Related Research Articles

Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and aesthetics have made him one of the most influential figures in modern Western philosophy.

In philosophy, the term idealism identifies and describes metaphysical perspectives which assert that "reality" is indistinguishable and inseparable from human perception and understanding; that reality is a mental construct closely connected to ideas. Idealist perspectives are in two categories: (i) Subjective idealism, which proposes that a material object exists only to the extent that a human being perceives the object; and (ii) Objective idealism, which proposes the existence of an objective consciousness that exists prior to and independently of human consciousness, thus the existence of the object is independent of human perception.

Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the first principles of being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity and possibility. It includes questions about the nature of consciousness and the relationship between mind and matter. The word "metaphysics" comes from two Greek words that, together, literally mean "after or behind or among [the study of] the natural". It has been suggested that the term might have been coined by a first century CE editor who assembled various small selections of Aristotle’s works into the treatise we now know by the name Metaphysics.
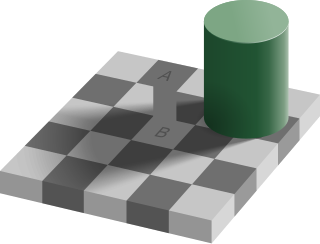
The philosophy of perception is concerned with the nature of perceptual experience and the status of perceptual data, in particular how they relate to beliefs about, or knowledge of, the world. Any explicit account of perception requires a commitment to one of a variety of ontological or metaphysical views. Philosophers distinguish internalist accounts, which assume that perceptions of objects, and knowledge or beliefs about them, are aspects of an individual's mind, and externalist accounts, which state that they constitute real aspects of the world external to the individual. The position of naïve realism—the 'everyday' impression of physical objects constituting what is perceived—is to some extent contradicted by the occurrence of perceptual illusions and hallucinations and the relativity of perceptual experience as well as certain insights in science. Realist conceptions include phenomenalism and direct and indirect realism. Anti-realist conceptions include idealism and skepticism. Recent philosophical work have expanded on the philosophical features of perception by going beyond the single paradigm of vision.
Solipsism is the philosophical idea that only one's mind is sure to exist. As an epistemological position, solipsism holds that knowledge of anything outside one's own mind is unsure; the external world and other minds cannot be known and might not exist outside the mind.
In philosophy, a noumenon is a posited object or event that exists independently of human sense and/or perception. The term noumenon is generally used in contrast with, or in relation to, the term phenomenon, which refers to any object of the senses. Immanuel Kant first developed the notion of the noumenon as part of his transcendental idealism, suggesting that while we know the noumenal world to exist because human sensibility is merely receptive, it is not itself sensible and must therefore remain otherwise unknowable to us. In Kantian philosophy, the unknowable noumenon is often identified with or associated with the unknowable "thing-in-itself". However, the nature of the relationship between the two is not made explicit in Kant's work, and remains a subject of debate among Kant scholars as a result.

German idealism was a philosophical movement that emerged in Germany in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It developed out of the work of Immanuel Kant in the 1780s and 1790s, and was closely linked both with Romanticism and the revolutionary politics of the Enlightenment. The best-known thinkers in the movement, besides Kant, were Johann Gottlieb Fichte, Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling, Arthur Schopenhauer, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, and the proponents of Jena Romanticism. August Ludwig Hülsen, Friedrich Heinrich Jacobi, Gottlob Ernst Schulze, Karl Leonhard Reinhold, Salomon Maimon and Friedrich Schleiermacher also made major contributions.

Critique of Pure Reason is a book by the German philosopher Immanuel Kant, in which the author seeks to determine the limits and scope of metaphysics. Also referred to as Kant's "First Critique", it was followed by his Critique of Practical Reason (1788) and Critique of Judgment (1790). In the preface to the first edition, Kant explains that by a "critique of pure reason" he means a critique "of the faculty of reason in general, in respect of all knowledge after which it may strive independently of all experience" and that he aims to reach a decision about "the possibility or impossibility of metaphysics."
Objective idealism is an idealistic metaphysics that postulates that there is ultimately only one perceiver, and that this perceiver is also that which is perceived. In this school of thought, the many individual beings and their local perceptions are united through a collective unconscious.

Transcendental idealism is a philosophical system founded by German philosopher Immanuel Kant in the 18th century. Kant's epistemological program is found throughout his Critique of Pure Reason (1781). By transcendental Kant means that his philosophical approach to knowledge transcends mere consideration of sensory evidence and requires an understanding of the mind's innate modes of processing that sensory evidence.
In philosophy of perception and philosophy of mind, naïve realism is the idea that the senses provide us with direct awareness of objects as they really are. When referred to as direct realism, naïve realism is often contrasted with indirect realism.

The question of direct or naïve realism, as opposed to indirect or representational realism, arises in the philosophy of perception and of mind and the debate over the nature of conscious experience; out of the epistemological question of whether the world we see around us is the real world itself or merely an internal perceptual copy of that world generated by neural processes in our brain.

Logical atomism is a philosophical view that originated in the early 20th century with the development of analytic philosophy. Its principal exponent was the British philosopher Bertrand Russell. It is also widely held that the early works of his Austrian-born pupil and colleague, Ludwig Wittgenstein, defend a version of logical atomism. Some philosophers in the Vienna Circle were also influenced by logical atomism. Gustav Bergmann also developed a form of logical atomism that focused on an ideal phenomenalistic language, particularly in his discussions of J.O. Urmson's work on analysis.

Absolute idealism is an ontologically monistic philosophy chiefly associated with G. W. F. Hegel and Friedrich Schelling, both of whom were German idealist philosophers in the 19th century. The label has also been attached to others such as Josiah Royce, an American philosopher who was greatly influenced by Hegel's work, and the British idealists. A form of idealism, absolute idealism is Hegel's account of how being is ultimately comprehensible as an all-inclusive whole. Hegel asserted that in order for the thinking subject to be able to know its object at all, there must be in some sense an identity of thought and being. Otherwise, the subject would never have access to the object and we would have no certainty about any of our knowledge of the world. To account for the differences between thought and being, however, as well as the richness and diversity of each, the unity of thought and being cannot be expressed as the abstract identity "A=A". Absolute idealism is the attempt to demonstrate this unity using a new "speculative" philosophical method, which requires new concepts and rules of logic. According to Hegel, the absolute ground of being is essentially a dynamic, historical process of necessity that unfolds by itself in the form of increasingly complex forms of being and of consciousness, ultimately giving rise to all the diversity in the world and in the concepts with which we think and make sense of the world.
Philosophical realism is usually not treated as a position of its own but as a stance towards other subject matters. Realism about a certain kind of thing is the thesis that this kind of thing has mind-independent existence, i.e. that it is not just a mere appearance in the eye of the beholder. This includes a number of positions within epistemology and metaphysics which express that a given thing instead exists independently of knowledge, thought, or understanding. This can apply to items such as the physical world, the past and future, other minds, and the self, though may also apply less directly to things such as universals, mathematical truths, moral truths, and thought itself. However, realism may also include various positions which instead reject metaphysical treatments of reality entirely.
Neopragmatism, sometimes called post-Deweyan pragmatism, linguistic pragmatism, or analytic pragmatism, is the philosophical tradition that infers that the meaning of words is a result of how they are used, rather than the objects they represent.
In metaphysics, metaphysical solipsism is the variety of idealism which asserts that nothing exists externally to this one mind, and since this mind is the whole of reality then the "external world" was never anything more than an idea. It can also be expressed by the assertion "there is nothing external to these present experiences", in other words, no reality exists beyond whatever is presently being sensed. The aforementioned definition of solipsism entails the non-existence of anything presently unperceived including the external world, causation, other minds, the past or future, and a subject of experience. Despite their ontological non-existence, these entities may nonetheless be said to "exist" as useful descriptions of the various experiences and thoughts that constitute 'this' mind.
Epistemology or theory of knowledge is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature and scope (limitations) of knowledge. It addresses the questions "What is knowledge?", "How is knowledge acquired?", "What do people know?", "How do we know what we know?", and "Why do we know what we know?". Much of the debate in this field has focused on analyzing the nature of knowledge and how it relates to similar notions such as truth, belief, and justification. It also deals with the means of production of knowledge, as well as skepticism about different knowledge claims.

Speculative realism is a movement in contemporary Continental-inspired philosophy that defines itself loosely in its stance of metaphysical realism against its interpretation of the dominant forms of post-Kantian philosophy.
References
- ↑ J. T. Blackmore, Ludwig Boltzmann: His Later Life and Philosophy, 1900-1906, Springer, 1995, p. 51.
- ↑ Dorothy Emmet, The Nature of Metaphysical Thinking, Springer, 2015, p. 73 n. 1.