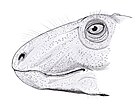
Edaphosaurus is a genus of extinct edaphosaurid synapsids that lived in what is now North America and Europe around 303.4 to 272.5 million years ago, during the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian. American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope first described Edaphosaurus in 1882, naming it for the "dental pavement" on both the upper and lower jaws, from the Greek edaphos έδαφος and σαῦρος ("lizard").

Sphenacodontia is a stem-based clade of derived synapsids. It was defined by Amson and Laurin (2011) as "the largest clade that includes Haptodus baylei, Haptodus garnettensis and Sphenacodon ferox, but not Edaphosaurus pogonias". They first appear during the Late Pennsylvanian epoch. From the end of the Carboniferous to the end of the Permian, most of them remained large, with only some secondarily becoming small in size.
Albisaurus was once thought to be a genus of dinosaur, but is now thought to be a non-dinosaurian archosaur. It was first described by Antonin Fritsch, a Czech palaeontologist, in 1893, but the remains are sparse. The validity of the species cannot be proven based on the fossil remains, and it is usually marked as a nomen dubium. It lived during the Turonian-Santonian stages of the Cretaceous period.

Ponerosteus is a dubious genus of extinct archosauromorph from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-aged) Korycanar Formation of the Czech Republic that was initially identified as a species of the dinosaur Iguanodon.

Cretornis is a pterosaur genus from the late Cretaceous period of what is now the Jizera Formation in the Czech Republic, dating to about 92 million years ago. It only contains a single species, Cretornis hlavaci.

Cochleosaurus (“spoon lizard”, from the Latin cochlear "spoon" and Greek sauros “lizard”_ were medium-sized edopoid temnospondyls that lived in Euramerica during the Muscovian period. Two species, C. bohemicus and C. florensis, have been identified from the fossil record.

Diplovertebron is an extinct genus of embolomere that lived in the Late Carboniferous period (Moscovian), about 310 million years ago. Diplovertebron was a medium-sized animal, around 50 cm in length. Members of the genus inhabited European Carboniferous swamps in what is now the Czech Republic. They were closely related to larger swamp-dwelling tetrapods like Proterogyrinus and Anthracosaurus. However, Diplovertebron were much smaller than these large, crocodile-like creatures. Known from a single species, Diplovertebron punctatum, this genus has had a complicated history closely tied to Gephyrostegus, another genus of small, reptile-like amphibians.

Cheliderpeton is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian. It lived during the Early Permian in what is now Europe. Fossils have been found from the Ruprechtice horizon of the Intrasudetic Basin of Bohemia in the Czech Republic, as well as the Saar-Nahe Basin of southwestern Germany. Cheliderpeton had a 16 cm skull, and reached about 65 cm in length.

Actinodon is an extinct genus of eryopoidean temnospondyl within the family Eryopidae.

Cimoliasaurus was a plesiosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of New Jersey.

Trematopidae is a family of dissorophoid temnospondyls spanning the late Carboniferous to the early Permian. Together with Dissorophidae, the family forms Olsoniformes, a clade comprising the medium-large terrestrial dissorophoids. Trematopids are known from numerous localities in North America, primarily in New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas, and from the Bromacker quarry in Germany.

Glaucosaurus is an extinct genus of small edaphosaurids from the Early Permian. The type species, G. megalops, was named in 1915.
The Priesener Formation is a Coniacian geologic formation in the Czech Republic. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Branchiosauridae is an extinct family of small amphibamiform temnospondyls with external gills and an overall juvenile appearance. The family has been characterized by hundreds of well-preserved specimens from the Permo-Carboniferous of Middle Europe. Specimens represent well defined ontogenetic stages and thus the taxon has been described to display paedomorphy (perennibranchiate). However, more recent work has revealed branchiosaurid taxa that display metamorphosing trajectories. The name Branchiosauridae refers to the retention of gills.

Furca is an extinct genus of marrellomorph arthropod known from the Sandbian stage of the Czech Republic, with a single currently described species, Furca bohemica. A tentative additional species, "Furca mauretanica": was proposed for specimens discovered in Morocco, but this species remains a nomen nudum until formally published, and probably belongs in a new separate genus.
This timeline of Permian research is a chronological listing of events in the history of geology and paleontology focused on the study of earth during the span of time lasting from 298.9–252.17 million years ago and the legacies of this period in the rock and fossil records.

Gordodon is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid that lived during the Early Permian of what is now Otero County, New Mexico. It was a member of the herbivorous sail-backed family Edaphosauridae and contains only a single species, the type species G. kraineri. Gordodon is unusual among early synapsids for its teeth, which were arranged similarly to those of modern mammals and unlike the simple, uniform lizard-like teeth of other early herbivorous synapsids. Gordodon had large incisor-like teeth at the front, followed by a prominent gap between them and a short row of peg-like teeth at the back. Gordodon was also relatively long-necked for an early synapsid, with elongated and gracile vertebrae in its neck and back. Like other edaphosaurids, Gordodon had a tall sail on its back made from the bony neural spines of its vertebrae. The spines also had bony knobs on them, a common trait of edaphosaurids, but the knobs of Gordodon are also unique for being more slender, thorn-like and randomly arranged along the spines. It is estimated to have been rather small at 1 m in length excluding the tail and 34 kg (75 lb) in weight.
Mattauschia is an extinct genus of trematopid temnospondyls from the Late Carboniferous of the Czech Republic.
Iserosaurus is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Late Cretaceous of Czech Republic.
Pipunculus is a genus of flies belonging to the family Pipunculidae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution.