| Parotid lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
| |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodi lymphoidei parotidei |
| Anatomical terminology | |
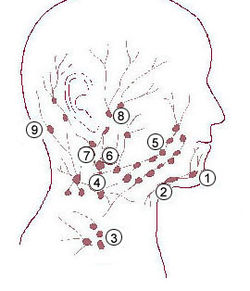
Parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found near the parotid gland in the immune system.
More specifically, it can refer to:
| Parotid lymph nodes | |
|---|---|

| |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodi lymphoidei parotidei |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found near the parotid gland in the immune system.
More specifically, it can refer to:
The word parotid comes from the Ancient Greek : πᾰρᾰ́ (pará, "beside; next to, near, from; against, contrary to") + ὠτ- (ōt-, from οὖςoûs, "ear") + -id, thus "next to, near the ear".

The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as parotid gland secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal adult human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27 mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3 mm.

The sublingual gland is a seromucous polystomatic exocrine gland. Located underneath the oral diaphragm, the sublingual gland is the smallest and most diffuse of the three major salivary glands of the oral cavity, with the other two being the submandibular and parotid. The sublingual gland provides approximately 3-5% of the total salivary volume.
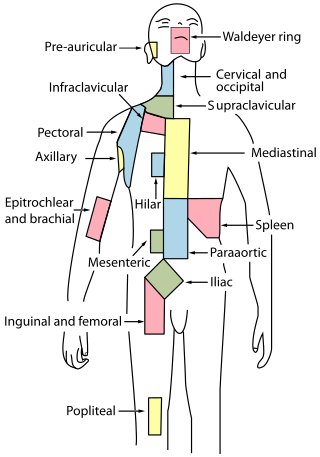
The periaortic lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs.
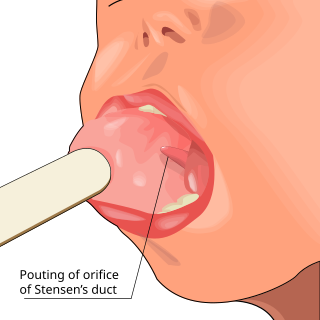
Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.

The pararectal lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are in contact with the muscular coat of the rectum.

The preaortic lymph nodes lie in front of the aorta, and may be divided into celiac lymph nodes, superior mesenteric lymph nodes, and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes groups, arranged around the origins of the corresponding arteries.

The mastoid lymph nodes are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear, on the mastoid insertion of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, beneath the posterior auricular muscle.

The preauricular deep parotid lymph nodes, from one to three in number, lie immediately in front of the tragus.

Supraclavicular lymph nodes are lymph nodes found above the clavicle, that can be felt in the supraclavicular fossa. The supraclavicular lymph nodes on the left side are called Virchow's nodes. It leads to an appreciable mass that can be recognized clinically, called Troisier sign.

The submandibular lymph nodes, are some 3-6 lymph nodes situated at the inferior border of the ramus of mandible.

The deep parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found below the parotid gland.

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:

The superficial parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes anterior to the ear.

The superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are found along the course of the external jugular vein, between the inferior aspect of the parotid gland and the supraclavicular nodes. The nodes are intercalated along the course of the vessels draining the parotid nodes and the infraauricular nodes. These nodes drain into the supraclavicular nodes, and on to the jugular trunk, followed by the thoracic duct on the left or the right lymphatic duct.

The Intraglandular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found inside the parotid gland.

The infra-auricular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found underneath the ear.
Ectopic salivary gland tissue which is located in sites other than the normal location is variously described as aberrant, accessory, ectopic, heterotopic or salivary gland choristoma.