A special election was held in Maryland's 3rd congressional district on December 8, 1794, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Uriah Forrest (P) on November 8 of the same year. [1]
| Elections in Maryland |
|---|
 |
A special election was held in Maryland's 3rd congressional district on December 8, 1794, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Uriah Forrest (P) on November 8 of the same year. [1]
| Candidate | Party | Votes [2] | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benjamin Edwards | Pro-Administration | 364 | 54.4% |
| Thomas Turner | Unknown | 281 | 42.0% |
| Richard Hall | Unknown | 24 | 3.6% |
Edwards took his seat in the 3rd Congress on January 2, 1795. [1]

The 1966 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives on November 8, 1966, to elect members to serve in the 90th United States Congress. They occurred in the middle of President Lyndon B. Johnson's second term. As the Vietnam War continued to escalate and race riots exploded in cities across the country, Johnson's popularity had fallen, and the opposition Republican Party was able to gain a net of 47 seats from Johnson's Democratic Party, which nonetheless maintained a clear majority in the House. This was also the first election that occurred after the Voting Rights Act of 1965 became law, the first time since 1870 that a Republican won a House seat in Arkansas, and the first since 1876 that the party did so in South Carolina.

The 1952 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 83rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 4, 1952, while Maine held theirs on September 8. This was the first election after the congressional reapportionment based on the 1950 census. It also coincided with the election of President Dwight Eisenhower. Eisenhower's Republican Party gained 22 seats from the Democratic Party, gaining a majority of the House. However, the Democrats had almost 250,000 more votes (0.4%) thanks to overwhelming margins in the Solid South, although this election did see the first Republican elected to the House from North Carolina since 1928, and the first Republicans elected from Virginia since 1930. It was also the last election when both major parties increased their share of the popular vote simultaneously, largely due to the disintegration of the American Labor Party and other third parties.

The 1842–43 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 1, 1842, and November 8, 1843. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 28th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1843. The exception was Maryland, who held theirs so late that they ran into February 1844. These elections occurred during President John Tyler's term. The congressional reapportionment based on the 1840 United States census unusually decreased the number of House seats, from 242 down to 223.

The 1828–29 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 9, 1828, and October 5, 1829. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 21st United States Congress convened on December 7, 1829. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.
The 1820–21 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 3, 1820, and August 10, 1821. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 17th United States Congress convened on December 3, 1821. They coincided with President James Monroe winning reelection unopposed.

The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810, and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
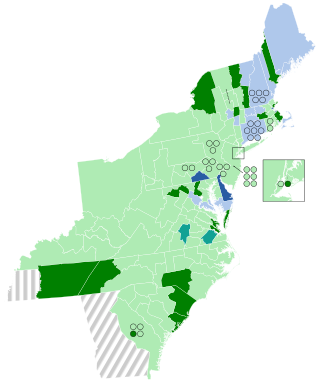
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804, and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.
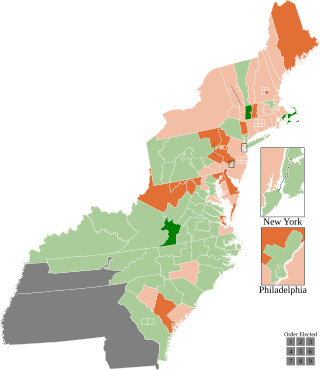
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
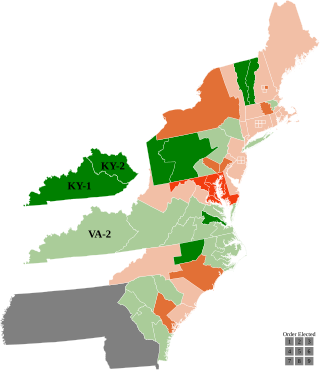
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.

Maryland's 2nd congressional district elects a representative to the United States House of Representatives every two years. The district comprises parts of Carroll and Baltimore counties, as well as small portions of the Baltimore City. The seat has been represented by Dutch Ruppersberger of the Democratic Party since 2003.

Maryland's 7th congressional district of the United States House of Representatives encompasses almost the entire city of Baltimore and some of Baltimore County. The district was created following the census of 1790, which gave Maryland one additional representative in the House. It was abolished in 1843 but was restored in 1950 as a west Baltimore district. It has been drawn as a majority-African American district since 1973. Democrat Kweisi Mfume is the current representative, winning a special election on April 28, 2020, to finish the term of Elijah Cummings, who died in October 2019. Mfume had previously held the seat from 1987 to 1996.

Maryland's 3rd congressional district covers all of Howard county as well as parts of Anne Arundel and Carroll counties. The seat is currently represented by John Sarbanes, a Democrat.

A special election was held in Maryland's 3rd congressional district in 1816 to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Alexander C. Hanson (F) upon being elected to the United States Senate.

A special election was held in Maryland's 3rd congressional district to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of William Pinkney (P) due to questions of ineligibility due to his residence

A special election was held in Maryland's 2nd congressional district on May 5, 1794, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of John Francis Mercer (A) on April 13, 1794

The 2020 United States House of Representatives elections in Maryland was held on November 3, 2020, to elect the eight U.S. representatives from the state of Maryland, one from each of the state's eight congressional districts. The elections coincided with the 2020 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate, and various state and local elections. On March 17, 2020, Governor Larry Hogan announced that the primary election would be postponed from April 28 to June 2 due to coronavirus concerns. On March 26, the Maryland Board of Elections met to consider whether in-person voting should be used for June's primary, and recommended that voting in June be mail-in only.

A special election was held on April 28, 2020, after a February 4, 2020 primary, to fill the remainder of the term in the United States House of Representatives for Maryland's 7th congressional district in the 116th U.S. Congress. Elijah Cummings, the incumbent representative, died in office on October 17, 2019.

The 1981 United States elections were off-year elections were held on Tuesday, November 3, 1981, comprising 2 gubernatorial races, 5 congressional special elections, and a plethora of other local elections across the United States. No Senate special elections were held.