
Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat families, specialised in many forms to occupy a range of habitats and ecological circumstances, and it is frequently observed or the subject of research. The facial features of the species are often simple, as they mainly rely on vocally emitted echolocation. The tails of the species are enclosed by the lower flight membranes between the legs. Over 300 species are distributed all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica. It owes its name to the genus Vespertilio, which takes its name from a word for bat, vespertilio, derived from the Latin term vesper meaning 'evening'; they are termed "evening bats" and were once referred to as "evening birds".

Shrews are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to different families or orders.

Tenrecomorpha is the suborder of otter shrews and tenrecs, a group of afrotherian mammals indigenous to equatorial Africa and Madagascar, respectively. The two families are thought to have split about 47–53 million years ago. Potamogalid otter shrews were formerly considered a subfamily of Tenrecidae. The suborder is also presumed to contain the extinct genus Plesiorycteropus, a group of possibly fossorial insectivores similar to aardvarks, which is known to be more closely related to tenrecs of subfamily Tenrecinae than to golden moles of suborder Chrysochloridea.

A tenrec is a mammal belonging to any species within the afrotherian family Tenrecidae, which is endemic to Madagascar. Tenrecs are a very diverse group; as a result of convergent evolution, some resemble hedgehogs, shrews, opossums, rats, and mice. They occupy aquatic, arboreal, terrestrial, and fossorial environments. Some of these species, including the greater hedgehog tenrec, can be found in the Madagascar dry deciduous forests. However, the speciation rate in this group has been higher in humid forests.

Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs, bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia are also assigned to this group. The center of diversification for the Caniformia is North America and northern Eurasia. Caniformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, the Feliformia, the center of diversification of which was in Africa and southern Asia.

The red-toothed shrews of the subfamily Soricinae are one of three living subfamilies of shrews, along with Crocidurinae and Myosoricinae. In addition, the family contains the extinct subfamilies Limnoecinae, Crocidosoricinae, Allosoricinae and Heterosoricinae. These species are typically found in North America, northern South America, Europe and northern Asia. The enamel of the tips of their teeth is reddish due to iron pigment. The iron deposits serve to harden the enamel and are concentrated in those parts of the teeth most subject to wear. Members of the genera Chimarrogale, Nectogale, Neomys (Nectogalini) and some members of Sorex (Soricini) are known as water shrews, due to having a semi-aquatic lifestyle.
Water shrew may refer to any of several species of semiaquatic red-toothed shrews:

Myotragus is an extinct genus of goat-antelope in the tribe Caprini which lived on the Balearic Islands of Mallorca and Menorca in the western Mediterranean until its extinction around 4,500 years ago. The fossil record of Myotragus on the Balearic Islands extends over 5 million years back to the early Pliocene on Mallorca, where it presumably arrived after the evaporation of the Mediterranean Sea during the Messinian Salinity Crisis.
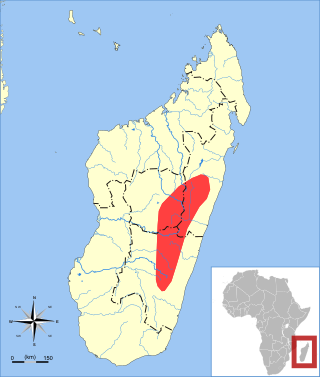
The web-footed tenrec, Malagasy otter shrew, or aquatic tenrec is the only known semiaquatic tenrec, and is found in eastern Madagascar, especially in and around Ranomafana National Park. It grows to between 25 and 39 cm, and was once thought to be extinct. It feeds on crabs, aquatic insects, and crayfish. The population is considered vulnerable. It was formerly placed in the monotypic genus Limnogale, but has been moved to Microgale based on molecular data showing it to be deeply nested within the latter.

Aquatic mammals and semiaquatic mammals are a diverse group of mammals that dwell partly or entirely in bodies of water. They include the various marine mammals who dwell in oceans, as well as various freshwater species, such as the European otter. They are not a taxon and are not unified by any distinct biological grouping, but rather their dependence on and integral relation to aquatic ecosystems. The level of dependence on aquatic life varies greatly among species. Among freshwater taxa, the Amazonian manatee and river dolphins are completely aquatic and fully dependent on aquatic ecosystems. Semiaquatic freshwater taxa include the Baikal seal, which feeds underwater but rests, molts, and breeds on land; and the capybara and hippopotamus which are able to venture in and out of water in search of food.
Microgale is a genus of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. There are 21 living species on the island of Madagascar and one extinct species known from a fossil. Some species have been discovered in the last twenty years.

Asoriculus is an extinct genus of terrestrial shrews in the subfamily Soricinae and tribe Nectogalini, native to Europe and North Africa, from the Late Miocene until the late Holocene. The genus is closely related and possibly ancestral to the also recently-extinct Balearic shrews (Nesiotites), with their closest living relative being the Himalayan shrew.
Interdigital webbing refers to the presence of skin membranes. Normally, in mammals, webbing is present but resorbed later in development, but in various mammal species, it occasionally persists in adulthood. In humans, it can be found in those suffering from LEOPARD syndrome and from Aarskog–Scott syndrome.
Episoriculus is a genus of shrew in the red-toothed shrew subfamily. Its common is brown-toothed shrew. It has been described as a subgenus to Soriculus in the past. The genus occurs at a number of locations in Asia, including Nepal and China.

The Taiwanese brown-toothed shrew is a species of shrew in the tribe Nectogalini. It is found only in Taiwan. It prefers dense ground cover in forests and subalpine shrublands in high mountains of central Taiwan. Its placement in Episoriculus has been questioned, with genetic analysis finding that it is more basal within Nectogalini than other members of Episoriculus.

Hypnomys, otherwise known as Balearic giant dormice, is an extinct genus of dormouse (Gliridae) in the subfamily Leithiinae. Its species are considered examples of insular gigantism. They were endemic to the Balearic Islands in the western Mediterranean from the Early Pliocene until their extinction around the 3rd millennium BC. They first appeared in the fossil record on Mallorca during the Early Pliocene, presumably as a result to the evaporation of the Mediterranean sea during the Messinian salinity crisis connecting the Balearic Islands with mainland Europe. They later spread to Menorca, and a possible molar is also known from Ibiza. Hypnomys became extinct during the late Holocene likely shortly after human arrival on the Balearics. They were one of only three native land mammals to the islands at the time of human arrival, alongside the shrew Nesiotites and goat-antelope Myotragus.

Nesiotites is an extinct genus of large red-toothed shrews belonging to the tribe Nectogalini that inhabited the Balearic Islands from the latest Miocene/Early Pliocene up until the arrival of humans on the islands during the late Holocene. It was present on Mallorca and Menorca. It represented one of only 3 native land mammals to the islands at the time of human arrival, alongside the goat-antelope Myotragus and the giant dormouse Hypnomys. The genus is closely related to the also recently extinct Corsican-Sardinian shrews belonging to the genus Asoriculus, with their closest living relatives being the Himalayan shrews of the genus Soriculus.

Soriculus is a genus of shrew native to the Himalayas, the adjacent Hengduan Mountains and surrounding areas. There is generally only one recognised species, Soriculus nigrescens,, though in 2023 and 2024 additional living species of the genus were proposed.















