
Eddy County is a county located in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 census, the population was 53,829. Its county seat and largest city is Carlsbad. The county was created in 1891 and later organized in 1892. It is north of the Texas state line.

Carlsbad is a city in and the county seat of Eddy County, New Mexico, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city population was 32,238. Carlsbad is centered at the intersection of U.S. Routes 62/180 and 285, and is the principal city of the Carlsbad-Artesia Micropolitan Statistical Area, which has a total population of 55,435. Located in the southeastern part of New Mexico, Carlsbad straddles the Pecos River and sits at the eastern edge of the Guadalupe Mountains.

The Pecos River originates in north-central New Mexico and flows into Texas, emptying into the Rio Grande. Its headwaters are on the eastern slope of the Sangre de Cristo mountain range in Mora County north of Pecos, New Mexico, at an elevation of over 12,000 feet (3,700 m). The river flows for 926 miles (1,490 km) before reaching the Rio Grande near Del Rio. Its drainage basin encompasses about 44,300 square miles (115,000 km2).

Derby Dam is a diversion dam built from 1903 to 1905 on the Truckee River, located about 20 miles (32 km) east of Reno in Storey and Washoe counties in Nevada, United States. It diverts water into the Truckee Canal that would otherwise enter Pyramid Lake. The canal feeds Lake Lahontan reservoir in the Carson River watershed, where it is used for irrigation.

The Columbia Basin Project in Central Washington, United States, is the irrigation network that the Grand Coulee Dam makes possible. It is the largest water reclamation project in the United States, supplying irrigation water to over 670,000 acres (2,700 km2) of the 1,100,000 acres (4,500 km2) large project area, all of which was originally intended to be supplied and is still classified irrigable and open for the possible enlargement of the system. Water pumped from the Columbia River is carried over 331 miles (533 km) of main canals, stored in a number of reservoirs, then fed into 1,339 miles (2,155 km) of lateral irrigation canals, and out into 3,500 miles (5,600 km) of drains and wasteways. The Grand Coulee Dam, powerplant, and various other parts of the CBP are operated by the Bureau of Reclamation. There are three irrigation districts in the project area, which operate additional local facilities.

Elephant Butte Dam or Elephant Butte Dike, originally Engle Dam, is a concrete gravity dam on the Rio Grande near Truth or Consequences, New Mexico. The dam impounds Elephant Butte Reservoir, which is used mainly for agriculture but also provides for recreation, hydroelectricity, and flood and sediment control. The construction of the dam has reduced the flow of the Rio Grande to a small stream for most of the year, with water being released only during the summer irrigation season or during times of exceptionally heavy snow melt.

Pineview Dam is located in Ogden Canyon, 7 miles (11 km) east of Ogden, Utah, United States.

Theodore Roosevelt Dam is a dam on the Salt River located northeast of Phoenix, Arizona. The dam is 357 feet (109 m) high and forms Theodore Roosevelt Lake as it impounds the Salt River. Originally built between 1905 and 1911, the dam was renovated and expanded in 1989–1996. The dam is named after President Theodore Roosevelt. Serving mainly for irrigation, water supply, and flood control, the dam also has a hydroelectric generating capacity of 36 megawatts.

James John (J.J.) Hagerman was an American industrialist who owned mines, railroads and corporate farms in the American West in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He was one of the most influential men in territorial New Mexico.

The Franklin Canal is an irrigation canal in the Upper Rio Grande Valley near El Paso, Texas. The canal acquires water from the Rio Grande via the American Canal. The canal is 28.4 miles (45.7 km) long with a capacity of 325 cubic feet per second (9.2 m3/s).
Brantley Lake is a reservoir on the Pecos River located within Brantley Lake State Park approximately 12 miles (19 km) north of Carlsbad, New Mexico off US 285.
The Central Utah Project is a US federal water project that was authorized for construction under the Colorado River Storage Project Act of April 11, 1956, as a participating project. In general, the Central Utah Project develops a portion of Utah's share of the yield of the Colorado River, as set out in the Colorado River Compact of 1922.
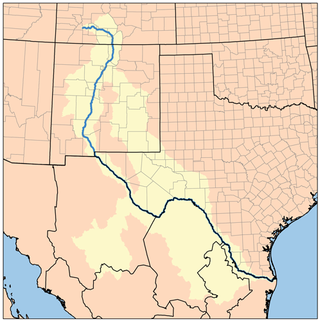
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

The Minidoka Project is a series of public works by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation to control the flow of the Snake River in Wyoming and Idaho, supplying irrigation water to farmlands in Idaho. One of the oldest Bureau of Reclamation projects in the United States, the project involves a series of dams and canals intended to store, regulate and distribute the waters of the Snake, with electric power generation as a byproduct. The water irrigates more than a million acres (4,000 km²) of otherwise arid land, producing much of Idaho's potato crop. Other crops include alfalfa, fruit and sugar beets. The primary irrigation district lies between Ashton in eastern Idaho and Bliss in the southwestern corner of the state. Five main reservoirs collect water, distributing it through 1,600 miles (2,600 km) of canals and 4,000 miles (6,400 km) of lateral distribution ditches.

Central Oregon Irrigation District is a municipal corporation to provide irrigation water for Central Oregon, U.S. The canals serve agricultural and industrial users in the arid lands between Alfalfa, Bend, Redmond, Terrebonne, and Powell Butte. Among its 4,000 or so individual customer accounts, it also provides municipal water to the city of Redmond, neighboring subdivisions, and parks and schools in Bend. The district manages more than 700 miles (1,100 km) of canals serving about 70.3 square miles (182 km2) of lands within a rough area of 280 square miles (730 km2).

The Grand Valley Diversion Dam is a diversion dam in the De Beque Canyon of the Colorado River, about 15 miles (24 km) northeast of Grand Junction, Colorado in the United States. It is a 14-foot (4.3 m) high, 546-foot (166 m) long concrete roller dam with six gates, which were the first and largest of their kind to be installed in the United States.
Brantley Dam is a flood-control and irrigation water-storage dam on the Pecos River in Eddy County, New Mexico, about 13 miles (21 km) north of Carlsbad, New Mexico, and 10 miles (16 km) upstream from Avalon Dam.

Avalon Dam is a small dam on the Pecos River about 5 miles (8.0 km) north of Carlsbad, New Mexico, United States. The dam is a storage and regulating reservoir, and diverts water into the main canal of the Carlsbad Project, an irrigation scheme.
Malaga is a census-designated place and unincorporated community in Eddy County, New Mexico, United States. Its population was 147 as of the 2010 census. Malaga has a post office with ZIP code 88263. U.S. Route 285 passes through the community. Formerly known as Kirkwell, Malaga was founded in the 1890s by Swiss immigrants and was named after the Spanish city of Málaga. Italian laborers were recruited to farm the area, and many settled in Malaga.

















