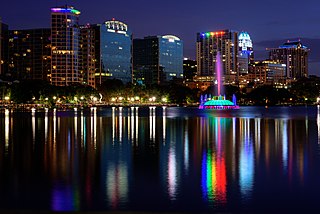Orange County is a county located in the central part of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the county had a population of 1,429,908, making it the fifth-most populous county in Florida and the 28th-most populous county in the United States. Its county seat is Orlando, which, along with it being the county's largest city, is the core of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2.67 million in 2020.

Seminole County is a county located in the central portion of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 470,856, making it the 13th-most populated county in Florida. Its county seat and largest city is Sanford. Seminole County is part of the Orlando-Kissimmee-Sanford, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Clermont is a city in Lake County in central Florida, United States, about 22 miles (35 km) west of Orlando and 22 miles (35 km) southeast of Leesburg. The population was 43,021 in 2020. The city is residential in character and its economy is centered in retail trade, lodging, and tourism-oriented restaurants and bars. It is part of the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Ocoee is a city in Orange County, Florida, United States. It is part of the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area. According to the 2020 US Census, the city had a population of 47,295.

Pine Hills is a census-designated place (CDP) and unincorporated subdivision in Orange County, Florida, United States, west of Orlando. Per the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 66,111. It is a part of the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Winter Garden is a city in western Orange County, Florida, United States. Located 14 miles (23 km) west of Downtown Orlando, it is part of the Orlando metropolitan area. The population was 46,964 as of the 2020 census.

Altamonte Springs is a suburban city in Central Florida in Seminole County, Florida, United States, which had a population of 46,231 at the 2020 United States Census. The city is in the northern suburbs of the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford Metropolitan Statistical Area, which the United States Census Bureau estimated had a population of 2,673,376 in 2020.

Lake Mary is a suburban city that is located in the Greater Orlando metropolitan area in Seminole County, Florida, United States, and is located in Central Florida. The population was 16,798 at the 2020 census. Home of the 2024 Little League World Series Champions.

Sanford is a city and the county seat of Seminole County, Florida. It is located in Central Florida and its population was 61,051 as of the 2020 census. It is part of the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Wekiwa Springs is a census-designated place and an unincorporated area in Seminole County, Florida, United States. The population was 23,169 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area.

The Central Florida Expressway Authority (CFX) is a highway authority responsible for construction, maintenance and operation of toll roads in five counties of Greater Orlando. It was created in 2014 to replace the Orlando–Orange County Expressway Authority (OOCEA), which only had authority in Orange County, and as of 2016 no roads outside that county have been added to the system. Other toll roads in the area are operated by Florida's Turnpike Enterprise. The Osceola County Expressway Authority, which previously operated additional toll roads in the area, merged into CFX in 2018.
State Road 451 (SR 451) is a 1.9-mile (3.1 km) controlled-access toll road connecting SR 414 and SR 429 north to US 441. The entire route is within Apopka.
State Road 429 (SR 429), also known as the Daniel Webster Western Beltway or Western Expressway south of US 441, and the Wekiva Parkway north of US 441, is a controlled-access toll road built and maintained by the Central Florida Expressway Authority (CFX), the Florida's Turnpike Enterprise, and the Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT). Its mainline extends 51.77 miles (83.32 km) from I-4 (SR 400) in Four Corners north to I-4 in Sanford. Control cities are Apopka and Tampa although the control cities for traffic at the entrances at US 441 and north are Orlando, Tampa, and Daytona Beach. SR 429 was originally planned as a western half of SR 417.
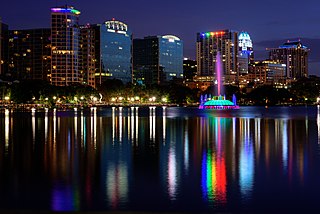
The Orlando metropolitan area is an inland metropolitan area in the central region of the U.S. state of Florida. Its principal cities are Orlando, Kissimmee, and Sanford. The U.S. Office of Management and Budget defines it as consisting of the counties of Lake, Orange, Osceola, and Seminole.
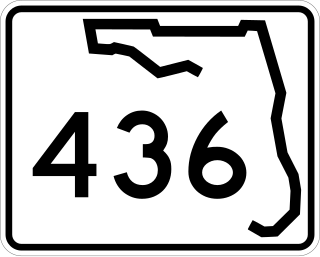
State Road 436, known as Semoran Boulevard for most of its length and Altamonte Drive in Altamonte Springs, is a north-south road in the Orlando area running from US 441 in Apopka to the Beachline Expressway near Orlando International Airport. Constructed in the late 1960s, the road passes through Seminole County, Florida and Orange County, Florida. Because of this, the common name for SR 436 is a portmanteau of the names of the two counties: "Sem" and "oran", hence "Semoran Boulevard." The common pronunciation of "Semoran" resembles that term of Cimarron.

The Central Florida Council serves Boy Scouts in Orange, Osceola, Seminole, Lake, Brevard, Volusia and Flagler Counties in Florida. Its headquarters was previously located in Orlando, Florida and is currently located in Apopka, Florida, just north of Orlando. Its primary Scout camp is Camp La-No-Che in Paisley, Florida, adjacent to the Ocala National Forest.

Apopka High School is in Apopka in northwest Orange County, Florida, United States. The school has been named a Blue Ribbon School of Excellence.

The Wekiva River is a 16.0-mile-long (25.7 km) river in Central Florida, north of Orlando in the United States. It originates in Apopka and joins the St. Johns River, the longest river in the state, in DeBary. The Wekiva River system includes the main stem joined by three main tributaries - Rock Springs Run, Blackwater Creek, and the Little Wekiva River - and about 30 contributing groundwater springs. It is designated as a Florida State Canoe Trail, an Outstanding Florida Water, and an Aquatic Preserve by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection. The Wekiva River system is also one of the two rivers in Florida federally designated as a National Wild and Scenic River for its scenery, recreation, geology, and diverse habitats.

Bryan Nelson is a Florida-based politician, serving as Mayor of Apopka since 2018. A Republican, he was a member of the Florida House of Representatives, representing the 31st District, which includes the cities of Apopka, Eustis, Mount Dora, Tavares, and Umatilla in northern Lake County and northern Orange County, since 2012. He served on the Orange County Commission for District 2 from 2014 until March 2018 when he won election for mayor of Apopka after support for the previous mayor deteriorated.

John Horting Land was Mayor of Apopka, Florida for a total of 61 years, from 1950 to 1968 and again from 1971 to 2014. He was the longest-serving mayor in the history of Florida and one of the longest-serving mayors in the United States. After having served continuously since 1971, Land was defeated in a bid for re-election by Joe Kilsheimer on April 8, 2014.