The term "United States," when used in the geographic sense, refers to the contiguous United States, Alaska, Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions. The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, the Bahamas, and many other countries, mainly in the Caribbeanin addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world's longest bi-national land border.

The Chihuahuan Desert is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lower Pecos Valley in New Mexico, and a portion of southeastern Arizona, as well as the central and northern portions of the Mexican Plateau. It is bordered on the west by the Sonoran Desert, the Colorado Plateau, and the extensive Sierra Madre Occidental range, along with northwestern lowlands of the Sierra Madre Oriental range. Its largest, continual expanse is located in Mexico, covering a large portion of the state of Chihuahua, along with portions of Coahuila, north-eastern Durango, the extreme northern part of Zacatecas, and small western portions of Nuevo León. With an area of about 501,896 km2 (193,783 sq mi), it is the largest hot desert in North America. The desert is fairly young, existing for only 8000 years.

The San Gabriel Mountains comprise a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Transverse Ranges and lies between the Los Angeles Basin and the Mojave Desert, with Interstate 5 to the west and Interstate 15 to the east. The range lies in, and is surrounded by, the Angeles and San Bernardino National Forests, with the San Andreas Fault as its northern border.

The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the Crab Orchard Mountains. Their highest peak, with an elevation of 4,223 feet (1,287 m) above mean sea level, is High Knob, which is located near Norton, Virginia.

The San Jacinto Mountains are a mountain range in Riverside County, located east of Los Angeles in southern California in the United States. The mountains are named for one of the first Black Friars, Saint Hyacinth, who is a popular patron in Latin America.

The Sangre de Cristo Mountains are the southernmost subrange of the Rocky Mountains. They are located in southern Colorado and northern New Mexico in the United States. The mountains run from Poncha Pass in South-Central Colorado, trending southeast and south, ending at Glorieta Pass, southeast of Santa Fe, New Mexico. The mountains contain a number of fourteen thousand foot peaks in the Colorado portion, as well as several peaks in New Mexico which are over thirteen thousand feet.

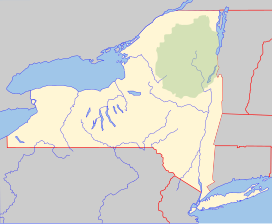
The Beaverhead–Deerlodge National Forest is the largest of the National Forests in Montana, United States. Covering 3.36 million acres (13,600 km2), the forest is broken into nine separate sections and stretches across eight counties in the southwestern area of the state. President Theodore Roosevelt named the two forests in 1908 and they were merged in 1996. Forest headquarters are located in Dillon, Montana. In Roosevelt's original legislation, the Deerlodge National Forest was called the Big Hole Forest Reserve. He created this reserve because the Anaconda Copper Mining Company, based in Butte, Montana, had begun to clearcut the upper Big Hole River watershed. The subsequent erosion, exacerbated by smoke pollution from the Anaconda smelter, was devastating the region. Ranchers and conservationists alike complained to Roosevelt, who made several trips to the area. (Munday 2001)

The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km². The range is bounded by the Rocky Mountain Trench on the east, and the Kootenai River on the south; their western boundary is the edge of the Interior Plateau. Seventy-five percent of the range is located in Canada and the remaining twenty-five percent in the United States; American geographic classifications place the Columbia Mountains as part of the Rocky Mountains complex, but this designation does not apply in Canada. Mount Sir Sandford is the highest mountain in the range, reaching 3,519 metres (11,545 ft).

The Big Maria Mountains are located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of California, near the Colorado River and Arizona. The range lies between Blythe and Vidal, and west of U.S. Route 95 in California and east of Midland. The mountains are home to the Eagle Nest Mine and reach an elevation of 1,030 m (3,380 ft). A power line that runs from Parker Dam to Yuma, Arizona runs through the range. A smaller range, the Little Maria Mountains, lie to the west of the Big Marias.

Big Hatchet Peak is the high point of the Big Hatchet Mountains, a small but rugged range in the southwest corner of New Mexico, in the United States. The mountains are located in southeast Hidalgo County, about 50 miles (80 km) southwest of Deming. The range runs roughly northwest-southeast, and is about 12 miles (19 km) long; the southeastern edge of the range is within 3.5 miles (6 km) of the border with Mexico. They lie primarily on BLM land.

The Lost River Range is a high mountain range of the Rocky Mountains, located in Central Idaho, in the Northwestern United States.

Phelps Mountain is a mountain located in Essex County, New York. The mountain is named after Orson Schofield "Old Mountain" Phelps (1817–1905), who cut the first trail up Mount Marcy and named several of the Adirondack peaks. It is the 32nd highest peak in New York. Phelps Mountain is flanked to the southeast by Table Top Mountain.
Big Indian Mountain is a mountain located in Ulster County, New York. The mountain is part of the Catskill Mountains. It is flanked to the northwest by Eagle Mountain, to the southeast by Fir Mountain, and to the southwest by Doubletop Mountain.
The Sylvania Mountains Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located 30 miles (48 km) east of Bishop in the state of California. The wilderness is 18,677acres in size and is managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The California Desert Protection Act of 1994 created the Sylvania Mountains Wilderness and was added to the National Wilderness Preservation System. The wilderness is bordered by Nevada stateline on the east, Piper Mountain Wilderness on the west and Death Valley National Park to the south.

The Ochoco Mountains are a mountain range in central Oregon in the United States, located at the western end of the Blue Mountains. They were formed when Permian, Triassic, and Jurassic rocks were slowly uplifted by volcanic eruptions to form the Clarno Formation. Today, the highest point in the range is Lookout Mountain. The dominant vegetation on the west side of the range is old-growth ponderosa pine; on the east side, western juniper is common. The western area of the mountains is administered by the Ochoco National Forest, while the southeastern section is part of the Malheur National Forest. The Ochoco Mountains draw visitors for hiking, camping, bird watching, rockhounding, and hunting, as well as cross-country skiing in the winter.

The Alamo Hueco Mountains are a 15-mile (24 km) long mountain range, located in the southeast of the New Mexico Bootheel region, southeast Hidalgo County, New Mexico, adjacent to the border of Chihuahua state, Mexico. The range lies near the southern end of the mountains bordering the extensive north–south Playas Valley; the Little Hatchet and Big Hatchet Mountains are adjacent, and mostly attached north; the mountain range series, ends south into the flatland plains of the Chihuahuan Desert. The much smaller Dog Mountains are adjacent south.

The Mountain states form one of the nine geographic divisions of the United States that are officially recognized by the United States Census Bureau. It is a subregion of the Western United States.

Humpy Peak is a peak located in the Uinta Mountain Range in northern Utah. It is approximately 27.56 miles (44 km) south of Evanston, Wyoming and 21.29 miles (34 km) east of Coalville, Utah. The summit has an elevation of 10,875 feet (3,315 m).

The Boulder Mountains are part of the Rocky Mountains in the western United States. Located in central Idaho, they stretch from a few miles north of Ketchum to north to near Challis, and part of the range is within the Sawtooth National Recreation Area (SNRA) and partially within the Hemingway–Boulders Wilderness. The highest point in the range is Ryan Peak, at 11,714 feet (3,570 m) above sea level.
Big Sandy Mountain is located in the southern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Big Sandy Mountain sits along the Continental Divide, less than 1 mi (1.6 km) southeast of Dog Tooth Peak.