
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype.

Interferons are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis.
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Transmission of HDV can occur either via simultaneous infection with HBV (coinfection) or superimposed on chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B carrier state (superinfection).

Hepadnaviridae is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinomas, and cirrhosis. It is the sole accepted family in the order Blubervirales.

The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small, enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer and lymphomas in humans.
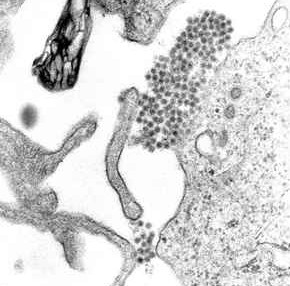
Dengue virus (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae; genus Flavivirus. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, and a reported fifth has yet to be confirmed, all of which can cause the full spectrum of disease. Nevertheless, scientists' understanding of dengue virus may be simplistic as, rather than distinct antigenic groups, a continuum appears to exist. This same study identified 47 strains of dengue virus. Additionally, coinfection with and lack of rapid tests for Zika virus and chikungunya complicate matters in real-world infections.
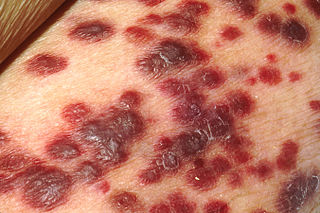
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the ninth known human herpesvirus; its formal name according to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) is Human gammaherpesvirus 8, or HHV-8 in short. Like other herpesviruses, its informal names are used interchangeably with its formal ICTV name. This virus causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer commonly occurring in AIDS patients, as well as primary effusion lymphoma, HHV-8-associated multicentric Castleman's disease and KSHV inflammatory cytokine syndrome. It is one of seven currently known human cancer viruses, or oncoviruses. Even after many years since the discovery of KSHV/HHV8, there is no known cure for KSHV associated tumorigenesis.
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are molecules that closely resemble viruses, but are non-infectious because they contain no viral genetic material. They can be naturally occurring or synthesized through the individual expression of viral structural proteins, which can then self assemble into the virus-like structure. Combinations of structural capsid proteins from different viruses can be used to create recombinant VLPs. Both in-vivo assembly and in-vitro assembly have been successfully shown to form virus-like particles. VLPs derived from the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and composed of the small HBV derived surface antigen (HBsAg) were described in 1968 from patient sera. VLPs have been produced from components of a wide variety of virus families including Parvoviridae, Retroviridae, Flaviviridae, Paramyxoviridae and bacteriophages. VLPs can be produced in multiple cell culture systems including bacteria, mammalian cell lines, insect cell lines, yeast and plant cells.
The genome and proteins of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) have been the subject of extensive research since the discovery of the virus in 1983. "In the search for the causative agent, it was initially believed that the virus was a form of the Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV), which was known at the time to affect the human immune system and cause certain leukemias. However, researchers at the Pasteur Institute in Paris isolated a previously unknown and genetically distinct retrovirus in patients with AIDS which was later named HIV." Each virion comprises a viral envelope and associated matrix enclosing a capsid, which itself encloses two copies of the single-stranded RNA genome and several enzymes. The discovery of the virus itself occurred two years following the report of the first major cases of AIDS-associated illnesses.

Envelope glycoprotein GP120 is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1988. The 120 in its name comes from its molecular weight of 120 kDa. Gp120 is essential for virus entry into cells as it plays a vital role in attachment to specific cell surface receptors. These receptors are DC-SIGN, Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and a specific interaction with the CD4 receptor, particularly on helper T-cells. Binding to CD4 induces the start of a cascade of conformational changes in gp120 and gp41 that lead to the fusion of the viral membrane with the host cell membrane. Binding to CD4 is mainly electrostatic although there are van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonds.

A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the envelope, which may be acquired by the capsid from an infected host cell.

Murine coronavirus (M-CoV) is a virus in the genus Betacoronavirus that infects mice. Belonging to the subgenus Embecovirus, murine coronavirus strains are enterotropic or polytropic. Enterotropic strains include mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) strains D, Y, RI, and DVIM, whereas polytropic strains, such as JHM and A59, primarily cause hepatitis, enteritis, and encephalitis. Murine coronavirus is an important pathogen in the laboratory mouse and the laboratory rat. It is the most studied coronavirus in animals other than humans, and has been used as an animal disease model for many virological and clinical studies.
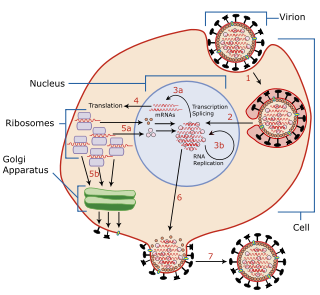
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Despite the variation among viruses, there are several shared generalities concerning viral entry.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 11,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.

E1 is one of two subunits of the envelope glycoprotein found in the hepatitis C virus. The other subunit is E2. This protein is a type 1 transmembrane protein with a highly glycosylated N-terminal ectodomain and a C-terminal hydrophobic anchor. After being synthesized the E1 glycoproteins associates with the E2 glycoprotein as a noncovalent heterodimer.

Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus Orthohepadnavirus and a member of the Hepadnaviridae family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.

The envelope (E) protein is the smallest and least well-characterized of the four major structural proteins found in coronavirus virions. It is an integral membrane protein less than 110 amino acid residues long; in SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of Covid-19, the E protein is 75 residues long. Although it is not necessarily essential for viral replication, absence of the E protein may produce abnormally assembled viral capsids or reduced replication. E is a multifunctional protein and, in addition to its role as a structural protein in the viral capsid, it is thought to be involved in viral assembly, likely functions as a viroporin, and is involved in viral pathogenesis.

The membrane (M) protein is an integral membrane protein that is the most abundant of the four major structural proteins found in coronaviruses. The M protein organizes the assembly of coronavirus virions through protein-protein interactions with other M protein molecules as well as with the other three structural proteins, the envelope (E), spike (S), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins.













