
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.
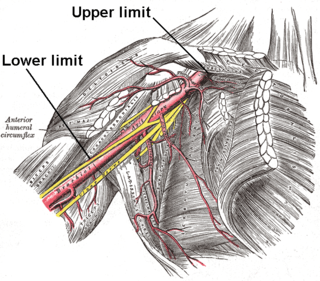
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.

The thoracodorsal nerve is a nerve present in humans and other animals, also known as the middle subscapular nerve or the long subscapular nerve. It supplies the latissimus dorsi muscle.

The inferior phrenic artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the abdominal cavity which represents the main source of arterial supply to the diaphragm. Each artery usually arises either from the coeliac trunk or the abdominal aorta, however, their origin is highly variable and the different sites of origin are different for the left artery and right artery. The superior suprarenal artery is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery.

The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.

The lower subscapular nerve, also known as the inferior subscapular nerve, is the third branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It innervates the inferior portion of the subscapularis muscle and the teres major muscle.

The upper (superior) subscapular nerve is the first branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The upper subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the C5 and C6 cervical spinal nerves. It innervates the superior portion of the subscapularis muscle. The inferior portion of the subscapularis is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve.

Subscapular nerves can refer to:

The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.

The submandibular ganglion is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck..

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer, and metastases from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease.

The renal fascia is a dense, elastic connective tissue envelope enclosing the kidney and adrenal gland, together with the layer of perirenal fat surrounding these two.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:
In anatomy, a fossa is a depression or hollow usually in a bone, such as the hypophyseal fossa. Some examples include:

















