This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.
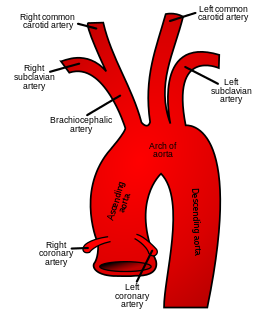
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

In anatomy, the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine is named the axis or epistropheus.

The levator scapulae is a skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.

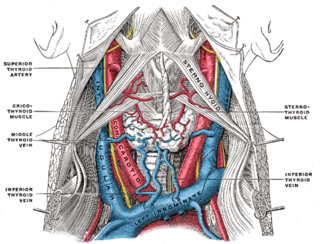
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its superior belly serves as the most lateral member of the infrahyoid muscles, located lateral to both the sternothyroid and thyrohyoid muscles. Its name derives from the Greek "omos" meaning shoulder, giving one of its attachments, and "hyoid", giving the other attachment - the hyoid bone.

The cervical plexus is a plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which arise from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side. There is anastomosis with accessory nerve, hypoglossal nerve and sympathetic trunk.
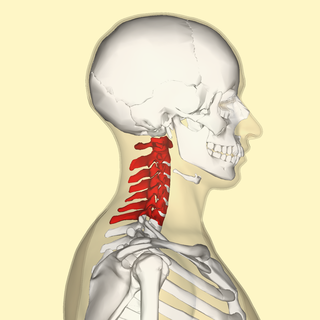
In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

The scalene muscles are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene. They are innervated by the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical spinal nerves (C4-C6).

The splenius cervicis is a muscle in the back of the neck. It arises by a narrow tendinous band from the spinous processes of the third to the sixth thoracic vertebrae; it is inserted, by tendinous fasciculi, into the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the upper two or three cervical vertebrae.
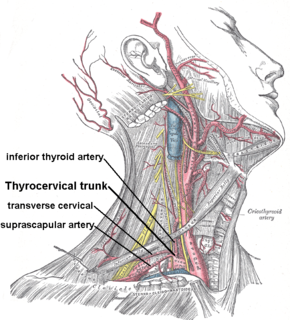
The thyrocervical trunk is a branch of the subclavian artery arising from the first portion of this vessel, i.e. between the origin of the subclavian artery and the inner border of the scalenus anterior muscle. It is located distally to the vertebral artery and proximally to the costocervical trunk.

The cervical branch of the facial nerve runs forward beneath the platysma, and forms a series of arches across the side of the neck over the suprahyoid region. This nerve innervates the posterior belly of the Digastric muscle and the Stylohyoid muscle.

Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation.

The posterior branches of cervical nerves branch from the dorsal rami of the cervical nerves.

The cervical spinal nerve 5 (C5) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.

The superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are found in proximity to the external jugular vein.

The lateral cervical lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found in the lateral side of the neck.

The spinal root of accessory nerve is firm in texture, and its fibers arise from the motor cells in the lateral part of the anterior column of the gray substance of the medulla spinalis as low as the fifth cervical nerve.

The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord.