
Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility is a United States Navy shipyard covering 179 acres (0.7 km²) on Puget Sound at Bremerton, Washington in uninterrupted use since its establishment in 1891; it has also been known as Navy Yard Puget Sound, Bremerton Navy Yard, and Puget Sound Naval Shipyard.

Harvard Yard, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is the oldest part of the Harvard University campus, its historic center and modern crossroads. It contains most of the freshman dormitories, Harvard's most important libraries, Memorial Church, several classroom and departmental buildings, and the offices of senior University officials including the President of Harvard University.

The third USS Salem (CA-139) is one of three Des Moines-class heavy cruisers completed for the United States Navy shortly after World War II. Commissioned in 1949, she was the world's last heavy cruiser to enter service and the only one still in existence. She was decommissioned in 1959, after serving in the Atlantic and Mediterranean. She is open to the public as a museum ship in Quincy, Massachusetts.

The Freedom Trail is a 2.5-mile-long (4.0 km) path through downtown Boston, Massachusetts, that passes by 16 locations significant to the history of the United States. Marked largely with brick, it winds between Boston Common to the Bunker Hill Monument in Charlestown. Stops along the trail include simple explanatory ground markers, graveyards, notable churches and buildings, and a historic naval frigate. While most of the sites are free or suggest donations, the Old South Meeting House, the Old State House, and the Paul Revere House charge admission. The Freedom Trail is overseen by the City of Boston's Freedom Trail Commission and is supported in part by grants from various nonprofits and foundations, private philanthropy, and Boston National Historical Park.

South Bay is a 10-acre site in Boston, Massachusetts between Chinatown and the Leather District. It is roughly bounded by Kneeland Street, Hudson Street, the Massachusetts Turnpike mainline, and the Interstate 93 mainline. Currently owned by the Massachusetts Turnpike Authority (MTA), the area is taken up by a major highway interchange between 90, 93, and local streets. There were originally plans to re-develop the area with a 600-foot tall office tower, but no such project has taken place.
Maverick Square is a section of the neighborhood of East Boston in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. The square is intersected by several thoroughfares, but is most notably recognized by the convergence of Chelsea Street and Meridian Street. At the heart of the square is Maverick Station, which is part of the Blue Line of the MBTA.
North Quincy is a neighborhood of Quincy, Massachusetts. It is separated from the city of Boston by the Neponset River, and borders the Quincy neighborhoods of Squantum, Montclair and Wollaston. It contains the smaller neighborhoods of Atlantic and Norfolk Downs, as well as much of Wollaston Beach.

Boston College Main Campus Historic District encompasses the historic heart of the campus of Boston College in the Chestnut Hill area of Newton, Massachusetts. It consists of a collection of six Gothic Revival stone buildings, centered on Gasson Hall, designed by Charles Donagh Maginnis and begun in 1909.

The Victory Destroyer Plant was a United States Naval Shipbuilding yard operational from 1918 to 1920 in Quincy, Massachusetts. It was then reused as a civil airport, and later Naval Air Station Squantum. It was owned by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation, and was constructed in order to relieve destroyer construction at the nearby Fore River Shipyard.
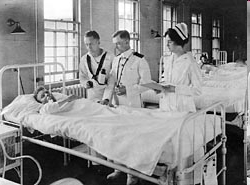
Naval Hospital Boston was a hospital in Chelsea, Massachusetts. With the closure of the nearby Boston Navy Yard, the hospital closed in 1974.

George Lawley & Son was a shipbuilding firm operating in Massachusetts from 1866 to 1945. It began in Scituate, then moved to Boston. After founder George Lawley (1823–1915) retired in 1890, his son, grandson and great-grandson upheld the business, which continued until 1945. Of the hundreds of ships built by the Lawleys, highlights include the yachts Puritan and Mayflower, respective winners of the 1885 and 1886 America's Cup.

The South Boston Naval Annex, was a 167-acre (68 ha) United States Navy shipyard annex located in South Boston. It was the annex of the Boston Navy Yard, and was operational from the 1920 to 1974, when it was closed along with the main shipyard. The annex is also home to Dry Dock Number 3, the one of the largest dry docks on the East Coast.
The South Boston Army Base, was a 58-acre United States Army annex located in South Boston. During World War II, it was used as the Boston Port of Embarkation. It was operational from 1920 to 1974.

Raymond L. Flynn Marine Park, formerly known as the Boston Marine Industrial Park, is an industrial park which has been created on the Commonwealth Flats in South Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Before its creation, the site was used as the location for the South Boston Naval Annex, the South Boston Army Base, and was used as a general seaport district for many years. Currently, the park is in the process of being redeveloped, and utilizes many of the former military buildings. The Black Falcon Cruise Terminal is also located on the site of the former Army base.

The Charlestown Ropewalk is a former ropewalk facility located in Charlestown, Massachusetts at the former Boston Navy Yard. At over 1,300 feet (400 m) long, it is the only standing ropewalk facility still existent in the United States. It is a pending Boston Landmark.
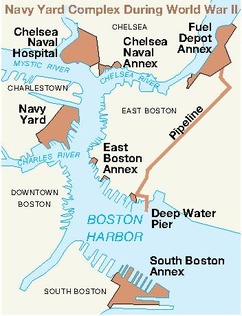
The East Boston Naval Annex, was United States Navy shipyard annex located in East Boston. It was the annex of the Boston Navy Yard.

The Boston Naval Yard Fuel Depot Annex, was a United States Navy fuel depot annex located in East Boston, Massachusetts. It was the annex of Boston Navy Yard.

Camp Meigs is a former American Civil War training camp that existed from 1862 to 1865 in Readville, Massachusetts. It existed near the former Camp Brigham and Camp Massasoit and trained the 54th Regiment Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry, among others. The 54th regiment was one of the first official African-American units in the United States during the Civil War.

The Second Great Chelsea fire was a conflagration that occurred on October 14, 1973, in Chelsea, Massachusetts. The fire burned 18 acres (7.3 ha), and was spread by strong winds and a lack of adequate water supply in the neighborhood of the fire. The fire started 200 yards (180 m) away from the origin of the Great Chelsea Fire of 1908.

The Great Chelsea fire of 1908, also known as the First great Chelsea fire, was a conflagration that occurred on 12 April 1908, in Chelsea, Massachusetts. Nineteen people were killed, fifteen thousand people were left homeless, and 350 acres (140 ha) were burned in the fire. The fire started two hundred yards away from the Great Chelsea fire of 1973.





















