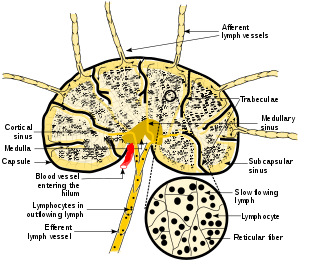
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function.

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.

The cisterna chyli or receptaculum chyli is a dilated sac at the lower end of the thoracic duct in most mammals into which lymph from the intestinal trunk and two lumbar lymphatic trunks flow. It receives fatty chyle from the intestines and thus acts as a conduit for the lipid products of digestion. It is the most common drainage trunk of most of the body's lymphatics. The cisterna chyli is a retroperitoneal structure.
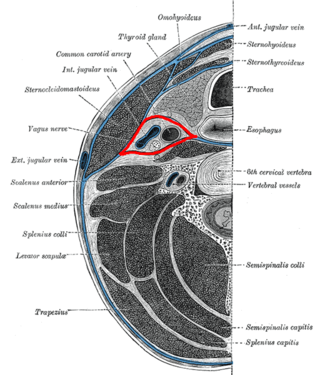
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve, and ansa cervicalis. The carotid sheath helps protects the structures contained therein.
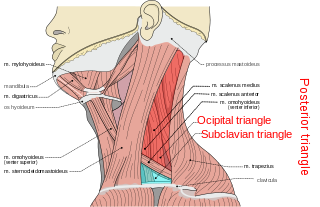
The posterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The anterior jugular vein is a vein in the neck.

The right lymphatic duct is an important lymphatic vessel that drains the right upper quadrant of the human body. It forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes in the neck that form a chain along the internal jugular vein within the carotid sheath.

The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes are one of the two groups of the deep cervical lymph nodes.

The superior deep cervical lymph nodes are the deep cervical lymph nodes that are situated adjacent to the superior portion of the internal jugular vein. They drain either to the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes or into the jugular trunk.

The superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.

The efferent vessels of the tracheobronchial lymph nodes ascend upon the trachea and unite with efferents of the internal mammary and anterior mediastinal glands to form the right and left bronchomediastinal trunks.
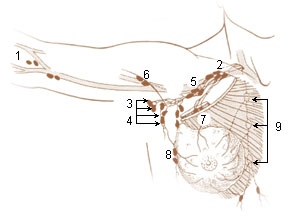
The parasternal lymph nodes are placed at the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces, by the side of the internal thoracic artery.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The deep lateral cervical lymph nodes are found near the upper part of the internal jugular vein in the neck, lateral or posterior to the carotid sheath.

The superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are found along the course of the external jugular vein, between the inferior aspect of the parotid gland and the supraclavicular nodes. The nodes are intercalated along the course of the vessels draining the parotid nodes and the infraauricular nodes. These nodes drain into the supraclavicular nodes, and on to the jugular trunk, followed by the thoracic duct on the left or the right lymphatic duct.

The pretracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the trachea in the neck.

The lateral cervical lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found in the lateral side of the neck.













