The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' comes from the Ancient Greek word lárunx ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ

The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum.

An ear is the organ that enables hearing and body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most animals, the word "ear" often refers to the external part alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ear is a self cleaning organ through its relationship with earwax and the ear canals. The ears of vertebrates are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head, an arrangement that aids sound localization.

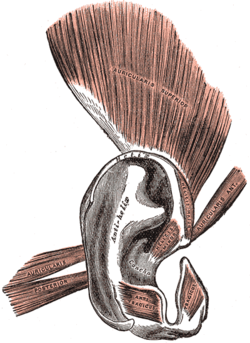
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna, a term that is used more in zoology.
Otoplasty is a procedure for correcting the deformities and defects of the pinna, whether these defects are congenital conditions or caused by trauma. Otoplastic surgeons may reshape, move, or augment the cartilaginous support framework of the pinna to correct these defects.

The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes or stirrup bone of the middle ear.

The helix is the prominent rim of the auricle. Where the helix turns downwards posteriorly, a small tubercle is sometimes seen, namely the auricular tubercle of Darwin.

The tragus is a small pointed eminence of the external ear, situated in front of the concha, and projecting backward over the meatus. It also is the name of hair growing at the entrance of the ear. Its name comes the Ancient Greek tragos, meaning 'goat', and is descriptive of its general covering on its under surface with a tuft of hair, resembling a goat's beard. The nearby antitragus projects forwards and upwards.

In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery.

The temporal styloid process is a slender bony process of the temporal bone extending downward and forward from the undersurface of the temporal bone just below the ear. The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments.

The antitragus is a feature of mammalian ear anatomy.

The posterior auricular nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the facial nerve. It communicates with branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve. Its auricular branch supplies the posterior auricular muscle, the intrinsic muscles of the auricle, and gives sensation to the auricle. Its occipital branch supplies the occipitalis muscle.

The antitragicus is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The oblique muscle of auricle is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The transverse muscle of auricle is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The Helicis minor is a small skeletal muscle. The helicis minor is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear. The muscle runs obliques and covers the helical crus, part of the helix located just above the tragus.

The helicis major is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The anterior auricular branches of the superficial temporal artery are distributed to the anterior portion of the auricula, the lobule, and part of the external meatus, anastomosing with the posterior auricular. They supply the external acoustic meatus and the visible part of the ear.

For people with the surname, see Porion (surname).

Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.