
Mumbai is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the de facto financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second-most populous city in India after Delhi and the eighth-most populous city in the world with a population of roughly 2 crore. As per the Indian government population census of 2011, Mumbai was the most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 1.25 crore (12.5 million) living under the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation. Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 2.3 crore. Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an alpha world city. It has the highest number of millionaires and billionaires among all cities in India.

Powai Lake is an artificial lake, situated in Mumbai, in the Powai valley, where a Powai village with a cluster of huts existed. The city suburb called Powai shares its name with the lake. Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, one of the premier institutions of science and technology in India, is located to the east of the lake. Another famous institution, the National Institute of Industrial Engineering (NITIE), is also located close to the lake. Housing complexes and plush hotels are developed all around the lake periphery. Population around the lake has thus substantially increased over the years.

Powai is an upscale residential neighbourhood located in central Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It is situated on the banks of Powai Lake, and is bound by the hills of Vikhroli Parksite to the south-east, Chandivali to the south-west, the L.B.S. Marg to the north-east and the Sanjay Gandhi National Park to the north beyond the lake. The Jogeshwari-Vikhroli Link Road, one of the city's busiest thoroughfares linking the western and eastern suburbs, passes through Powai,. The place also hosts thousands of devotees every year during the Ganesh Chaturthi festival for the visarjan processions.

Mahim is a neighbourhood in Mumbai, India. The Mahim railway station is in the Mahim area, on the Mumbai suburban railway on the Western Railway line. Mahim is diverse and has a church, mosque and fire-temple existing within a few meters of each other.

Sanjay Gandhi National Park, also known as SGNP, is an 87 km2 (34 sq mi) protected area in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It was established in 1969 with its headquarters situated at Borivali.

Salsette Island is an island in Konkan division of the state of Maharashtra on India's west coast. Administratively known as the Greater Mumbai, the city district of Mumbai, Mumbai Suburban District, Mira Bhayander and a portion of Thane lie within it, making it very populous and one of the most densely populated islands in the world. It has a population of more 20 million inhabitants living on an area of about 619 square kilometres (239 sq mi).

Tulsi Lake is a fresh water lake in northern Mumbai. It is stated to be the second largest lake in Mumbai and supplies part of the city's potable water. This is one of the three lakes located in the Salsette Island; the other two being Powai Lake and Vihar Lake. Both Tulsi lake and Vihar lake are located within the densely forested Sanjay Gandhi National Park or also known popularly as the Borivali National Park (BNP).

Mumbai (Bombay) is India's most populous city with a population of 20 Million. It is located on Salsette Island off the coast of Maharashtra. The original seven islands of Bombay were merged by the British in the 18th century, to form one large island.

The Mithi River is a river on Salsette Island, the island of the city of Mumbai, India. It is a confluence of tail-water discharges of the Powai and Vihar lakes. The river is seasonal and rises during the monsoons. The overflowing lakes also contribute to the river flow, which is stopped by a dam at other times. During this season, the gutter is a favourite with anglers, who can catch large fish that have escaped from the lakes. Chattrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport is located right next to the section of river at Andheri (E).
The Brihanmumbai Stormwater Disposal System is a project planned to overhaul Mumbai's water drainage system. The estimated budget for implementing the project is Rs. 12 billion as of August 2005. Such a high-budget project would require funds from the Central Government. Mumbai has a drainage system, which in many places, are more than 100 years old, consisting of 2,000 km of open drains, 440 km of closed drains, 186 outfalls and more than 30,000 water entrances. The capacity of most of the drains is around 25 mm of rain per hour during low tide, which is exceeded routinely during the monsoon season in Mumbai, which witness more than 1400 mm during June and July. The drain system works with the aid of gravity, with no pumping stations to speed up the drainage. Most of the storm water drains are also choked due to the dumping of garbage by citizens. Portions of Mumbai like Bombay Central and Tardeo remain below sea level. Reclamation of ponds and obstructions in drains due to cables and gas pipe exacerbate the problem.

Mumbai Suburban district is the second most populous district of Maharashtra in the Konkan Division. With its administrative headquarters in Bandra, the district consists of three subdivisions or tehsils (townships): Kurla, Andheri, and Borivali. The district along with Mumbai City district and other suburban localities make up Greater Mumbai. The district occupies an area of 446 km2.

Mahim Bay is a bay, part of the Arabian Sea in Mumbai, India. The southern end is Worli, northern end is Bandra Reclamation and Mahim is in the centre. The bay was named after the islands of Mahim and Salsette were merged in the early 19th century. The Mithi River drains into Mahim Creek which drains into the Bay, and forms the border between the city and its suburbs.

Dahisar River is a river on Salsette island that runs through Dahisar, a suburb of Mumbai, India. It originates in the Tulsi Lake in Sanjay Gandhi National Park in the northern reaches of the city. The River flows roughly North-West for a total of 12 kilometres through the localities of the National Park, Sri Krishna Nagar, Daulatnagar, Leprosy Colony, Kandar Pada, Sanjay Nagar, and Dahisar Gaothan before meeting the Arabian sea via the Manori Creek. Its total Catchment area is 3488 hectares.
The 2006 Mumbai "sweet" seawater incident was a strange phenomenon during which residents of Mumbai claimed that the water at Mahim Creek had suddenly turned sweet. Within hours, residents of Gujarat claimed that seawater at Tithal beach had turned sweet as well. This caused a mass hysteria among people who started coming in large numbers to drink the sea water.
River Tasso is a river in Mumbai (Bombay), India which empties into the Vihar Lake. It originates in the Sanjay Gandhi National Park. In 1872, the plan was made to dam and redirect the river into the Tulsi Lake at a then cost of Rs. 40 lakh (4,000,000).

The Western Suburbs is the western precinct of the city of Mumbai, India. The Western Suburbs consist of Andheri, Bandra, Bhayander, Borivali, Dahisar, Goregaon, Jogeshwari, Juhu, Kandivali, Khar, Malad, Mira Road, Santacruz and Vile Parle. Geographically, the Western Suburbs lie at the western part of Salsette Island, is a continuous urban sprawl spanning the areas from Bandra to Bhayander, which is separated by the Vasai Creek from Vasai-Virar city and Mithi River from Mumbai city.

East Mumbai consists the localities of Bhandup, Ghatkopar, Kanjurmarg, Kurla, Mulund, Nahur, Powai, Thane, Vidyavihar and Vikhroli. To the south-east lie the neighborhoods of Chembur, Govandi, Mankhurd, Trombay and Wadala.
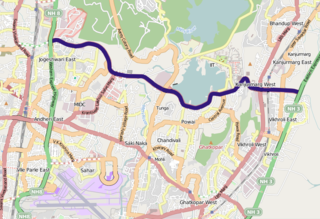
The Jogeshwari – Vikhroli Link Road (JVLR), is a 10.6-kilometre-long (6.6 mi) 6-lane road with a central median in Mumbai which connects the Western Express Highway and Eastern Express Highway providing speedier access from Jogeshwari in the Western Suburbs to Vikhroli in the Eastern Suburbs. It was opened to traffic in 1994, and widened from two to six lanes in 2012 at a cost of ₹221.45 crore. The under-construction Line 6 of the Mumbai Metro is being constructed on this link road.

Tourism in Mumbai (Bombay) is an industry that attracts almost 6 million tourists per year, making it the 30th-most visited location worldwide. According to United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai was the second most populous city in India after Delhi and the seventh most populous city in the world with a population of 19.98 million.



























