
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 22-member intergovernmental body devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, the ESA was founded in 1975. Its 2024 annual budget was €7.8 billion.

The Soyuz programme is a human spaceflight programme initiated by the Soviet Union in the early 1960s. The Soyuz spacecraft was originally part of a Moon landing project intended to put a Soviet cosmonaut on the Moon. It was the third Soviet human spaceflight programme after the Vostok (1961–1963) and Voskhod (1964–1965) programmes.
Human spaceflight programs have been conducted, started, or planned by multiple countries and companies. Until the 21st century, human spaceflight programs were sponsored exclusively by governments, through either the military or civilian space agencies. With the launch of the privately funded SpaceShipOne in 2004, a new category of human spaceflight programs – commercial human spaceflight – arrived. By the end of 2022, three countries and one private company (SpaceX) had successfully launched humans to Earth orbit, and two private companies had launched humans on a suborbital trajectory.

The Automated Transfer Vehicle, originally Ariane Transfer Vehicle or ATV, was an expendable cargo spacecraft developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), used for space cargo transport in 2008–2015. The ATV design was launched to orbit five times, exclusively by the Ariane 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. It effectively was a larger European counterpart to the Russian Progress cargo spacecraft for carrying upmass to a single destination—the International Space Station (ISS)—but with three times the capacity.

The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos, is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research.

Kliper was an early-2000s proposed partially-reusable crewed spacecraft concept by RSC Energia. Due to lack of funding from the ESA and RSA, the project was indefinitely postponed by 2006.

The Crew Return Vehicle (CRV), sometimes referred to as the Assured Crew Return Vehicle (ACRV), was a proposed dedicated lifeboat or escape module for the International Space Station (ISS). A number of different vehicles and designs were considered over two decades – with several flying as developmental test prototypes – but none became operational. Since the arrival of the first permanent crew to the ISS in 2000, the emergency return capability has been fulfilled by Soyuz spacecraft and, more recently, SpaceX's Crew Dragon – each rotated every 6 months.
Space logistics is "the theory and practice of driving space system design for operability and supportability, and of managing the flow of materiel, services, and information needed throughout a space system lifecycle." It includes terrestrial logistics in support of space travel, including any additional "design and development, acquisition, storage, movement, distribution, maintenance, evacuation, and disposition of space materiel", movement of people in space, and contracting and supplying any required support services for maintaining space travel. The space logistics research and practice primarily focus on the modeling and management of the astro-logistics supply chain from Earth and on to destinations throughout the solar system as well as the system architecture strategies to minimize both logistics requirements and operational costs of human and robotic operations in space.

Soyuz TMA-19 was a crewed spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) and is part of the Soyuz programme. It was launched on 15 June 2010 carrying three members of the Expedition 24 crew to the International Space Station, who remained aboard the station for around six months. Soyuz TMA-19 was the 106th crewed flight of a Soyuz spacecraft, since the first mission which was launched in 1967. The spacecraft remained docked to the space station for the remainder of Expedition 24, and for Expedition 25, to serve as an emergency escape vehicle. It undocked from ISS and landed in Kazakhstan on 26 November 2010. It was the 100th mission to be conducted as part of the International Space Station programme since assembly began in 1998.

The International Space Station programme is tied together by a complex set of legal, political and financial agreements between the fifteen nations involved in the project, governing ownership of the various components, rights to crewing and utilisation, and responsibilities for crew rotation and resupply of the International Space Station. It was conceived in September 1993 by the United States and Russia after 1980s plans for separate American (Freedom) and Soviet (Mir-2) space stations failed due to budgetary reasons. These agreements tie together the five space agencies and their respective International Space Station programmes and govern how they interact with each other on a daily basis to maintain station operations, from traffic control of spacecraft to and from the station, to utilisation of space and crew time. In March 2010, the International Space Station Program Managers from each of the five partner agencies were presented with Aviation Week's Laureate Award in the Space category, and the ISS programme was awarded the 2009 Collier Trophy.

The Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) is the name given to the components of the International Space Station (ISS) constructed in Russia and operated by the Russian Roscosmos. The ROS handles Guidance, Navigation, and Control for the entire Station.

Orel or Oryol, formerly Federation, and PPTS, is a project by Roscosmos to develop a new-generation, partially reusable crewed spacecraft.

Soyuz TMA-03M was a spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS). It launched on 21 December 2011 from Site One at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan, carrying three members of Expedition 30 to the ISS. TMA-03M was the 112th flight of a Russian Soyuz spacecraft, since the first in 1967, and the third flight of the modernised Soyuz-TMA-M version. The docking with the International Space Station took place at 19:19 Moscow Time on 23 December, three minutes ahead of schedule.

Orion is a partially reusable crewed spacecraft used in NASA's Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin and the European Service Module (ESM) manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. Capable of supporting a crew of four beyond low Earth orbit, Orion can last up to 21 days undocked and up to six months docked. It is equipped with solar panels, an automated docking system, and glass cockpit interfaces modeled after those used in the Boeing 787 Dreamliner. A single AJ10 engine provides the spacecraft's primary propulsion, while eight R-4D-11 engines, and six pods of custom reaction control system engines developed by Airbus, provide the spacecraft's secondary propulsion. Orion is intended to be launched atop a Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, with a tower launch escape system.

The European contribution to the International Space Station comes from 10 members of the European Space Agency (ESA) and amounts to an 8% share in the programme. It consists of a number of modules in the US Orbital Segment, ATV supply ships, launchers, software and €8 billion.

The European Service Module (ESM) is the service module component of the Orion spacecraft, serving as its primary power and propulsion component until it is discarded at the end of each mission. In January 2013, NASA announced that the European Space Agency (ESA) will contribute the service module for Artemis I, based on the ESA's Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV). It was delivered by Airbus Defence and Space in Bremen, in northern Germany to NASA at the end of 2018. After approval of the first module, the ESA will provide the ESMs from Artemis II to Artemis VI.
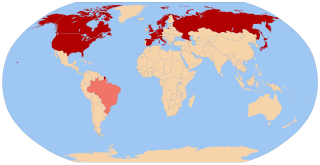
The politics of the International Space Station have been affected by superpower rivalries, international treaties, and funding arrangements. The Cold War was an early factor, overtaken in recent years by the United States' distrust of China. The station has an international crew, with the use of their time, and that of equipment on the station, being governed by treaties between participant nations.

The Commercial Crew Program (CCP) provides commercially operated crew transportation service to and from the International Space Station (ISS) under contract to NASA, conducting crew rotations between the expeditions of the International Space Station program. American space manufacturer SpaceX began providing service in 2020, using the Crew Dragon spacecraft, and NASA plans to add Boeing when its Boeing Starliner spacecraft becomes operational no earlier than 2025. NASA has contracted for six operational missions from Boeing and fourteen from SpaceX, ensuring sufficient support for ISS through 2030.

Soyuz MS-22 was a Russian Soyuz spaceflight to the International Space Station with a crew of three launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome on 21 September 2022. The launch, previously planned for 13 September 2022, was subsequently delayed to 21 September 2022 for a mission length of 188 days.





















