
The 2006 Illinois gubernatorial election took place on November 7, 2006. Incumbent Democratic Governor Rod Blagojevich won re-election to a second four-year term scheduled to have ended on January 10, 2011. However, Blagojevich did not complete his term, as he was impeached and removed from office in 2009. This was the first election since 1964 that a Democrat was re-elected governor.

The lieutenant governor of Illinois is the second highest executive of the State of Illinois. In Illinois, the lieutenant governor and governor run on a joint ticket and are directly elected by popular vote. Gubernatorial candidates select their running mates when filing for office and appear on the primary election ballot together. When the governor of Illinois becomes unable to discharge the duties of that office, the lieutenant governor becomes acting governor. If the governor dies, resigns or is removed from office, the lieutenant governor becomes governor. Under the Illinois Constitution, the Attorney General is next in line of succession to the Governor's office after the lieutenant governor, but does not succeed to the lieutenant governor's office. From the impeachment of Rod Blagojevich in 2009, until the inauguration of Sheila Simon in 2011, Attorney General Lisa Madigan would have become governor if Pat Quinn had vacated the office. Historically, the lieutenant governor has been from either the Democratic Party or Republican Party. The current lieutenant governor is Democrat Juliana Stratton.

Thomas J. Dart is an American attorney, politician, and law enforcement officer serving as the Sheriff of Cook County, Illinois. He previously served as a member of both chambers of the Illinois General Assembly.
Illinois is a Democratic stronghold in presidential elections and one of the "Big Three" Democratic strongholds alongside California and New York. It is one of the most Democratic states in the nation with all state executive offices and both state legislative branches held by Democrats. For most of its history, Illinois was widely considered to be a swing state, voting for the winner of all but two presidential elections in the 20th century. Political party strength in Illinois is highly dependent upon Cook County, and the state's reputation as a blue state rests upon the fact that over 40% of its population and political power is concentrated in Chicago, Cook County, and the Chicago metropolitan area. Outside of Chicago, the suburban collar counties continue trending Democratic while downstate Illinois can be considered more conservative with several Democratic leaning regions including Champaign-Urbana, Bloomington-Normal, Rockford, Peoria, the Quad Cities, and suburban St. Louis.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 7, 1978, in 36 states and two territories. The Republicans had a net gain of six seats, Democrats sustained a net loss of five seats, and there would be no governors of any other parties following these elections.

The 2010 Illinois gubernatorial election took place on November 2, 2010. Incumbent Democratic Governor Pat Quinn was elected to a full term in office, having become governor in 2009 following the impeachment and removal of Governor Rod Blagojevich. Quinn was elected as the Democratic nominee, the Illinois Green Party nominee was attorney and 2006 nominee Rich Whitney, the Republican nominee was State Senator Bill Brady, the Libertarian Party nominee was Lex Green, and Scott Lee Cohen ran as an independent.

The 1998 Illinois gubernatorial election took place on November 3, 1998. Incumbent Republican Governor Jim Edgar did not run for a third term in office. Republican nominee George Ryan, the Illinois Secretary of State, narrowly won the election against Democratic Congressman Glenn Poshard.

The 1986 Illinois gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1986. Republican candidate James R. Thompson won a fourth term in office, defeating the Illinois Solidarity Party nominee, former United States Senator Adlai Stevenson III, by around 400,000 votes.

The 1838 Illinois gubernatorial election was the sixth quadrennial election for this office. Democrat Thomas Carlin was elected by a bare majority of the voters in a close election. He defeated Cyrus Edwards, the brother of former governor Ninian Edwards for the office.

The 1848 Illinois gubernatorial election was the ninth election for this office. Democratic governor Augustus C. French was easily re-elected. This was the first gubernatorial election in Illinois that was held on the same date as the United States presidential election.

The 1852 Illinois gubernatorial election was the tenth election for this office. Democratic governor Augustus C. French did not seek re-election. Democrat Joel Aldrich Matteson was elected to succeed him. At this time in Illinois history the Lieutenant Governor was elected on a separate ballot from the governor. This remained the case until the adoption of the 1970 constitution.

The 1860 Illinois gubernatorial election was the twelfth election for this office. Republican governor William Henry Bissell died early in his term, and incumbent governor John Wood did not seek re-election. Former Democratic Congressman and former Clerk of the U.S. House James C. Allen was the Democratic nominee. A Number of third-party candidates ran as well; none received over one percent of the vote. At this time in Illinois history the Lieutenant Governor was elected on a separate ballot from the governor. This would remain the case until the adoption of the 1970 constitution.

The 1978 Illinois gubernatorial election was held on Tuesday, November 7, 1978. Republican James R. Thompson easily won a second term in office, defeating Democratic nominee Michael Bakalis by nearly 600,000 votes.

The 1864 Illinois gubernatorial election was the thirteenth election for this office and took place during the American Civil War. Republican governor Richard Yates did not run for re-election, but was instead elected to serve in the United States Senate. Major General Richard J. Oglesby resigned his commission to run as the Republican nominee. Congressman James Carroll Robinson was the Democratic nominee. At this time in Illinois history, the Lieutenant Governor was elected on a separate ballot from the governor. This would remain the case until the adoption of the 1970 constitution.

Elections were held in Illinois on Tuesday, November 7, 1972.
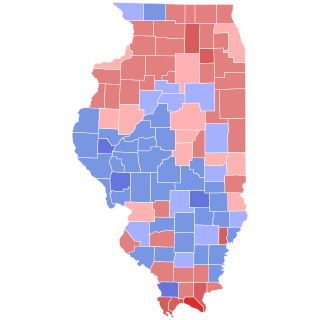
The 1908 Illinois gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1908.

The 1912 Illinois gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 1912. Incumbent second-term Republican governor Charles S. Deneen was defeated by the Democratic nominee, former mayor of Chicago Edward Fitzsimmons Dunne.

The 1948 Illinois gubernatorial election took place on November 2, 1948. Incumbent Governor Dwight H. Green, a Republican seeking a third term, lost reelection to Democratic nominee Adlai Stevenson II.

The 1876 Illinois gubernatorial election was the sixteenth election for this office. Representative Shelby Moore Cullom narrowly defeated businessman Lewis Steward for the Governorship of Illinois. This was the narrowest victory for a Republican Governor since 1856, when William H. Bissell narrowly won the office in a plurality. Cullom's victory was the sixth consecutive victory for the Republican Party. Cullom also slightly overperformed Republican candidate Rutherford B. Hayes in the concurrent Presidential election.


















