
The Kennebec River is a 170-mile-long (270 km) river within the U.S. state of Maine. It rises in Moosehead Lake in west-central Maine. The East and West Outlets join at Indian Pond and the river flows southward. Harris Station Dam, the largest hydroelectric dam in the state, was constructed near that confluence. The river is joined at The Forks by its tributary the Dead River, also called the West Branch.
Mount Kelsey is a mountain located in the western portion of Millsfield, New Hampshire. The western slopes of the mountain are contained within the township of Erving's Location, New Hampshire. The summit is occupied by part of the Granite Reliable Wind Farm, with road access from the Phillips Brook watershed to the south.

Cobscook Bay is located in Washington County in the state of Maine. It opens into Passamaquoddy Bay, within the Bay of Fundy. Cobscook Bay is immediately south of the island city of Eastport, the main island of which straddles the two bays. In the 1930s, Cobscook Bay was part of the aborted Passamaquoddy Bay Tidal Power Project to generate electricity from its large tidal range.

The Carrabassett River, a tributary of the Kennebec River, is located in Franklin County and Somerset County, Maine, in the United States. It rises near Sugarloaf Mountain, east of Rangeley Lake, and runs for 33.8 miles (54.4 km), flowing southeast past Kingfield and joining the Kennebec River in the town of Anson.

Crocker Mountain is a 4,228 ft (1,289 m) peak located in Carrabassett Valley, Franklin County, Maine, in the United States. Crocker Mountain is the fourth highest mountain in the state after the Katahdins and Sugarloaf Mountain, and is part of the Appalachian Mountains. Crocker Mountain is traversed by the Appalachian Trail (AT), a 2,170 mi (3,490 km) National Scenic Trail from Georgia to Maine.

Saddleback Mountain is a mountain located in Sandy River Plantation, Franklin County, Maine, near the resort town of Rangeley. Saddleback is one of the highest mountains in the State of Maine, and one of the fourteen with more than 2,000 ft (610 m) of topographic prominence. The mountain is the site of Saddleback ski resort.

Equinox Mountain is a mountain in Bennington County, Vermont, United States, in the town of Manchester. The mountain is the highest peak of the Taconic Range, and the highest point of Bennington County. It is one of thirteen peaks in Vermont with a topographic prominence over 2,000 feet (610 m), ranked third behind Mansfield and Killington. Equinox is the second highest peak in southern Vermont, after Stratton Mountain.

Mount Redington is a mountain located in Franklin County, Maine. Redington is flanked to the northeast by South Crocker Mountain and to the west by Black Nubble. Redington stands just northeast of the U.S. Navy Survival Escape and Evasion Training Facility (USSEAETF).

The Horn is a mountain located in Franklin County, Maine. The Horn is flanked to the southwest by the main summit of Saddleback Mountain, to the northeast by Saddleback Junior, and to the northwest by Potato Nubble.

South Crocker Mountain is a mountain located in Franklin County, Maine. South Crocker Mountain is flanked to the north by Crocker Mountain, and to the southwest by Mount Redington.
Coburn Mountain is a mountain located in Somerset County, Maine.

Kibby Mountain is a mountain located in Franklin County, Maine, about 3.5 mi (5.6 km) east of the Canada–United States border. Kibby Mountain is flanked to the southeast by Spencer Bale Mountain.

Saddleback Junior is a mountain located in Franklin County, Maine. Saddleback Junior is flanked to the southwest by Saddleback Horn, and to the northeast by Poplar Ridge. The mountain is on the south border of the U.S. Navy Survival Escape and Evasion Training Facility (USSEAETF).
Stetson Mountain is a small mountain located in Washington County, Maine; a 8-mile (13 km) long ridge running roughly north–south. The summit elevation is between 1,080 ft (330 m) and 1,090 ft (330 m). Stetson is approximately 10 miles (16 km) from the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick.

Kibby Wind Power Project is a wind farm on Kibby Mountain in Franklin County, Maine, United States of America.
There are a number of wind power projects in the state of Maine, totaling more than 900 megawatts (MW) in capacity. In 2020 they were responsible for 24% of in-state electricity production. In 2019, Maine had more wind capacity than the other five New England states combined, at 923 MW.

Wind power in New Hampshire began in 1980, with the installation of the world's first wind farm at Crotched Mountain, consisting of 20 30 kW wind turbines, although it closed decades ago. As of 2020, five wind power projects are operating in the state of New Hampshire – Lempster Mountain, which opened in 2008, Granite Reliable Wind Farm, which opened in late 2011, Groton Wind, which opened in 2012, Jericho Mountain, which opened in 2015, and Antrim Wind, which opened in 2020.
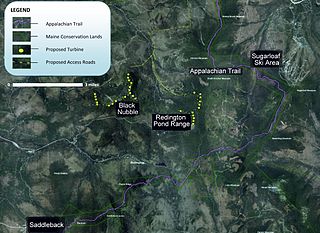
The Sugarloaf Community Wind Farm is a wind power project in western Maine under development by Endless Energy Corporation. The wind farm is planned to be situated between the Sugarloaf and the Saddleback Maine ski resorts on Redington Pond Range and Black Nubble Mountains.

Harris Station Dam is a hydroelectric dam in Northeast Somerset, Somerset County, Maine. Also known as the Indian Pond Project, the dam was built from 1952 to 1954 as the largest hydroelectric dam in the state of Maine. It impounds the Kennebec River at the southern end of the natural Indian Pond, about 12 miles (19 km) downstream from Moosehead Lake.
Shutdown Mountain is a mountain located in Somerset County, Maine.














