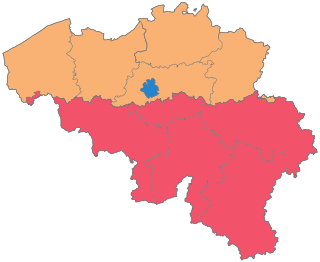
The country of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, the Flemish Region or Flanders, and Walloon Region, or Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, the Brussels-Capital Region, is not divided into provinces, as it was originally only a small part of a province itself.
The Provinces of the Philippines are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 81 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and by an elected governor.
A city is one of the units of local government in the Philippines. All Philippine cities are chartered cities, whose existence as corporate and administrative entities is governed by their own specific municipal charters in addition to the Local Government Code of 1991, which specifies their administrative structure and powers. As of December 12, 2015, there were 145 cities.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2006 took place on Sunday 8 October 2006. The electors have elected the municipal councillors of 589 cities and towns as well as the ten provincial councils. The voters in the town of Antwerp have also been able to vote for the city's district councils. In seven Flemish municipalities with a special language statute and in the Walloon municipality of Comines-Warneton the aldermen and the members of the OCMW/CPAS council have also been directly elected.

The 2007 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 27 May 2007, to elect all 66,131 councillors in the 8,111 municipalities of Spain and all 1,038 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.
The politics of the Western Cape are more complex than in most other provinces of South Africa, because, unlike the other provinces, the African National Congress (ANC) does not dominate the political landscape.
In South Africa, a provincial legislature is the legislative branch of the government of a province. The provincial legislatures are unicameral and vary in size from 30 to 80 members, depending on the population of the province. Each legislature is chaired by a Speaker and a Deputy Speaker.
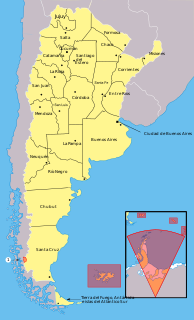
Most Provinces of Argentina held executive and legislative elections during 2011, electing Governors and provincial legislatures. The only exceptions are Santiago del Estero Province, whose executive and legislative elections were elected in 2012; and Corrientes Province, whose governor election was elected in 2013.

The 2011 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 22 May 2011, to elect all 68,230 councillors in the 8,116 municipalities of Spain and all 1,040 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 2011 Italian local elections were held on 15–16 May, with a second round on 29–30 May. In Italy, direct elections were held in all 1,177 municipalities and 11 provinces: in each municipality (comune) were chosen mayor and members of the City Council, in each province were chosen president and members of the Provincial Council. Of the 1,177 municipalities, 30 were provincial capital municipalities and only 105 had a population higher than 15,000 inhabitants.

The 2010 Italian local elections were held on different dates; most on 29–30 March oncurrently with the Regional elections.

The 2015 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 24 May 2015, to elect all 67,515 councillors in the 8,122 municipalities of Spain and all 1,040 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 1979 Spanish local elections were held on Tuesday, 3 April 1979, to elect all 67,505 councillors in the 7,870 municipalities of Spain and all 1,152 seats in 43 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with local elections in the four foral deputations of the Basque Country and Navarre and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 1983 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 8 May 1983, to elect all 67,505 councillors in the 7,781 municipalities of Spain and all 1,024 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 1987 Spanish local elections were held on Wednesday, 10 June 1987, to elect all 65,577 councillors in the 8,062 municipalities of Spain and all 1,028 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country, the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands and the 1987 European Parliament election.

The 1991 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 26 May 1991, to elect all 66,308 councillors in the 8,060 municipalities of Spain and all 1,032 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 1995 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 28 May 1995, to elect all 65,869 councillors in the 8,067 municipalities of Spain and all 1,034 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 1999 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 13 June 1999, to elect all 65,201 councillors in the 8,104 municipalities of Spain and all 1,034 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country, the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands and the 1999 European Parliament election.

The 2003 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 25 May 2003, to elect all 65,510 councillors in the 8,108 municipalities of Spain and all 1,036 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 2019 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 26 May 2019, to elect all councillors in the municipalities of Spain and all seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in twelve autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country, the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands and the 2019 European Parliament election.















