Related Research Articles

Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges,vacuum gauges or compound gauges. The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge.
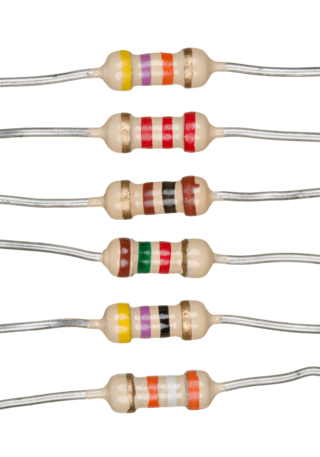
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements, or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.
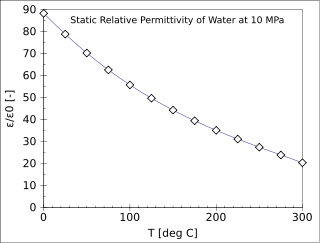
The relative permittivity is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insulator measures the ability of the insulator to store electric energy in an electrical field.

Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two differently-charged objects when brought close together or when the dielectric between them breaks down, often creating a visible spark associated with the static electricity between the objects.

A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.

Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor.
Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) are a class of devices integrating electrical and mechanical functionality on the nanoscale. NEMS form the next logical miniaturization step from so-called microelectromechanical systems, or MEMS devices. NEMS typically integrate transistor-like nanoelectronics with mechanical actuators, pumps, or motors, and may thereby form physical, biological, and chemical sensors. The name derives from typical device dimensions in the nanometer range, leading to low mass, high mechanical resonance frequencies, potentially large quantum mechanical effects such as zero point motion, and a high surface-to-volume ratio useful for surface-based sensing mechanisms. Applications include accelerometers and sensors to detect chemical substances in the air.
An electroactive polymer (EAP) is a polymer that exhibits a change in size or shape when stimulated by an electric field. The most common applications of this type of material are in actuators and sensors. A typical characteristic property of an EAP is that they will undergo a large amount of deformation while sustaining large forces.
Metal rubber is a broad, informal name for several conductive plastic polymers with metal ions produced by NanoSonic Inc. in cooperation with Virginia Tech. This self-assembling nanocomposite is flexible and durable to high and low pressures, temperatures, tensions, and most chemical reactions, and retains all of its physical and chemical properties upon being returned to a ground state. NanoSonic’s Metal rubber™ is an electrically conductive and flexible elastomer. It can be mechanically strained to greater than 1000% of its original dimensions while remaining electrically conductive. As Metal rubber can carry data and electrical power and is environmentally rugged, it can be used as a flexible and stretchable electrical conductor in the aerospace/defense, electronics, and bioengineering markets.
An antistatic agent is a compound used for treatment of materials or their surfaces in order to reduce or eliminate buildup of static electricity. Static charge may be generated by the triboelectric effect or by a non-contact process using a high voltage power source. Static charge may be introduced on a surface as part of an in-mold label printing process.

A piezoelectric sensor is a device that uses the piezoelectric effect to measure changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, strain, or force by converting them to an electrical charge. The prefix piezo- is Greek for 'press' or 'squeeze'.
The piezoresistive effect is a change in the electrical resistivity of a semiconductor or metal when mechanical strain is applied. In contrast to the piezoelectric effect, the piezoresistive effect causes a change only in electrical resistance, not in electric potential.
Level sensors detect the level of liquids and other fluids and fluidized solids, including slurries, granular materials, and powders that exhibit an upper free surface. Substances that flow become essentially horizontal in their containers because of gravity whereas most bulk solids pile at an angle of repose to a peak. The substance to be measured can be inside a container or can be in its natural form. The level measurement can be either continuous or point values. Continuous level sensors measure level within a specified range and determine the exact amount of substance in a certain place, while point-level sensors only indicate whether the substance is above or below the sensing point. Generally the latter detect levels that are excessively high or low.

An antistatic device is any device that reduces, dampens, or otherwise inhibits electrostatic discharge, or ESD, which is the buildup or discharge of static electricity. ESD can damage electrical components such as computer hard drives, and even ignite flammable liquids and gases.

A force-sensing resistor is a material whose resistance changes when a force, pressure or mechanical stress is applied. They are also known as force-sensitive resistor and are sometimes referred to by the initialism FSR.
Quantum tunnelling composites (QTCs) are composite materials of metals and non-conducting elastomeric binder, used as pressure sensors. They use quantum tunnelling: without pressure, the conductive elements are too far apart to conduct electricity; when pressure is applied, they move closer and electrons can tunnel through the insulator. The effect is far more pronounced than would be expected from classical (non-quantum) effects alone, as classical electrical resistance is linear (proportional to distance), while quantum tunnelling is exponential with decreasing distance, allowing the resistance to change by a factor of up to 1012 between pressured and unpressured states.
A MEMSmagnetic field sensor is a small-scale microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) device for detecting and measuring magnetic fields (Magnetometer). Many of these operate by detecting effects of the Lorentz force: a change in voltage or resonant frequency may be measured electronically, or a mechanical displacement may be measured optically. Compensation for temperature effects is necessary. Its use as a miniaturized compass may be one such simple example application.
Electronic skin refers to flexible, stretchable and self-healing electronics that are able to mimic functionalities of human or animal skin. The broad class of materials often contain sensing abilities that are intended to reproduce the capabilities of human skin to respond to environmental factors such as changes in heat and pressure.

Electrostatic discharge materials are plastics that reduce static electricity to protect against damage to electrostatic-sensitive devices (ESD) or to prevent the accidental ignition of flammable liquids or gases.
A conductive elastomer is a form of elastomer, often natural rubber or other rubber substitute, that is manufactured to conduct electricity. This is commonly accomplished by distributing carbon or other conductive particles throughout the raw material prior to setting it. Carbon black and silica are common additives to induce conductivity in elastomers. Silica has been studied more so than other additives due to its low cost however, its conductance is also lower. These additives can not only enable conductance but can increase the mechanical properties of the elastomer.
References
- ↑ Drake, N. (1996). Polymeric Materials for Electrostatic Applications. Rapra Technology. p. 131. ISBN 978-1-85957-076-0.
- ↑ Mims, Forrest M. (2000). Mims Circuit Scrapbook. Newnes. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-878707-49-9.
- ↑ "3M Completes Sale of Static Control Business to Desco Industries Inc". 3M News | United States. Archived from the original on 2018-07-02. Retrieved 2018-05-15.
- ↑ Dzedzickis, Andrius; Sutinys, Ernestas; Bucinskas, Vytautas; Samukaite-Bubniene, Urte; Jakstys, Baltramiejus; Ramanavicius, Arunas; Morkvenaite-Vilkonciene, Inga (2020). "Polyethylene-Carbon Composite (Velostat®) Based Tactile Sensor". Polymers. 12 (12): 2905. doi: 10.3390/polym12122905 . ISSN 2073-4360. PMC 7761878 . PMID 33287414.
- ↑ "Pressure-Sensitive Conductive Sheet (Velostat/Linqstat)". adafruit.com. Retrieved 12 February 2015.