outlet, in the case of thoracic outlet syndrome. A lower thoracic opening is the inferior thoracic aperture.

The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, and arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11. The intercostal nerves are distributed chiefly to the thoracic pleura and abdominal peritoneum, and differ from the anterior rami of the other spinal nerves in that each pursues an independent course without plexus formation.

The thyrocervical trunk is a short artery of the neck. It arises from the subclavian artery, then promptly divides into its branches: the inferior thyroid artery, suprascapular artery, and (sometimes) the transverse cervical artery.

The anterior corticospinal tract is a small bundle of descending fibers that connect the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Descending tracts are pathways by which motor signals are sent from upper motor neurons in the brain to lower motor neurons which then directly innervate muscle to produce movement. The anterior corticospinal tract is usually small, varying inversely in size with the lateral corticospinal tract, which is the main part of the corticospinal tract.
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.

The anterior divisions of the seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh thoracic intercostal nerves are continued anteriorly from the intercostal spaces into the abdominal wall; hence they are named thoraco-abdominal nerves.
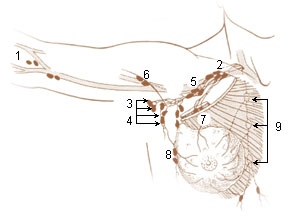
A brachial lymph nodes are group of four to six lymph nodes which lies in relation to the medial and posterior aspects of the axillary vein; the afferents of these glands drain the whole arm with the exception of that portion whose vessels accompany the cephalic vein.

An apical group of six to twelve glands is situated partly posterior to the upper portion of the pectoralis minor and partly above the upper border of this muscle.

The parasternal lymph nodes are placed at the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces, by the side of the internal thoracic artery.
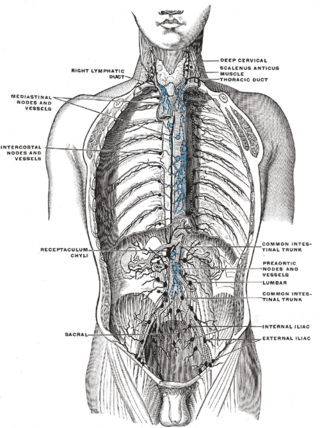
The intercostal lymph nodes occupy the posterior parts of the intercostal spaces, in relation to the intercostal vessels.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:



















