The Apiales are an order of flowering plants. The families are those recognized in the APG III system. This is typical of the newer classifications, though there is some slight variation and in particular, the Torriceliaceae may also be divided.

Asterales is an order of dicotyledonous flowering plants that includes the large family Asteraceae known for composite flowers made of florets, and ten families related to the Asteraceae. While asterids in general are characterized by fused petals, composite flowers consisting of many florets create the false appearance of separate petals.

The Laurales are an order of flowering plants. They are magnoliids, related to the Magnoliales.

The Magnoliales are an order of flowering plants.

Illiciales is an order of flowering plants that is not recognized by the current most widely used system of plant classification, the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group's APG III system. The order was comprised differently in various systems of plant taxonomy, but is composed of 2-4 families of shrubs, trees, and lianas native to Australasia, south eastern Asia, and the southeastern United States. The families all contain species with essential oils, and flowers with a perianth with bracts, sepals, and petals incompletely distinguished from each other and not arranged in definite whorls. The families of the order had been variably placed in other orders in different taxonomies.

The Celastrales are an order of flowering plants found throughout the tropics and subtropics, with only a few species extending far into the temperate regions. The 1200 to 1350 species are in about 100 genera. All but seven of these genera are in the large family Celastraceae. Until recently, the composition of the order and its division into families varied greatly from one author to another.

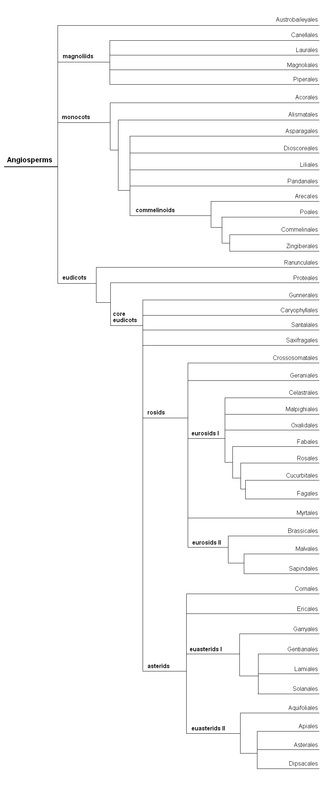
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants (angiosperms) which are mainly characterized by having two seed leaves (cotyledons) upon germination. The term derives from dicotyledon. Previously, they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by past authors. The current botanical terms were introduced in 1991, by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton, to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots.

The rosids are members of a large clade of flowering plants, containing about 70,000 species, more than a quarter of all angiosperms.

In the APG IV system (2016) for the classification of flowering plants, the name asterids denotes a clade. Asterids is the largest group of flowering plants, with more than 80,000 species, about a third of the total flowering plant species. Well-known plants in this clade include the common daisy, forget-me-nots, nightshades, the common sunflower, petunias, yacon, morning glory, lettuce, sweet potato, coffee, lavender, lilac, olive, jasmine, honeysuckle, ash tree, teak, snapdragon, sesame, psyllium, garden sage, blueberries, table herbs such as mint, basil, and rosemary, and rainforest trees such as Brazil nut.
The APG system of plant classification is the first version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy. Published in 1998 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, it was replaced by the improved APG II in 2003, APG III system in 2009 and APG IV system in 2016.

In plant taxonomy, commelinids is a clade of flowering plants within the monocots, distinguished by having cell walls containing ferulic acid.

Escalloniaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of about 130 species in eight genera. In the APG II system it is one of eight families in the euasterids II clade (campanulids) that are unplaced as to order. More recent research has provided evidence that two of those families, Eremosynaceae and Tribelaceae, arose from within Escalloniaceae; the Angiosperm Phylogeny Website therefore merges these two families into Escalloniaceae, and also places the family alone in order Escalloniales.

Magnoliids, Magnoliidae or Magnolianae are a clade of flowering plants. With more than 10,000 species, including magnolias, nutmeg, bay laurel, cinnamon, avocado, black pepper, tulip tree and many others, it is the third-largest group of angiosperms after the eudicots and monocots. The group is characterized by trimerous flowers, pollen with one pore, and usually branching-veined leaves.

The basal angiosperms are the flowering plants which diverged from the lineage leading to most flowering plants. In particular, the most basal angiosperms were called the ANITA grade, which is made up of Amborella, Nymphaeales and Austrobaileyales.

Tribeles australis, the sole species in the genus Tribeles, is a prostrate shrub native to Chile and Argentina.

The Paracryphiaceae are a family of woody shrubs and trees native to Australia, southeast Asia, and New Caledonia. In the APG III system of 2009, the family is placed in its own order, Paracryphiales, in the campanulid clade of the asterids. In the earlier APG II system, the family was unplaced as to order and included only Paracryphia.
The APG III system of flowering plant classification is the third version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). Published in 2009, it was superseded in 2016 by a further revision, the APG IV system.

The superrosids are members of a large clade of flowering plants, containing more than 88,000 species, and thus more than a quarter of all angiosperms.

In phylogenetic nomenclature, the Pentapetalae are a large group of eudicots that were informally referred to as the "core eudicots" in some papers on angiosperm phylogenetics. They comprise an extremely large and diverse group accounting for about 65% of the species richness of the angiosperms, with wide variability in habit, morphology, chemistry, geographic distribution, and other attributes. Classical systematics, based solely on morphological information, was not able to recognize this group. In fact, the circumscription of the Pentapetalae as a clade is based on strong evidence obtained from DNA molecular analysis data.

The superasterids are members of a large clade of flowering plants, containing more than 122,000 species.