Shrews are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to different families or orders.
Borna disease, also known as sad horse disease, is an infectious neurological syndrome of warm-blooded animals, caused by Borna disease viruses 1 and 2 (BoDV-1/2). BoDV-1/2 are neurotropic viruses of the species Mammalian 1 orthobornavirus, and members of the Bornaviridae family within the Mononegavirales order.

The white-toothed shrews or Crocidurinae are one of three subfamilies of the shrew family Soricidae.

The northern short-tailed shrew is the largest shrew in the genus Blarina, and occurs in the northeastern region of North America. It is a semifossorial, highly active, and voracious insectivore and is present in a variety of habitats like broadleaved and pine forests among shrubs and hedges as well as grassy river banks. It is notable in that it is one of the few venomous mammals. The specific epithet, brevicauda, is a combination of the Latin brevis and cauda, meaning "short tail".

The lesser white-toothed shrew is a small species of shrew with a widespread distribution in Africa, Asia and Europe. Its preferred habitat is scrub and gardens and it feeds on insects, arachnids, worms, gastropods, newts and small rodents, though its diet usually varies according to the biotope where it lives. The closely related Asian lesser white-toothed shrew was once included in this species, but is now considered to be a separate species.

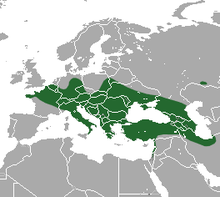
The greater white-toothed shrew is a small insectivorous mammal found in Europe and North Africa. It is the most common of the white-toothed shrews. This species is found along the Mediterranean, Netherlands, Belgium, Ireland, Germany and Portugal; in addition, the Osorio shrew of the Canary island of Gran Canaria, originally described as a separate species, was later discovered to be a population of introduced greater white-toothed shrew. Furthermore, a subspecies of the greater white-toothed shrew, Crocidura russula ibicensis, is found on the Mediterranean island of Ibiza. In April 2008, the greater white-toothed shrew was discovered in Ireland as well. Its preferred habitats are grassland and woodland. It is slightly larger than the lesser white-toothed shrew but otherwise very similar and can often be distinguished only by close inspection of its teeth which are unpigmented.

The gray four-eyed opossum is an opossum species from Central and South America, ranging from southern Mexico to Peru, Bolivia and southwestern Brazil, at altitudes from sea level to 1600 m, but generally below 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). Its habitats include primary, secondary and disturbed forest. It is one of many opossum species in the order Didelphimorphia and the family Didelphidae.

The genus Crocidura is one of nine genera of the shrew subfamily Crocidurinae. Members of the genus are commonly called white-toothed shrews or musk shrews, although both also apply to all of the species in the subfamily. With over 180 species, Crocidura contains the most species of any mammal genus. The name Crocidura means "woolly tail", because the tail of Crocidura species are covered in short hairs interspersed with longer ones.

The Cyrenaica shrew or Alexander's shrew is a species of white-toothed shrew in the family Soricidae which is endemic to Libya.

The Sulawesi shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to the central and northern provinces of Sulawesi in Indonesia. It is a fairly common species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The swamp musk shrew, or musk shrew, is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It occurs in Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Zambia and Zimbabwe. Its natural habitat is swamps, and it is a common species in suitable habitats, with the International Union for Conservation of Nature listing it as being of "least concern".

The black-footed shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to northern and central Sulawesi, Indonesia where it lives on the floor of the tropical forests. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The African giant shrew is a species of white-toothed shrew. It also is known as, Mann's musk shrew, Euchareena's musk shrew, or Olivier's shrew. It is native to Africa, where it has a widespread distribution and occurs in many types of habitat. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forest, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest, subtropical or tropical moist montane forest, dry savanna, moist savanna, arable land, rural gardens, urban areas, and heavily degraded former forest. In the Nile Valley it is found near human habitation, where it is considered to be a pest. It is a common species and is listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being of "least concern".

The Egyptian pygmy shrew or sacred shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Egypt. Its natural habitat is arable land. It is threatened by habitat loss, partially caused by the construction of the Aswan Dam. They are 48–62 mm (1.9–2.4 in) in length and weigh 7 g (0.25 oz), making them one of the smallest shrews in Egypt.

The Sulawesi white-handed shrew or Temboan shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. It is a fairly common species and the population seems stable so the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Whitaker's shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Western Sahara, Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, rocky and sandy coasts. It is a fairly common species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The Christmas Island shrew, also known as the Christmas Island musk-shrew is an extremely rare or possibly extinct shrew from Christmas Island. It was variously placed as subspecies of the Asian gray shrew or the Southeast Asian shrew, but morphological differences and the large distance between the species indicate that it is an entirely distinct species.

Tupaia is a treeshrew genus in the family Tupaiidae that was first described by Thomas Stamford Raffles in 1821. The name of this genus derives from the Malay word tupai meaning squirrel or small animal resembling a squirrel.
Crocidura kornfeldi is an extinct species of shrew that inhabited central and southern Europe between the Pliocene and Pleistocene. It is the first species of the widespread, extremely speciose genus Crocidura known with certainty to have colonized Europe. It is a widespread, well-documented species, with fossils known from Spain, Italy, Greece, Hungary, Romania, and Crimea.