In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic red-brown solids. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is the usual compound of commerce. It is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis.

Sodium thioantimoniate or sodium tetrathioantimonate(V) is an inorganic compound with the formula Na3SbS4. The nonahydrate of this chemical, Na3SbS4·9H2O, is known as Schlippe's salt, named after Johann Karl Friedrich von Schlippe (1799–1867). These compounds are examples of sulfosalts. They were once of interest as species generated in qualitative inorganic analysis.

Antimony oxychloride, known since the 15th century, has been known by a plethora of alchemical names. Since the compound functions as both an emetic and a laxative, it was originally used as a purgative.
Titanium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl3. At least four distinct species have this formula; additionally hydrated derivatives are known. TiCl3 is one of the most common halides of titanium and is an important catalyst for the manufacture of polyolefins.

Tungsten hexachloride is an inorganic chemical compound of tungsten and chlorine with the chemical formula WCl6. This dark violet-blue compound exists as volatile crystals under standard conditions. It is an important starting reagent in the preparation of tungsten compounds. Other examples of charge-neutral hexachlorides are rhenium(VI) chloride and molybdenum(VI) chloride. The highly volatile tungsten hexafluoride is also known.

Antimony trichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SbCl3. It is a soft colorless solid with a pungent odor and was known to alchemists as butter of antimony.

Zeise's salt, potassium trichloro(ethylene)platinate(II) hydrate, is the chemical compound with the formula K[PtCl3(C2H4)]·H2O. The anion of this air-stable, yellow, coordination complex contains an η2-ethylene ligand. The anion features a platinum atom with a square planar geometry. The salt is of historical importance in the area of organometallic chemistry as one of the first examples of a transition metal alkene complex and is named for its discoverer, William Christopher Zeise.
Technetium compounds are chemical compounds containing the chemical element technetium. Technetium can form multiple oxidation states, but often forms in the +4 and +7 oxidation states. Because technetium is radioactive, technetium compounds are extremely rare on Earth.
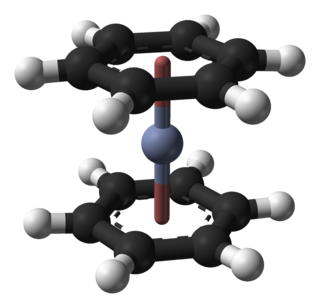
Bis(benzene)chromium is the organometallic compound with the formula Cr(η6-C6H6)2. It is sometimes called dibenzenechromium. The compound played an important role in the development of sandwich compounds in organometallic chemistry and is the prototypical complex containing two arene ligands.
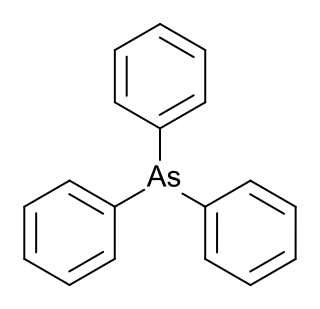
Triphenylarsine is the chemical compound with the formula As(C6H5)3. This organoarsenic compound, often abbreviated AsPh3, is a colorless crystalline solid that is used as a ligand and a reagent in coordination chemistry and organic synthesis. The molecule is pyramidal with As-C distances of 1.942–1.956 Å and C-As-C angles of 99.6–100.5°.
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.
Organoantimony chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a carbon to antimony (Sb) chemical bond. Relevant oxidation states are SbV and SbIII. The toxicity of antimony limits practical application in organic chemistry.

Rhodium carbonyl chloride is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(CO)4. It is a red-brown volatile solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is a precursor to other rhodium carbonyl complexes, some of which are useful in homogeneous catalysis.

Trithiazyl trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula (NSCl)3. A white solid, it is a precursor to other sulfur nitrides, but has no commercial applications.
Nickel is one of the metals that can form Tutton's salts. The singly charged ion can be any of the full range of potassium, rubidium, cesium, ammonium (), or thallium. As a mineral the ammonium nickel salt, (NH4)2Ni(SO4)2 · 6 H2O, can be called nickelboussingaultite. With sodium, the double sulfate is nickelblödite Na2Ni(SO4)2 · 4 H2O from the blödite family. Nickel can be substituted by other divalent metals of similar sized to make mixtures that crystallise in the same form.
Niobium(III) chloride also known as niobium trichloride is a compound of niobium and chlorine. The binary phase NbCl3 is not well characterized but many adducts are known.
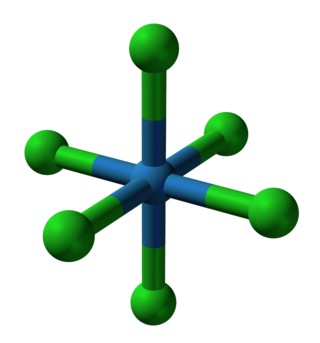
In chemistry, a transition metal chloride complex is a coordination complex that consists of a transition metal coordinated to one or more chloride ligand. The class of complexes is extensive.

Pentaphenylantimony is an organoantimony compound containing five phenyl groups attached to one antimony atom. It has formula Sb(C6H5)5 (or SbPh5).


















