The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as the parotid secretion rises to 50%.

The paired sublingual glands are major salivary glands in the mouth. They are the smallest, most diffuse, and the only unencapsulated major salivary glands. They provide only 3-5% of the total salivary volume. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and Parotid glands.

Inguinal lymph nodes are the lymph nodes in the inguinal region (groin). They are located in the femoral triangle, and are grouped into superficial lymph nodes, and deep lymph nodes. The superficial lymph nodes have three divisions – the superomedial, superolateral, and inferior superficial lymph nodes.

The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels.

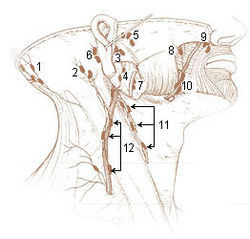
The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.

The preaortic lymph nodes lie in front of the aorta, and may be divided into celiac lymph nodes, superior mesenteric lymph nodes, and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes groups, arranged around the origins of the corresponding arteries.
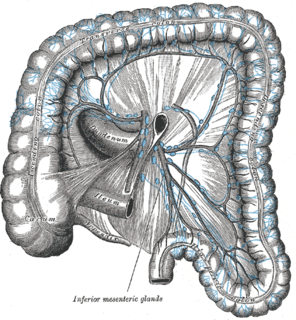
The inferior mesenteric lymph nodes consist of:

The internal iliac lymph nodes surround the internal iliac artery and its branches, and receive the lymphatics corresponding to the distribution of the branches of it, i. e., they receive lymphatics from all the pelvic viscera, from the deeper parts of the perineum, including the membranous and cavernous portions of the urethra, and from the buttock and back of the thigh. The internal iliac lymph nodes also drain the superior half of the rectum, above the pectinate line.

The mastoid lymph nodes are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear, on the mastoid insertion of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, beneath the posterior auricular muscle.

The preauricular deep parotid lymph nodes, from one to three in number, lie immediately in front of the tragus.

Supraclavicular lymph nodes are lymph nodes found superior to the clavicle, palpable in the supraclavicular fossa. The supraclavicular lymph nodes on the left side are called Virchow's nodes.

The submandibular lymph nodes, three to six in number, are placed beneath the body of the mandible in the submandibular triangle, and rest on the superficial surface of the submandibular gland.

The deep parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found below the parotid gland.
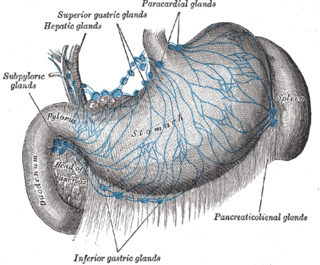
The celiac lymph nodes are associated with the branches of the celiac artery. Other lymph nodes in the abdomen are associated with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries. The celiac lymph nodes are grouped into three sets: the gastric, hepatic and splenic lymph nodes.

Parotid lymph nodes are lymph nodes found near the parotid gland in the immune system.

The superficial parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes anterior to the ear.

The infra-auricular deep parotid lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes found underneath the ear.
Auricular glands can refer to:
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.