| Neosaurus Temporal range: Late Carboniferous-Early Permian, | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Holotype | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Family: | † Sphenacodontidae |
| Genus: | † Neosaurus Nopsca, 1923 |
| Type species | |
| †Neosaurus cynodus (Gervais, 1869) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
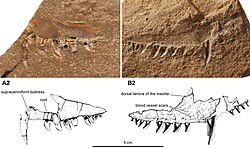
Neosaurus ('New Lizard') is an extinct genus of pelycosaur-grade synapsids from the Late Carboniferous-Early Permian of the Jura region of France. It is known only from a partial maxilla or upper jaw bone and an associated impression of the bone. [1] The teardrop shape of the teeth in the jaw indicate that Neosaurus belongs to the family Sphenacodontidae, which includes the better-known Dimetrodon from the Southwestern United States. The maxilla was first attributed to an early diapsid reptile in 1857, [2] [3] and later a crocodylomorph in 1869, [4] before finally being identified as a sphenacodont synapsid in 1899, [5] a classification that still holds today. [6]
A species of the hadrosaur dinosaur Hypsibema , H. missouriensis , is also called Neosaurus , although because the name was already in use, that species was renamed Parrosaurus before being reassigned to Hypsibema. [7]





