
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.
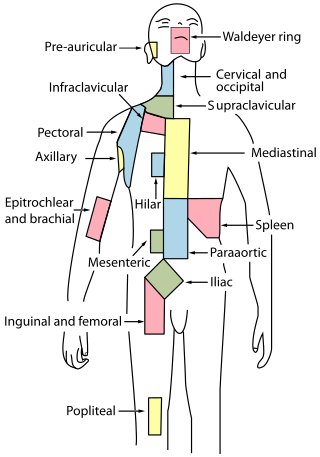
The periaortic lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs.

In human anatomy, the groin, also known as the inguinal region or iliac region, is the junctional area between the torso and the thigh. The groin is at the front of the body on either side of the pubic tubercle, where the lower part of the abdominal wall meets the thigh. A fold or crease is formed at this junction known as the inguinal groove, or crease. This is also the area of the medial compartment of the thigh that contains attachments of the adductor muscles of the hip or the groin muscles. The groin is the common site for a hernia.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.

The cisterna chyli or receptaculum chyli is a dilated sac at the lower end of the thoracic duct in most mammals into which lymph from the intestinal trunk and two lumbar lymphatic trunks flow. It receives fatty chyle from the intestines and thus acts as a conduit for the lipid products of digestion. It is the most common drainage trunk of most of the body's lymphatics. The cisterna chyli is a retroperitoneal structure.

A nerve plexus is a plexus of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve plexuses, except in the thoracic region, as well as other forms of autonomic plexuses, many of which are a part of the enteric nervous system. The nerves that arise from the plexuses have both sensory and motor functions. These functions include muscle contraction, the maintenance of body coordination and control, and the reaction to sensations such as heat, cold, pain, and pressure. There are several plexuses in the body, including:

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The femoral sheath is a funnel-shaped downward extension of abdominal fascia within which the femoral artery and femoral vein pass between the abdomen and the thigh. The femoral sheath is subdivided by two vertical partitions to form three compartments ; the medial compartment is known as the femoral canal and contains lymphatic vessels and a lymph node, whereas the intermediate canal and the lateral canal accommodate the femoral vein and the femoral artery (respectively). Some neurovascular structures perforate the femoral sheath. Topographically, the femoral sheath is contained within the femoral triangle.

The lumbosacral trunk is nervous tissue that connects the lumbar plexus with the sacral plexus. It is formed by the union of parts of the fourth and fifth lumbar nerves and descends to join the sacral plexus.

The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.

The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer, and metastases from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease.

The retroaortic lymph nodes are placed below the cisterna chyli, on the bodies of the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae.

The common iliac lymph nodes, four to six in number, are grouped behind and on the sides of the common iliac artery, one or two being placed below the bifurcation of the aorta, in front of the fifth lumbar vertebra.

The popliteal lymph nodes, small in size and some six or seven in number, are embedded in the fat contained in the popliteal fossa, sometimes referred to as the 'knee pit'. One lies immediately beneath the popliteal fascia, near the terminal part of the small saphenous vein, and drains the region from which this vein derives its tributaries, such as superficial regions of the posterolateral aspect of the leg and the plantar aspect of the foot.

One or two deltopectoral lymph nodes are found beside the cephalic vein, between the pectoralis major and deltoideus, immediately below the clavicle.

The efferent vessels of the tracheobronchial lymph nodes ascend upon the trachea and unite with efferents of the internal mammary and anterior mediastinal glands to form the right and left bronchomediastinal trunks.
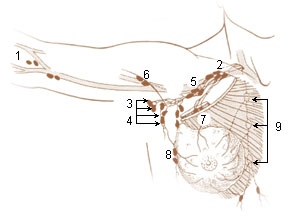
The parasternal lymph nodes are placed at the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces, by the side of the internal thoracic artery.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
Lymph trunk is a collection of lymph vessels that carries lymph, and is formed by confluence of many efferent lymph vessels. It in turn drains into one of the two lymph ducts.
The superior diaphragmatic lymph nodes lie on the thoracic aspect of the diaphragm, and consist of three sets – anterior, middle, and posterior.
















