
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit wouldn't be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities.
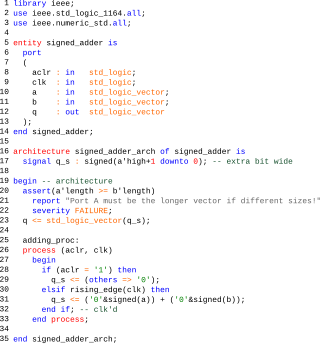
VHDL is a hardware description language that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gates, for design entry, documentation, and verification purposes. The language was developed for the US military VHSIC program in the 1980s, and has been standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as IEEE Std 1076; the latest version of which is IEEE Std 1076-2019. To model analog and mixed-signal systems, an IEEE-standardized HDL based on VHDL called VHDL-AMS has been developed.
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. It is also used in the verification of analog circuits and mixed-signal circuits, as well as in the design of genetic circuits. In 2009, the Verilog standard was merged into the SystemVerilog standard, creating IEEE Standard 1800-2009. Since then, Verilog has been officially part of the SystemVerilog language. The current version is IEEE standard 1800-2023.
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, usually to design application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and to program field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs).

An application-specific integrated circuit is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips.
The MicroBlaze is a soft microprocessor core designed for Xilinx field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA). As a soft-core processor, MicroBlaze is implemented entirely in the general-purpose memory and logic fabric of Xilinx FPGAs.
Specman is an EDA tool that provides advanced automated functional verification of hardware designs. It provides an environment for working with, compiling, and debugging testbench environments written in the e Hardware Verification Language. Specman also offers automated testbench generation to boost productivity in the context of block, chip, and system verification.

OrCAD Systems Corporation was a software company that made OrCAD, a proprietary software tool suite used primarily for electronic design automation (EDA). The software is used mainly by electronic design engineers and electronic technicians to create electronic schematics, and perform mixed-signal simulation and electronic prints for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs). OrCAD was taken over by Cadence Design Systems in 1999 and was integrated with Cadence Allegro in 2005.

Quite Universal Circuit Simulator (Qucs) is a free-software electronics circuit simulator software application released under GPL. It offers the ability to set up a circuit with a graphical user interface and simulate the large-signal, small-signal and noise behaviour of the circuit. Pure digital simulations are also supported using VHDL and/or Verilog. Only a small set of digital devices like flip flops and logic gates can be used with analog circuits. Qucs uses its own SPICE-incompatible backend simulator Qucsator, however the Qucs-S fork supports some SPICE backends.
Intel Quartus Prime is programmable logic device design software produced by Intel; prior to Intel's acquisition of Altera the tool was called Altera Quartus Prime, earlier Altera Quartus II. Quartus Prime enables analysis and synthesis of HDL designs, which enables the developer to compile their designs, perform timing analysis, examine RTL diagrams, simulate a design's reaction to different stimuli, and configure the target device with the programmer. Quartus Prime includes an implementation of VHDL and Verilog for hardware description, visual editing of logic circuits, and vector waveform simulation.
C to HDL tools convert C language or C-like computer code into a hardware description language (HDL) such as VHDL or Verilog. The converted code can then be synthesized and translated into a hardware device such as a field-programmable gate array. Compared to software, equivalent designs in hardware consume less power and execute faster with lower latency, more parallelism and higher throughput. However, system design and functional verification in a hardware description language can be tedious and time-consuming, so systems engineers often write critical modules in HDL and other modules in a high-level language and synthesize these into HDL through C to HDL or high-level synthesis tools.
Flow to HDL tools and methods convert flow-based system design into a hardware description language (HDL) such as VHDL or Verilog. Typically this is a method of creating designs for field-programmable gate array, application-specific integrated circuit prototyping and digital signal processing (DSP) design. Flow-based system design is well-suited to field-programmable gate array design as it is easier to specify the innate parallelism of the architecture.
Semulation is a computer science-related portmanteau of simulation and emulation, signifying the process of controlling an emulation through a simulator.
ModelSim is a multi-language environment by Siemens for simulation of hardware description languages such as VHDL, Verilog and SystemC, and includes a built-in C debugger. ModelSim can be used independently, or in conjunction with Intel Quartus Prime, PSIM, Xilinx ISE or Xilinx Vivado. Simulation is performed using the graphical user interface (GUI), or automatically using scripts.

Verilator is a free and open-source software tool which converts Verilog to a cycle-accurate behavioral model in C++ or SystemC. The generated models are cycle-accurate and 2-state; as a consequence, the models typically offer higher performance than the more widely used event-driven simulators, which can model behavior within the clock cycle. Verilator is now used within academic research, open source projects and for commercial semiconductor development. It is part of the growing body of free electronic design automation (EDA) software.
Field-programmable gate array prototyping, also referred to as FPGA-based prototyping, ASIC prototyping or system-on-chip (SoC) prototyping, is the method to prototype system-on-chip and application-specific integrated circuit designs on FPGAs for hardware verification and early software development.
Catapult C Synthesis, a commercial electronic design automation product of Mentor Graphics, is a high-level synthesis tool, sometimes called algorithmic synthesis or ESL synthesis. Catapult C takes ANSI C/C++ and SystemC inputs and generates register transfer level (RTL) code targeted to FPGAs and ASICs.
This page is a comparison of electronic design automation (EDA) software which is used today to design the near totality of electronic devices. Modern electronic devices are too complex to be designed without the help of a computer. Electronic devices may consist of integrated circuits (ICs), printed circuit boards (PCBs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) or a combination of them. Integrated circuits may consist of a combination of digital and analog circuits. These circuits can contain a combination of transistors, resistors, capacitors or specialized components such as analog neural networks, antennas or fuses.

EVE/ZeBu is a provider of hardware-assisted verification tools for functional verification of Application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and system on chip (SOC) designs and for validation of embedded software ahead of implementation in silicon. EVE's hardware acceleration and hardware emulation products work in conjunction with Verilog, SystemVerilog, and VHDL-based simulators from Synopsys, Cadence Design Systems and Mentor Graphics. EVE's flagship product is ZeBu.

Xilinx ISE is a discontinued software tool from Xilinx for synthesis and analysis of HDL designs, which primarily targets development of embedded firmware for Xilinx FPGA and CPLD integrated circuit (IC) product families. It was succeeded by Xilinx Vivado. Use of the last released edition from October 2013 continues for in-system programming of legacy hardware designs containing older FPGAs and CPLDs otherwise orphaned by the replacement design tool, Vivado Design Suite.








