
Albertosaurus is a genus of large tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in northwestern North America during the early to middle Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period, about 71 million years ago. The type species, A. sarcophagus, was apparently restricted in range to the modern-day Canadian province of Alberta, after which the genus is named, although an indeterminate species has been discovered in the Corral de Enmedio and Packard Formations of Mexico. Scientists disagree on the content of the genus and some recognize Gorgosaurus libratus as a second species.

Daspletosaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Laramidia between about 78 and 74.4 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. The genus Daspletosaurus contains three named species. Fossils of the earlier type species, D. torosus, have been found in Alberta, while fossils of a later species, D. horneri, have been found only in Montana. D. wilsoni has been suggested as an intermediate species between D. torosus and D. horneri that evolved through anagenesis, but this theory has been disputed by other researchers.

Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discoveries of complete and articulated specimens, have helped to increase understanding about this group. Anatomical studies, particularly studies of the most primitive troodontids, like Sinovenator, demonstrate striking anatomical similarities with Archaeopteryx and primitive dromaeosaurids, and demonstrate that they are relatives comprising a clade called Paraves.

Troodon is a former wastebasket taxon and a potentially dubious genus of relatively small, bird-like theropod dinosaurs definitively known from the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period. It includes at least one species, Troodon formosus, known from Montana. Discovered in October 1855, T. formosus was among the first dinosaurs found in North America, although it was thought to be a lizard until 1877. Several well-known troodontid specimens from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta were once believed to be members of this genus. However, recent analyses in 2017 have found this genus to be undiagnostic and referred some of these specimens to the genus Stenonychosaurus some to the genus Latenivenatrix, and some to the genus Pectinodon. The genus name is Ancient Greek for "wounding tooth", referring to the teeth, which were different from those of most other theropods known at the time of their discovery. The teeth bear prominent, apically oriented serrations. These "wounding" serrations, however, are morphometrically more similar to those of herbivorous reptiles, and suggest a possibly omnivorous diet.

Dromaeosaurus is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, sometime between 80 and 69 million years ago, in Alberta, Canada and the western United States. The type species is Dromaeosaurus albertensis, which was described by William Diller Matthew and Barnum Brown in 1922. Its fossils were unearthed in the Hell Creek Formation, Horseshoe Canyon Formation and Dinosaur Park Formation. Teeth attributed to this genus have been found in the Prince Creek Formation. Dromaeosaurus is the type genus of both Dromaeosauridae and Dromaeosaurinae, which include many genera with similar characteristics to Dromaeosaurus such as possibly its closest relative Dakotaraptor. Dromaeosaurus was heavily built, more so than other dromaeosaurs that are similar in size, like Velociraptor.
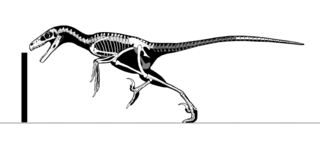
Saurornitholestes is a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Canada (Alberta) and the United States.

Pachyrhinosaurus is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discovered by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, and named in 1950. Over a dozen partial skulls and a large assortment of other fossils from various species have been found in Alberta and Alaska. A great number were not available for study until the 1980s, resulting in a relatively recent increase of interest in Pachyrhinosaurus.

Philip John Currie is a Canadian palaeontologist and museum curator who helped found the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology in Drumheller, Alberta and is now a professor at the University of Alberta in Edmonton. In the 1980s, he became the director of the Canada-China Dinosaur Project, the first cooperative palaeontological partnering between China and the West since the Central Asiatic Expeditions in the 1920s, and helped describe some of the first feathered dinosaurs. He is one of the primary editors of the influential Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs, and his areas of expertise include theropods, the origin of birds, and dinosaurian migration patterns and herding behavior. He was one of the models for palaeontologist Alan Grant in the film Jurassic Park.

Anchiceratops is an extinct genus of chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 to 71 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Alberta, Canada. Anchiceratops was a medium-sized, heavily built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore that could grow up to an estimated 4.3 metres (14 ft) long. Its skull featured two long brow horns and a short horn on the nose. The skull frill was elongated and rectangular, its edges adorned by coarse triangular projections. About a dozen skulls of the genus have been found.
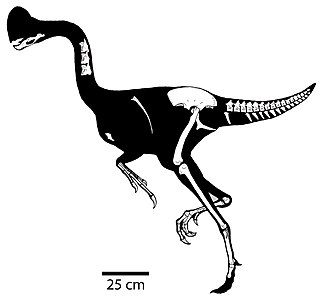
Chirostenotes is a genus of oviraptorosaurian dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada. The type species is Chirostenotes pergracilis.

Montanoceratops is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. Montanoceratops was a small sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated 2.5 m (8.2 ft) in length and 170 kg (370 lb) in body mass.

Pectinodon is a genus of troodontid theropod dinosaurs from the end of the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period (66 mya). It currently contains a single valid species, Pectinodon bakkeri, known only from teeth.

The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is a stratigraphic unit of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in southwestern Alberta. It takes its name from Horseshoe Canyon, an area of badlands near Drumheller.

Dromaeosaurinae is a subfamily of the theropod group Dromaeosauridae. The earliest dromaeosaurine is Utahraptor, dating back to the Early Cretaceous in North America. Some isolated teeth seems to represent an indeterminate species of dromaeosaurine, coming from the Late Jurassic in Africa, which could potentially push their range to an earlier time period.

Edmontosaurus regalis is a species of comb-crested hadrosaurid dinosaur. Fossils of E. regalis have been found in rocks of western North America that date from the late Campanian age of the Cretaceous Period 73 million years ago, but it may have possibly lived into the early Maastrichtian.

Albertonykus is an alvarezsaurid dinosaur from the Maastrichtian-age rocks of the Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada. It is known from forelimb and hindlimb remains from multiple individuals. All but two of the specimens come from a bonebed dominated by Albertosaurus, located at the top of Unit 4 of the Horseshoe Canyon Formation, dating to ~68.5 million years ago.

Acheroraptor is an extinct genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the latest Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation of Montana, United States. It contains a single species, Acheroraptor temertyorum. A. temertyorum is one of the two geologically youngest known species of dromaeosaurids, the other being Dakotaraptor, which is also known from Hell Creek. A basal cousin of Velociraptor, Acheroraptor is known from upper and lower jaw material.

This timeline of dromaeosaurid research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the dromaeosaurids, a group of sickle-clawed, bird-like theropod dinosaurs including animals like Velociraptor. Since the Native Americans of Montana used the sediments of the Cloverly Formation to produce pigments, they may have encountered remains of the dromaeosaurid Deinonychus hundreds of years before these fossils came to the attention of formally trained scientists.






























