
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments: vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.
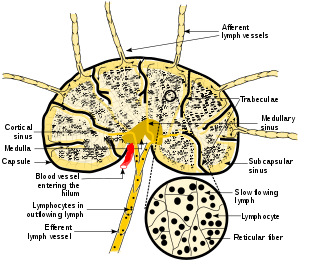
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function.
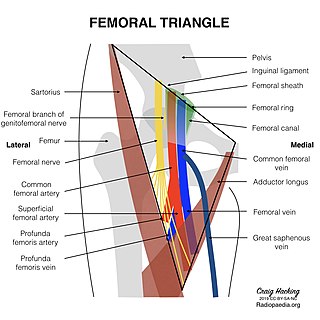
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula.

Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the groin. They are situated in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region. They are subdivided into two groups: the superficial inguinal lymph nodes and deep inguinal lymph nodes.
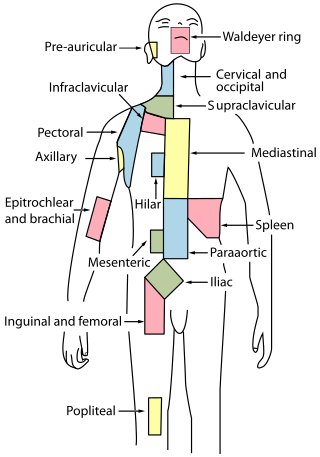
The periaortic lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs.

The neck dissection is a surgical procedure for control of neck lymph node metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck. The aim of the procedure is to remove lymph nodes from one side of the neck into which cancer cells may have migrated. Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma into the lymph nodes of the neck reduce survival and is the most important factor in the spread of the disease. The metastases may originate from SCC of the upper aerodigestive tract, including the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx, as well as the thyroid, parotid and posterior scalp.

The right and left paratracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the neck situated lateral to the trachea and esophagus alongside the recurrent laryngeal nerve. They drain to the deep cervical lymph nodes.
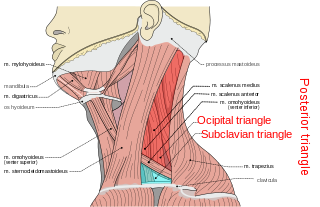
The posterior triangle is a region of the neck.

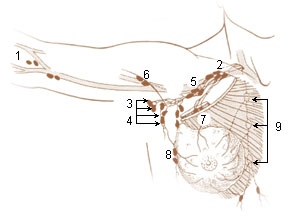
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation.

The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer, and metastases from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease.
A brachial lymph nodes are group of four to six lymph nodes which lies in relation to the medial and posterior aspects of the axillary vein; the afferents of these glands drain the whole arm with the exception of that portion whose vessels accompany the cephalic vein.

The deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes in the neck that form a chain along the internal jugular vein within the carotid sheath.

The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes are one of the two groups of the deep cervical lymph nodes.

Supraclavicular lymph nodes are lymph nodes found above the clavicle, that can be felt in the supraclavicular fossa. The supraclavicular lymph nodes on the left side are called Virchow's nodes. It leads to an appreciable mass that can be recognized clinically, called Troisier sign.

The superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.

The deep lateral cervical lymph nodes are found near the upper part of the internal jugular vein in the neck, lateral or posterior to the carotid sheath.

The superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are found along the course of the external jugular vein, between the inferior aspect of the parotid gland and the supraclavicular nodes. The nodes are intercalated along the course of the vessels draining the parotid nodes and the infraauricular nodes. These nodes drain into the supraclavicular nodes, and on to the jugular trunk, followed by the thoracic duct on the left or the right lymphatic duct.

Cervical lymphadenopathy refers to lymphadenopathy of the cervical lymph nodes. The term lymphadenopathy strictly speaking refers to disease of the lymph nodes, though it is often used to describe the enlargement of the lymph nodes. Similarly, the term lymphadenitis refers to inflammation of a lymph node, but often it is used as a synonym of lymphadenopathy.














