The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments: vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.
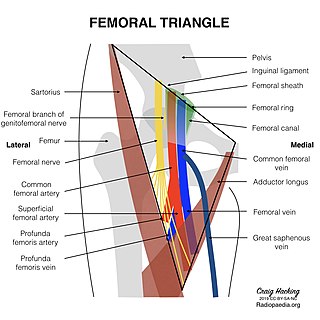
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.

The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.

The ansa cervicalis is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root and an inferior root - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath.
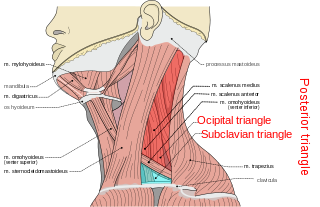
The posterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The anterior jugular vein is a vein in the neck.

The retromandibular vein is a major vein of the face. It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein, while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein.

The submental triangle is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The subclavian triangle, the smaller division of the posterior triangle, is bounded, above, by the inferior belly of the omohyoideus; below, by the clavicle; its base is formed by the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus.

The occipital triangle, the larger division of the posterior triangle, is bounded, in front, by the Sternocleidomastoideus; behind, by the Trapezius; below, by the Omohyoideus.
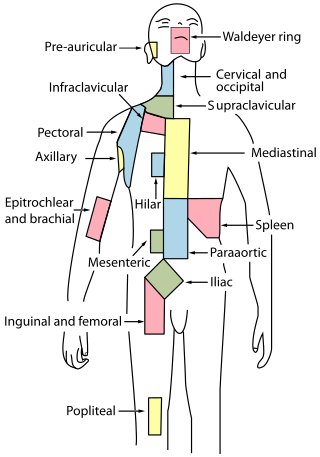
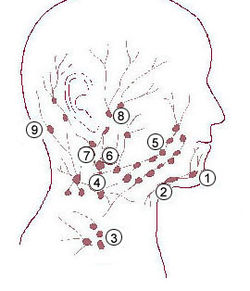
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation.

The deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes in the neck that form a chain along the internal jugular vein within the carotid sheath.

The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes are one of the two groups of the deep cervical lymph nodes.

The superior deep cervical lymph nodes are the deep cervical lymph nodes that are situated adjacent to the superior portion of the internal jugular vein. They drain either to the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes or into the jugular trunk.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The pretracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the trachea in the neck.