
Trachodon is a dubious genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur based on teeth from the Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana, U.S. It is a historically important genus with a convoluted taxonomy that has been all but abandoned by modern dinosaur paleontologists.

Hadrosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation in New Jersey about 83.6-77.9 Ma. The holotype specimen was found in fluvial marine sedimentation, meaning that the corpse of the animal was transported by a river and washed out to sea.

Hadrosaurids, or hadrosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as Edmontosaurus and Parasaurolophus, was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Late Jurassic/Early Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, and South America.

Claosaurus is a genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period (Santonian-Campanian).

Shantungosaurus is a genus of very large saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous Wangshi Group of the Shandong Peninsula in China, containing a single species, Shantungosaurus giganteus. The stratigraphic interval of Shantungosaurus ranges from the top of the Xingezhuang Formation to the middle of the Hongtuya Formation, middle to late Campanian in age. Shantungosaurus is so far the largest hadrosauroid taxon in the world, with size estimates around 15–17 metres (49–56 ft) in length and 13–16 metric tons in body mass.

Dryptosaurus is a genus of eutyrannosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived on the island continent of Appalachia approximately 67.6 million years ago during the end of the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period. Dryptosaurus was a large, bipedal, ground-dwelling carnivore that could grow up to 7.5 metres (25 ft) long and weigh up to 756–1,500 kilograms (1,667–3,307 lb). Although it is now largely unknown outside of academic circles, the famous 1897 painting of the genus by Charles R. Knight made Dryptosaurus one of the more widely known dinosaurs of its time, in spite of its poor fossil record. First described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1866 and later renamed by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1877, Dryptosaurus is among the first theropod dinosaurs ever known to science.

Lophorhothon is a genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Alabama and North Carolina. It was the first genus of dinosaur discovered in Alabama, in the United States.
Arstanosaurus is a genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur from the Santonian-Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Bostobe Formation, Kazakhstan. It has had a confusing history, being considered both a hadrosaurid and a ceratopsid, or both at the same time (chimeric).

Anasazisaurus is a genus of saurolophine hadrosaurid ("duckbill") ornithopod dinosaur that lived about 74 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous Period. It was found in the Farmington Member of the Kirtland Formation, in the San Juan Basin of New Mexico, United States. Only a partial skull has been found to date. It was first described as a specimen of Kritosaurus by Jack Horner, and has been intertwined with Kritosaurus since its description. It is known for its short nasal crest, which stuck out above and between its eyes for a short distance.
"Coelosaurus" antiquus is a dubious species of theropod dinosaurs. It was named by Joseph Leidy in 1865 for two tibiae found in the Navesink Formation of New Jersey.
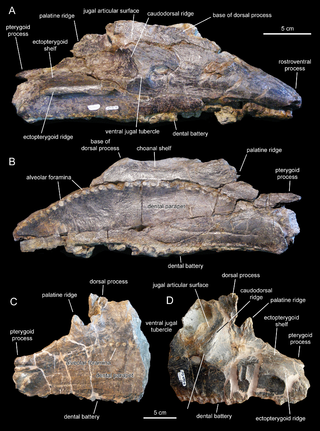
Pararhabdodon is a genus of tsintaosaurin hadrosaurid dinosaur, from the Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tremp Group of Spain. The first remains were discovered from the Sant Romà d’Abella fossil locality and assigned to the genus Rhabdodon, and later named as the distinct species Pararhabdodon isonensis in 1993. Known material includes assorted postcranial remains, mostly vertebrae, as well as maxillae from the skull. Specimens from other sites, including remains from France, a maxilla previously considered the distinct taxon Koutalisaurus kohlerorum, an additional maxilla from another locality, the material assigned to the genera Blasisaurus and Arenysaurus, and the extensive Basturs Poble bonebed have been considered at different times to belong to the species, but all of these assignments have more recently been questioned. It was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known from the fossil record that went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

Mandschurosaurus is an extinct genus of hadrosaurids based on material from the Late Cretaceous of China and possibly also the Early Cretaceous of Laos. It was the first dinosaur genus named from China.

Saurolophinae is a subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. It has since the mid-20th century generally been called the Hadrosaurinae, a group of largely non-crested hadrosaurs related to the crested sub-family Lambeosaurinae. However, the name Hadrosaurinae is based on the genus Hadrosaurus which was found in more recent studies to be more primitive than either lambeosaurines or other traditional "hadrosaurines", like Edmontosaurus and Saurolophus. As a result of this, the name Hadrosaurinae was dropped or restricted to Hadrosaurus alone, and the subfamily comprising the traditional "hadrosaurines" was renamed the Saurolophinae. Recent phylogenetic work by Hai Xing indicates that Hadrosaurus is placed within the monophyletic group containing all non-lambeosaurine hadrosaurids. Under this view, the traditional Hadrosaurinae is resurrected, with the Hadrosauridae being divided into two clades: Hadrosaurinae and Lambeosaurinae.
The Merchantville Formation is a geological formation in the northeastern United States whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous, around the time of the Santonian and Campanian age. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
The Marshalltown Formation is a Mesozoic geologic formation. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Hypsibema missouriensis is a species of plant-eating dinosaur in the genus Hypsibema, and the state dinosaur of the U.S. state Missouri. One of the few official state dinosaurs, bones of the species were discovered in 1942, at what later became known as the Chronister Dinosaur Site near Glen Allen, Missouri. The remains of Hypsibema missouriensis at the site, which marked the first known discovery of dinosaur remains in Missouri, are the only ones to have ever been found. Although first thought to be a sauropod, later study determined that it was a hadrosaur, or "duck-billed" dinosaur, whose snouts bear likeness to ducks' bills. Some of the species' bones found at the Chronister Dinosaur Site are housed in Washington, D.C.'s Smithsonian Institution.

During most of the Late Cretaceous the eastern half of North America formed Appalachia, an island land mass separated from Laramidia to the west by the Western Interior Seaway. This seaway had split North America into two massive landmasses due to a multitude of factors such as tectonism and sea-level fluctuations for nearly 40 million years. The seaway eventually expanded, divided across the Dakotas, and by the end of the Cretaceous, it retreated towards the Gulf of Mexico and the Hudson Bay.
The Black Creek Group is a Late Cretaceous -aged geologic group in the southeastern United States, where it is known from the coastal plain of North Carolina and South Carolina. Deposited in brackish or nearshore marine conditions, it preserves fossils, including a diversity of dinosaurs and marine reptiles.

This timeline of hadrosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the hadrosauroids, a group of herbivorous ornithopod dinosaurs popularly known as the duck-billed dinosaurs. Scientific research on hadrosaurs began in the 1850s, when Joseph Leidy described the genera Thespesius and Trachodon based on scrappy fossils discovered in the western United States. Just two years later he published a description of the much better-preserved remains of an animal from New Jersey that he named Hadrosaurus.

Bonapartesaurus is an extinct genus of herbivorous ornithopod dinosaur belonging to Hadrosauridae, which lived in the area of modern Argentina during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous.















