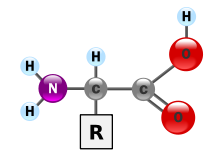
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three other carbon atoms). It is classified as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it. Essential amino acids are necessary in the human diet. In plants isoleucine can be synthesized from threonine and methionine. In plants and bacteria, isoleucine is synthesized from a pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes. It is encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA.

Threonine is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as E. coli. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC.

Methylmalonic acidemias, also called methylmalonic acidurias, are a group of inherited metabolic disorders, that prevent the body from properly breaking down proteins and fats. This leads to a buildup of a toxic level of methylmalonic acid in body liquids and tissues. Due to the disturbed branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) metabolism, they are among the classical organic acidemias.
Propionic acidemia, also known as propionic aciduria or propionyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency, is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder, classified as a branched-chain organic acidemia.
Inborn errors of metabolism form a large class of genetic diseases involving congenital disorders of enzyme activities. The majority are due to defects of single genes that code for enzymes that facilitate conversion of various substances (substrates) into others (products). In most of the disorders, problems arise due to accumulation of substances which are toxic or interfere with normal function, or due to the effects of reduced ability to synthesize essential compounds. Inborn errors of metabolism are often referred to as congenital metabolic diseases or inherited metabolic disorders. Another term used to describe these disorders is "enzymopathies". This term was created following the study of biodynamic enzymology, a science based on the study of the enzymes and their products. Finally, inborn errors of metabolism were studied for the first time by British physician Archibald Garrod (1857–1936), in 1908. He is known for work that prefigured the "one gene–one enzyme" hypothesis, based on his studies on the nature and inheritance of alkaptonuria. His seminal text, Inborn Errors of Metabolism, was published in 1923.

Isovaleric acidemia is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder which disrupts or prevents normal metabolism of the branched-chain amino acid leucine. It is a classical type of organic acidemia.

Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a rare, inherited metabolic disorder that affects the body's ability to metabolize amino acids due to a deficiency in the activity of the branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKAD) complex. It particularly affects the metabolism of amino acids—leucine, isoleucine, and valine. With MSUD, the body is not able to properly break down these amino acids, therefore leading to the amino acids to build up in urine and become toxic. The condition gets its name from the distinctive sweet odor of affected infants' urine and earwax due to the buildup of these amino acids.

Hartnup disease is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting the absorption of nonpolar amino acids. Niacin is a precursor to nicotinamide, a necessary component of NAD+.
Glutaric acidemia type 1 (GA1) is an inherited disorder in which the body is unable to completely break down the amino acids lysine, hydroxylysine and tryptophan. Excessive levels of their intermediate breakdown products can accumulate and cause damage to the brain, but particularly the basal ganglia, which are regions that help regulate movement. GA1 causes secondary carnitine deficiency, as glutaric acid, like other organic acids, is detoxified by carnitine. Mental retardation may occur.

Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting amino acid transport. It is characterised by the body's inability to properly digest and use certain proteins. This condition leads to various metabolic complications and is typically diagnosed in infancy or early childhood.
Glutaric acidemia type 2 is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that is characterised by defects in the ability of the body to use proteins and fats for energy. Incompletely processed proteins and fats can build up, leading to a dangerous chemical imbalance called acidosis. It is a metabolic myopathy, categorized under fatty acid metabolism disorder as that is the bioenergetic system that it affects the most. It also affects choline metabolism.

Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase is a mitochondrial homodimer apoenzyme that focuses on the catalysis of methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl CoA. The enzyme is bound to adenosylcobalamin, a hormonal derivative of vitamin B12 in order to function. Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency is caused by genetic defect in the MUT gene responsible for encoding the enzyme. Deficiency in this enzyme accounts for 60% of the cases of methylmalonic acidemia.

William Leo Nyhan is an American physician best known as the co-discoverer of Lesch–Nyhan syndrome.

Hyperprolinemia is a condition which occurs when the amino acid proline is not broken down properly by the enzymes proline oxidase or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, causing a buildup of proline in the body.
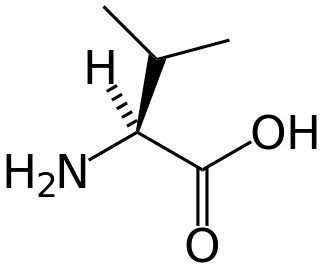
Hypervalinemia is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which urinary and serum levels of the branched-chain amino acid valine are elevated, without related elevation of the branched-chain amino acids leucine and isoleucine. It is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme valine transaminase.
Organic acidemia is a term used to classify a group of metabolic disorders which disrupt normal amino acid metabolism, particularly branched-chain amino acids, causing a buildup of acids which are usually not present.
A broad classification for genetic disorders that result from an inability of the body to produce or utilize an enzyme or transport protein that is required to oxidize fatty acids. They are an inborn error of lipid metabolism, and when it affects the muscles also a metabolic myopathy.
Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA), also called combined malonic and methylmalonic acidemia is an inherited metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of malonic acid and methylmalonic acid. However, the methylmalonic acid levels exceed those of malonic acid. CMAMMA is not only an organic aciduria but also a defect of mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFASII). Some researchers have hypothesized that CMAMMA might be one of the most common forms of methylmalonic acidemia, and possibly one of the most common inborn errors of metabolism. Due to being infrequently diagnosed, it most often goes undetected.