Horlivka, also known as Gorlovka, is a city in Donetsk Oblast of Ukraine. Its population is 239,828.

Arsen Borysovych Avakov is a Ukrainian statesman and politician of Armenian origin. Minister of Internal Affairs of Ukraine in 2014–2021. Member of Parliament of Ukraine (2012–2014), Chairman of the Kharkiv Regional State Administration (2005–2010), Member of the National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine, Member of Euro 2012 Organizing Committee (2007). Member of the National Union of Journalists of Ukraine. Honored Economist of Ukraine (2007).

From the end of February 2014, in the aftermath of the Euromaidan and the Revolution of Dignity, which resulted in the ousting of Russian-leaning Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych, demonstrations by Russian-backed, pro-Russian, and anti-government groups took place in Crimea, Donetsk, Luhansk, Kharkiv and Odesa. The unrest, which was supported by the Russian military and intelligence services, belongs to the early stages of the Russo-Ukrainian War.

The National Guard of Ukraine is the Ukrainian national gendarmerie and internal military force. It is part of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, responsible for public security. Originally created as an agency under the direct control of the Verkhovna Rada on 4 November 1991, following Ukrainian independence, it was later disbanded and merged into the Internal Troops of Ukraine in 2000 by President Leonid Kuchma as part of a "cost-saving" scheme. Following the 2014 Revolution of Dignity, amidst the Russian intervention, the National Guard was re-established, and the Internal Troops were disbanded.
The following lists events that happened in 2014 in Russia.

This is a timeline of the 2014 pro-Russian unrest that has erupted in Ukraine, in the aftermath of the Ukrainian revolution and the Euromaidan movement.
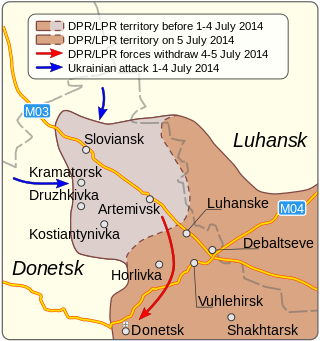
The siege of Sloviansk was conducted by Ukraine between 12 April 2014 and 5 July 2014. It began immediately after Sloviansk was seized by the separatist group, the Donetsk People's Republic, which, having received support from Russia, declared itself independent from Ukraine on 7 April. Following three months of heavy fighting between the Armed Forces of Ukraine and the DPR People's Militia, the Ukrainian government retook the city as the pro-Russia rebels retreated to Donetsk. The engagement in Sloviansk marked the first military engagement of the War in Donbas.

The war in Donbas, also known as the Donbas war, was a phase of the Russo-Ukrainian War in the Donbas region of Ukraine. The war began in April 2014, when a commando unit headed by Russian citizen Igor Girkin seized Sloviansk in Donetsk oblast. The Ukrainian military launched an operation against them. The war continued until subsumed by the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022.

A series of armed skirmishes and confrontations between the Armed Forces of Ukraine and pro-Russian separatists affiliated with the Donetsk People's Republic took place from 12 April until 5 July 2014, and is known as the Battle of Kramatorsk.

The 12th Special Operations Brigade "Azov" is a formation of the National Guard of Ukraine formerly based in Mariupol, in the coastal region of the Sea of Azov, from which it derives its name. It was founded in May 2014 as the Azov Battalion, a self-funded volunteer militia under the command of Andriy Biletsky, to fight Russian-backed forces in the Donbas War. It was formally incorporated into the National Guard on 11 November 2014, and redesignated Special Operations Detachment "Azov", also known as the Azov Regiment. In February 2023, the Ukrainian Ministry of Internal Affairs announced that Azov was to be expanded as a brigade of the new Offensive Guard.

The Donbas Battalion is a unit of the National Guard of Ukraine under the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Ukraine and formerly based in Severodonetsk. It was created in 2014 as a volunteer unit by Semen Semenchenko after the Russian occupation of Crimea and an anticipated invasion of continental Ukraine. The unit was formed in the spring during the 2014 pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine. The unit was initially formed as an independent force, but has been fully integrated into the National Guard as the 2nd Special Purpose Battalion "Donbas" in the 15th Regiment of the National Guard.

In late August and early September 2014, Russian and Russian-backed separatist troops supporting the Donetsk People's Republic advanced on the government-controlled port city of Mariupol in southern Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. This followed a wide offensive by Russian-allied forces, which led to their capture of Novoazovsk to the east. Fighting reached the outskirts of Mariupol on 6 September.

The Second Battle of Donetsk Airport was an engagement between the Ukrainian military and Russian military and its proxy forces of the Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) during the War in Donbas. An earlier battle in May 2014 had left Donetsk International Airport in Ukrainian control. Despite a ceasefire agreement, the Minsk Protocol, in place since 5 September 2014, fighting broke out between the warring parties on 28 September 2014.

Ukraine inherited its special forces (Spetsnaz) units from the remnants of the Soviet armed forces, GRU and KGB units. Ukraine now maintains its own Spetsnaz structure under the control of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and under the Ministry of Defence, while the Security Service of Ukraine maintains its own Spetsnaz force, the Alpha group. In 2016 the Special Operations Forces were created as an independent branch of the Armed Forces of Ukraine formed only by special forces units.
A rocket attack on Mariupol was launched on 24 January 2015 by Russian and pro-Russian forces against the strategic maritime city of Mariupol, defended by Ukrainian government forces. Mariupol had come under attack multiple times in the previous year in the course of the War in Donbas, including in May–June 2014, when the city was under the control of Russian controlled forces; and in the September 2014 offensive.

The Shyrokyne standoff was a battle for the control of the strategic village of Shyrokyne, located approximately 11 km (6.8 mi) east of Mariupol city limits, between Ukrainian forces led by the Azov Regiment, and Russian-backed separatists, between February and July 2015. It was part of the larger war in Donbas. On 10 February 2015, the Azov Regiment launched a surprise offensive against pro-Russian separatists associated with the Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) with the aim of pushing the separatist forces away from Mariupol city limits. The village is located just 10 km (6.2 mi) from the Ukrainian-controlled city of Mariupol, and was used as a launching point for separatist attacks on the city, which served as the administrative centre of Donetsk Oblast whilst DPR forces control Donetsk city. Fighting continued until 3 July 2015, when DPR forces unilaterally withdrew from Shyrokyne. Subsequently a cease-fire was declared in the area.

The Special Operations Forces of the Armed Forces of Ukraine are the special forces of Ukraine and one of the eight branches of the Armed Forces of Ukraine, with headquarters in Kyiv.
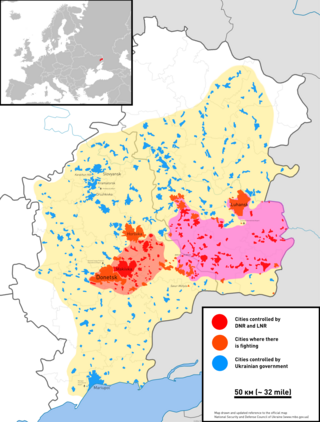
This is a timeline of the war in Donbas for the year 2014.
The combatants of the war in Donbas included foreign and domestic forces.

The siege of Mariupol began on 24 February 2022 and lasted until 20 May, as part of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. It saw fighting between the Russian Armed Forces and the Ukrainian Armed Forces for control over the city of Mariupol in southeastern Ukraine. Lasting for almost three months, the siege ended in a victory for Russia and the Donetsk People's Republic, as Ukraine lost control of the city amidst Russia's eastern Ukraine offensive and southern Ukraine offensive; all Ukrainian troops remaining in the city surrendered at the Azovstal Iron and Steel Works on 20 May 2022, after they were ordered to cease fighting.