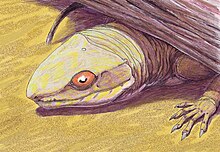
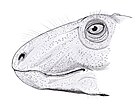
Synapsida is one of the two major clades of vertebrate animals in the group Amniota, the other being the Sauropsida. The synapsids were the dominant land animals in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic, but the only group that survived into the Cenozoic are mammals. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals.

Dimetrodon is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid belonging to the family Sphenacodontidae that lived during the Cisuralian age of the Early Permian period, around 295–272 million years ago. With most species measuring 1.7–4.6 m (5.6–15.1 ft) long and weighing 28–250 kg (62–551 lb), the most prominent feature of Dimetrodon is the large neural spine sail on its back formed by elongated spines extending from the vertebrae. It was an obligate quadruped and had a tall, curved skull with large teeth of different sizes set along the jaws. Most fossils have been found in the Southwestern United States, the majority of these coming from a geological deposit called the Red Beds of Texas and Oklahoma. More recently, its fossils have also been found in Germany and over a dozen species have been named since the genus was first erected in 1878.

Eupelycosauria is a large clade of animals characterized by the unique shape of their skull, encompassing all mammals and their closest extinct relatives. They first appeared 308 million years ago during the Early Pennsylvanian epoch, with the fossils of Echinerpeton and perhaps an even earlier genus, Protoclepsydrops, representing just one of the many stages in the evolution of mammals, in contrast to their earlier amniote ancestors.

Caseasauria is one of the two main clades of early synapsids, the other being the Eupelycosauria. Caseasaurs are currently known only from the Late Carboniferous and the Permian, and include two superficially different families, the small insectivorous or carnivorous Eothyrididae, and the large, herbivorous Caseidae. These two groups share a number of specialised features associated with the morphology of the snout and external naris.

Eothyrididae is an extinct family of very primitive, insectivorous synapsids. Only three genera are known, Eothyris, Vaughnictis and Oedaleops, all from the early Permian of North America. Their main distinguishing feature is the large caniniform tooth in front of the maxilla.

Caseidae are an extinct family of basal synapsids that lived from the Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian between about 300 and 265 million years ago. Fossils of these animals come from the south-central part of the United States, from various parts of Europe, and possibly from South Africa if the genus Eunotosaurus is indeed a caseid as some authors proposed in 2021. Caseids show great taxonomic and morphological diversity. The most basal taxa were small insectivorous and omnivorous forms that lived mainly in the Upper Carboniferous and Lower Permian, such as Eocasea, Callibrachion, and Martensius. This type of caseid persists until the middle Permian with Phreatophasma and may be Eunotosaurus. During the early Permian, the clade is mainly represented by many species that adopted a herbivorous diet. Some have evolved into gigantic forms that can reach 6–7 metres (20–23 ft) in length, such as Cotylorhynchus hancocki and Alierasaurus ronchii, making them the largest Permian synapsids. Caseids are considered important components of early terrestrial ecosystems in vertebrate history because the numerous herbivorous species in this family are among the first terrestrial tetrapods to occupy the role of primary consumer. The caseids experienced a significant evolutionary radiation at the end of the early Permian, becoming, with the captorhinid eureptiles, the dominant herbivores of terrestrial ecosystems in place of the edaphosaurids and diadectids.

Secodontosaurus is an extinct genus of "pelycosaur" synapsids that lived from between about 285 to 272 million years ago during the Early Permian. Like the well known Dimetrodon, Secodontosaurus is a carnivorous member of the Eupelycosauria family Sphenacodontidae and has a similar tall dorsal sail. However, its skull is long, low, and narrow, with slender jaws that have teeth that are very similar in size and shape—unlike the shorter, deep skull of Dimetrodon, which has large, prominent canine-like teeth in front and smaller slicing teeth further back in its jaws. Its unusual long, narrow jaws suggest that Secodontosaurus may have been specialized for catching fish or for hunting prey that lived or hid in burrows or crevices. Although no complete skeletons are currently known, Secodontosaurus likely ranged from about 2 to 2.7 metres (7–9 ft) in length, weighing up to 110 kilograms (250 lb).

Platyhystrix is an extinct temnospondyl amphibian with a distinctive sail along its back, similar to the unrelated synapsids, Dimetrodon and Edaphosaurus. It lived during the boundary between the latest Carboniferous and earliest Permian periods throughout what is now known as the Four Corners, Texas, and Kansas about 300 million years ago.
Casea is a genus of herbivorous caseid synapsids that lived during the late Lower Permian (Kungurian) in what is now Texas, United States. The genus is only represented by its type species, Casea broilii, named by Samuel Wendell Williston in 1910. The species is represented by a skull associated with a skeleton, a second skull, a partial skull with a better preserved dentition than that of the preceding skulls, and several incomplete postcranial skeletons. Three other Casea species were later erected, but these are considered today to be invalid or belonging to different genera. Casea was a small animal with a length of about 1.20 m and a weight of around 20 kg.
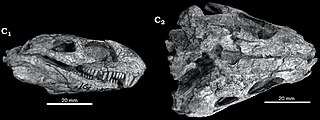
Eothyris is a genus of extinct synapsid in the family Eothyrididae from the early Permian. It was a carnivorous insectivorous animal, closely related to Oedaleops. Only the skull of Eothyris, first described in 1937, is known. It had a 6-centimetre-long (2.4-inch) skull, and its total estimated length was 30 centimetres. Eothyris is one of the most primitive synapsids known and is probably very similar to the common ancestor of all synapsids in many respects. The only known specimen of Eothyris was collected from the Artinskian-lower.

Cotylorhynchus is an extinct genus of herbivorous caseid synapsids that lived during the late Lower Permian (Kungurian) and possibly the early Middle Permian (Roadian) in what is now Texas and Oklahoma. The large number of specimens found make it the best-known caseid. Like all large herbivorous caseids, Cotylorhynchus had a short snout sloping forward and very large external nares. The head was very small compared to the size of the body. The latter was massive, barrel-shaped, and ended with a long tail. The limbs were short and robust. The hands and feet had short, broad fingers with powerful claws. The barrel-shaped body must have housed large intestines, suggesting that the animal had to feed on a large quantity of plants of low nutritional value. Caseids are generally considered to be terrestrial, though a semi-aquatic lifestyle has been proposed by some authors. The genus Cotylorhynchus is represented by three species, the largest of which could reach more than 6 m in length. However, a study published in 2022 suggests that the genus may be paraphyletic, with two of the three species possibly belonging to separate genera.
Angelosaurus is an extinct genus of herbivorous caseid synapsids that lived during the late Lower Permian (Kungurian) and early Middle Permian (Roadian) in what is now Texas and Oklahoma. Like other herbivorous caseids, it had a small head, large barrel-shaped body, long tail, and massive limbs. Angelosaurus differs from other caseids by the extreme massiveness of its bones, particularly those of the limbs, which show a strong development of ridges, processes, and rugosities for the attachment of muscles and tendons. Relative to its body size, the limbs of Angelosaurus were shorter and wider than those of other caseids. The ungual phalanges looked more like hooves than claws. The few known cranial elements show that the skull was short and more robust than that of the other representatives of the group. Angelosaurus is also distinguished by its bulbous teeth with shorter and wider crowns than those of other caseids. Their morphology and the high rate of wear they exhibit suggests a diet quite different from that of other large herbivorous caseids, and must have been based on particularly tough plants. A study published in 2022 suggests that the genus may be paraphyletic, with Angelosaurus possibly only represented by its type species A. dolani.

Ennatosaurus is an extinct genus of caseid synapsid that lived during the Middle Permian in northern European Russia. The genus is only represented by its type species, Ennatosaurus tecton, which was named in 1956 by Ivan Antonovich Efremov. The species is known from at least six skulls associated with their lower jaws, as well as from the postcranial bones of several juvenile individuals. Ennatosaurus has the typical caseid skull with a short snout tilted forward and very large external nares. However, it differs from other derived caseids by its postcranial skeleton with smaller proportions compared to the size of the skull. As with other advanced caseids, the teeth of Ennatosaurus were well suited for slicing and cutting vegetation. The presence of a highly developed hyoid apparatus indicates the presence of a massive and mobile tongue, which had to work in collaboration with the palatal teeth during swallowing. With a late Roadian - early Wordian age, Ennatosaurus is one of the last known caseids.

Aerosaurus is an extinct genus within Varanopidae, a family of non-mammalian synapsids. It lived between 252-299 million years ago during the Early Permian in North America. The name comes from Latin aes (aeris) “copper” and Greek sauros “lizard,” for El Cobre Canyon in northern New Mexico, where the type fossil was found and the site of former copper mines. Aerosaurus was a small to medium-bodied carnivorous synapsid characterized by its recurved teeth, triangular lateral temporal fenestra, and extended teeth row. Two species are recognized: A. greenleeorum (1937) and A. wellesi (1981).
Baldwinonus is an extinct genus of basal synapsids from the Early Permian. The type species is Baldwinonus trux, named in 1940 from the Cutler Formation of New Mexico. A second species, Baldwinonus dunkardensis, was named in 1952 from Ohio. Baldwinonus was first classified in the family Eothyrididae, but the group has since been recognized as a wastebasket taxon for many early synapsids. More recently, Baldwinonus has been placed in the family Ophiacodontidae. Its phylogenetic relationship to other early synapsids remains poorly understood because it is only known from a few fragments of bone.

Callibrachion is an extinct genus of caseid synapsids that lived in east-central France during the Lower Permian (Asselian). The holotype and only known specimen (MNHN.F.AUT490) is represented by an almost complete postcranial skeleton associated with skull fragments discovered at the end of the 19th century in the Permian Autun basin in Saône-et-Loire department, in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region. It belongs to an immature individual measuring less than 1.50 m in length. Callibrachion was long considered a junior synonym of the genus Haptodus and classified among the sphenacodontid pelycosaurs. In 2015, a new study found that Callibrachion was a different animal from Haptodus and that it was a caseasaur rather than a sphenacodontid. This was confirmed in 2016 by a cladistic analysis which recovered Callibrachion as a basal caseid. Callibrachion's sharp teeth and unenlarged ribcage indicate that this animal was likely faunivorous.
Ruthenosaurus is an extinct genus of caseid synapsids that lived in what is now Southern France during the Early Permian about 285 million years ago. It is known from the holotype MNHN.F.MCL-1 an articulated partial postcranial skeleton. It was collected by D. Sigogneau-Russell and D. Russell in 1970 in the upper part of the M2 Member, Grès Rouge Group, in the Rodez Basin, near the village of Valady, in Occitanie Region. It was first named by Robert R. Reisz, Hillary C. Maddin, Jörg Fröbisch and Jocelyn Falconnet in 2011, and the type species is Ruthenosaurus russellorum.

Euromycter is an extinct genus of caseid synapsids that lived in what is now Southern France during the Early Permian about 285 million years ago. The holotype and only known specimen of Euromycter (MNHN.F.MCL-2) includes the complete skull with lower jaws and hyoid apparatus, six cervical vertebrae with proatlas, anterior part of interclavicle, partial right clavicle, right posterior coracoid, distal head of right humerus, left and right radius, left and right ulna, and complete left manus. It was collected by D. Sigogneau-Russell and D. Russell in 1970 at the top of the M1 Member, Grès Rouge Group, near the village of Valady, Rodez Basin. It was first assigned to the species "Casea" rutena by Sigogneau-Russell and Russell in 1974. More recently, it was reassigned to its own genus, Euromycter, by Robert R. Reisz, Hillary C. Maddin, Jörg Fröbisch and Jocelyn Falconnet in 2011. The preserved part of the skeleton suggests a size between 1,70 m (5,5 ft) and 1,80 m (5,9 ft) in length for this individual.

Alierasaurus is an extinct genus of caseid synapsid that lived during the early Middle Permian (Roadian) in what is now Sardinia. It is represented by a single species, the type species Alierasaurus ronchii. Known from a very large partial skeleton found within the Cala del Vino Formation, Alierasaurus is one of the largest known caseids. It closely resembles Cotylorhynchus, another giant caseid from the San Angelo Formation in Texas. The dimensions of the preserved foot elements and caudal vertebrae suggest an estimated total length of about 6 or 7 m for Alierasaurus. In fact, the only anatomical features that differ between Alierasaurus and Cotylorhynchus are found in the bones of the feet; Alierasaurus has a longer and thinner fourth metatarsal and it has ungual bones at the tips of the toes that are pointed and claw-like rather than flattened as in other caseids. Alierasaurus and Cotylorhynchus both have very wide, barrel-shaped rib cages indicating that they were herbivores that fed primarily on high-fiber plant material.

Lalieudorhynchus is an extinct genus of caseid synapsids that lived during the Guadalupian in what is now Southern France. The genus is only known by its type species, Lalieudorhynchus gandi, which was named in 2022 by Ralf Werneburg, Frederik Spindler, Jocelyn Falconnet, Jean-Sébastien Steyer, Monique Vianey-Liaud, and Joerg W. Schneider. Lalieudorhynchus is represented by a partial postcranial skeleton discovered in the Lodève basin in the central part of the Hérault department in the Occitanie region. It belongs to an individual measuring approximately 3.75 m (12.3 ft) in length. The degree of ossification of its bones, however, indicates that it was a late juvenile or still growing young adult. Based on the internal structure of its bones, the describing authors interpreted Lalieudorhynchus as a semiaquatic animal that may have had a lifestyle similar to that of hippopotamus, spending part of its time in water but returning to land for food, though the idea that caseids were semi-aquatic has been previously contested by other authors. It is geologically one of the youngest known representatives of the caseids. The phylogenetic analysis proposed by Werneburg and colleagues identified Lalieudorhynchus as a derived caseid closely related to the North American species "Cotylorhynchus" hancocki.