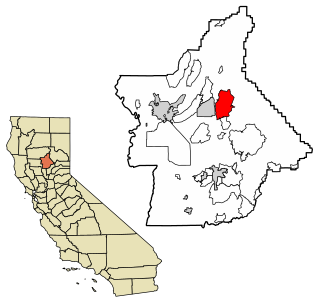
Concow is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in the Sierra Nevada foothills covering eastern Butte County, California. Due to a decline in employment and repeated wildfires, over the past hundred years the population declined from several thousand to several dozen. On November 8, 2018, a wildfire, the Camp Fire, destroyed most of Concow, as well as the adjacent municipality of Paradise.

Penutian is a proposed grouping of language families that includes many Native American languages of western North America, predominantly spoken at one time in British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and California. The existence of a Penutian stock or phylum has been the subject of debate among specialists. Even the unity of some of its component families has been disputed. Some of the problems in the comparative study of languages within the phylum are the result of their early extinction and limited documentation.

The Maidu are a Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather and American Rivers and in Humbug Valley. In Maiduan languages, maidu means "man".

Washo is an endangered Native American language isolate spoken by the Washo on the California–Nevada border in the drainages of the Truckee and Carson Rivers, especially around Lake Tahoe. While there were only 20 elderly native speakers of Washo as of 2011, since 1994 there had been a small immersion school that has produced a number of moderately fluent younger speakers. The immersion school has since closed its doors and the language program now operates through the Cultural Resource Department for the Washoe Tribe. The language is still very much endangered; however, there has been a renaissance in the language revitalization movement as many of the students who attended the original immersion school have become teachers.

Yokuts, formerly known as Mariposa, is an endangered language spoken in the interior of Northern and Central California in and around the San Joaquin Valley by the Yokuts people. The speakers of Yokuts were severely affected by disease, missionaries, and the Gold Rush. While descendants of Yokuts speakers currently number in the thousands, all constituent dialects apart from Valley Yokuts are now extinct.

Plateau Penutian is a family of languages spoken in northern California, reaching through central-western Oregon to northern Washington and central-northern Idaho.

The Pomoan, or Pomo, languages are a small family of seven languages indigenous to northern California spoken by the Pomo people, whose ancestors lived in the valley of the Russian River and the Clear Lake basin. Four languages are extinct, and all surviving languages except Kashaya have fewer than ten speakers.
Wintuan is a family of languages spoken in the Sacramento Valley of central Northern California.
The Nomlaki are a Wintun people native to the area of the Sacramento Valley, extending westward to the Coast Range in Northern California. Today some Nomlaki people are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes: Round Valley Indian Tribes, Grindstone Indian Rancheria or the Paskenta Band of Nomlaki Indians.

The Patwin are a band of Wintun people in Northern California. The Patwin comprise the southern branch of the Wintun group, native inhabitants of California since approximately 500.

The Mechoopda are a tribe of Maidu people, an Indigenous people of California. They are enrolled in the Mechoopda Indian Tribe of Chico Rancheria, a federally recognized tribe. Historically, the tribe has spoken Konkow, a language related to the Maidu language, and as of 2010, has created digital learning materials from old recordings of Emma Cooper, made during the 1940s as a part of the war effort.

Maiduan is a small endangered language family of northeastern California.

Maidu, also Northeastern Maidu or Mountain Maidu, is an extinct Maiduan language of California, United States. It was spoken by the Maidu peoples who traditionally inhabit the mountains east and south of Lassen Peak in the American River and Feather River basins. These river regions include such valleys in the northern Sierra Nevada mountains of California as: Indian Valley, American Valley, Butte Valley, and Big Meadows. Maidu may also refer to the related Konkow and Nisenan languages.

The Yuki–Wappo or Yukian languages are a small language family of western California consisting of two distantly related languages, both now extinct.

The Konkow language, also known as Northwest Maidu is a part of the Maiduan language group. It is spoken in California. It is severely endangered, with three remaining elders who learned to speak it as a first language, one of whom is deaf. As part of an effort to regain official recognition as a federally recognized tribe, an effort to provide language instruction amongst the descendants of the original tribe and affiliated family members has begun.

The Nisenan are a group of Native Americans and an Indigenous people of California from the Yuba River and American River watersheds in Northern California and the California Central Valley. According to a 1929 archeology and ethnology press release by University of California, Berkeley, the Nisenan people are classified as part of the larger group of Native Americans known as the Maidu, though some dispute the accuracy of this relationship, including the Nisesan themselves. According to the Nisenan website, the United States' claim that they are Maidu is a misclassification and is inaccurate. As the Nisenan put it,
"Like many other Tribes throughout the United States, the Nisenan have been misidentified and mislabeled. The Nisenan have been lumped together under inaccurate labels such as "Maidu", "digger" and "southern Maidu". However, the Nisenan are a separate Tribe with their own Cultural lifeways, their own leaders and holy people, a distinct geographic territory and their own ancient and unique language."

Stephen Powers (1840–1904) was an American journalist, ethnographer, and historian of Native American tribes in California. He traveled extensively to study and learn about their cultures, and wrote notable accounts of them. His articles were first published over a series of years in the Overland Monthly journal, but collected in The Tribes of California (1877) published by the US Geological Survey.
Maidu traditional narratives include myths, legends, tales, and oral histories preserved by the Maidu, Konkow, and Nisenan people of eastern Sacramento Valley and foothills in northeastern California.

Nisenan is a nearly extinct Maiduan language spoken by the Nisenan people of central California in the foothills of the Sierras, in the whole of the American, Bear and Yuba river drainages.

The Nome Cult Trail also known as the Concow Trail of Tears refers to the state-sanctioned forced removal of the Northern Californian Concow Maidu people during the 1860s to Round Valley Reservation. This historic trail is located in present-day Mendocino National Forest which follows Round Valley Road, through Rocky Ridge and the Sacramento Valley. On August 28, 1863, the Konkow Maidu were ordered by the California state militia to report to the Bidwell Ranch in Chico to be removed to the Round Valley Reservation at Covelo in Mendocino County. Any Native Americans remaining in the area were to be shot. 461 Concow Maidu were forced to march under guard west out of the Sacramento Valley and through to the Coastal Range. Only 277 reached Round Valley reservation on September 18, 1862 as 150 were too ill and malnourished to finish the march, 32 died en route, and 2 escaped.


















