Related Research Articles
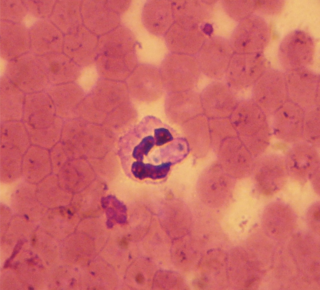
Hepatozoon is a genus of Apicomplexa alveolates which incorporates over 300 species obligate intraerythrocytic parasites. Species have been described from all groups of tetrapod vertebrates, as well as a wide range of haematophagous arthropods, which serve as both the vectors and definitive hosts of the parasite. By far the most biodiverse and prevalent of all haemogregarines, the genus is distinguished by its unique reciprocal trophic lifecycle which lacks the salivary transmission between hosts commonly associated with other apicomplexans. While particularly prevalent in amphibians and reptiles, the genus is more well known in veterinary circles for causing a tick-borne disease called hepatozoonosis in some mammals.

Adeleorina is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Protococcidiorida is an order within the subclass Conoidasida of the phylum Apicomplexia. All members of this order are parasitic protozoa. The order was created by Kheisin in 1956.
Dactylosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia.
Angeiocystis is a genus of parasitic alveolate eukaryotes belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa.
The Archigregarinorida are an order of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this order infect marine invertebrates — usually annelids, ascidians, hemichordates and sipunculids.
The Exoschizonidae are a family in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Blastogregarinorina is a suborder of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia
The Syncystidae are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this family infect insects (Aeshnidae).
The Schizocystidae are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this family infect insects.
Farinocystis is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect insects (Coleoptera).
Mattesia is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect insects.
Filipodium is a genus of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect marine invertebrates.
Siedleckia are a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect marine invertebrates.
Exoschizon is a genus in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Fusionidae is a family of the superfamily Fusionicae in the phylum Apicomplexa
Syncystis is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Machadoella is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Schizocystidae is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Lipocystis is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
References
- ↑ Stejskal M (1965) Gregarines parasitizing honey bees. Amer Bee J 105:374–375