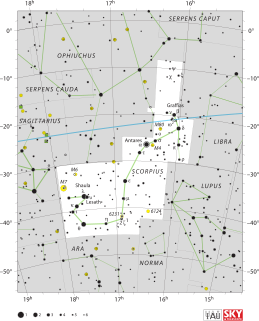
Scorpius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . Scorpius is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. It is an ancient constellation that pre-dates the Greeks. It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. It is a large constellation located in the southern hemisphere near the center of the Milky Way.

Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies.

Bubalus is a genus of Asiatic bovines that was proposed by Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. Bubalus and Syncerus form the subtribe Bubalina, the true buffaloes.

Hibbertopterus is a genus of eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Hibbertopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from the Devonian period in Belgium, Scotland and the United States to the Carboniferous period in Scotland, Ireland, the Czech Republic and South Africa. The type species, H. scouleri, was first named as a species of the significantly different Eurypterus by Samuel Hibbert in 1836. The generic name Hibbertopterus, coined more than a century later, combines his name and the Greek word πτερόν (pteron) meaning "wing".

Muraenosaurus is an extinct genus of cryptoclidid plesiosaur reptile from the Oxford Clay of Southern England. The genus was given its name due to the eel-like appearance of the long neck and small head. Muraenosaurus grew to lengths between 5 metres (16 ft) and 6 metres (20 ft) and dates roughly to between 160 Ma and 164 Ma in the Callovian of the middle Jurassic. Charles E. Leeds collected the first Muraenosaurus which was then described by H. G. Seeley. The specimen may have suffered some damage due to the casual style of Charles Leeds’ collection. The first Muraenosaur was recovered with pieces missing from the skull and many of the caudal vertebrae absent. Because the animal was described from Charles Leeds’ collection it was given the name Muraenosaurus Leedsi. M. leedsi is the most complete specimen belonging to the genus Muraenosaurus and also the only species that is undoubtedly a member of the genus.. Two other species have been tentatively referred to as members of the genus Muraenosaurus: M. reedii and Picrocleidus beloclis

The longnose pygmy shark is a rare species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae and the only member its genus. It is known only from a handful of specimens collected from the cold oceanic waters of the Southern Hemisphere, between the surface and a depth of 502 m (1,647 ft). Reaching 37 cm (15 in) in length, this diminutive shark is characterized by a slender, dark brown body with a very long, bulbous snout. In addition, it has two spineless dorsal fins of nearly equal size, with the origin of the first lying over the pectoral fin bases. The longnose pygmy shark does not appear substantially threatened by fisheries, and has been assessed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

The Guadalcanal monkey-faced bat is a megabat endemic to Solomon Islands. It is listed as an endangered species. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation.

Carcinosoma is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Carcinosoma are restricted to deposits of late Silurian age. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, which the genus lends its name to, Carcinosoma contains seven species from North America and Great Britain.

Myoxocephalus scorpius, typically known as the shorthorn sculpin or bull-rout, is a species of fish in the family Cottidae. It is a demersal species of the Northern Atlantic and adjacent subarctic and Arctic seas. The species has many English names that are used less frequently or in small parts of its range, including Arctic sculpin, daddy sculpin, European sculpin, father-lasher, goat sculpin, Greenland sculpin, guffy, horny whore, pig-fish, scully, scummy, short-spined sea scorpion and warty sculpin.

The longspined bullhead, also known as the longspined sea-scorpion, is a coastal fish of the sculpin family Cottidae, inhabiting marine waters of Europe.

The Atka mackerel is a mackerel in the family Hexagrammidae. Atka mackerel are common to the northern Pacific ocean, and are one of only two members of the genus Pleurogrammus - the other being the Arabesque greenling. The Atka mackerel was named for Atka Island, the largest island of the Andreanof islands, a branch of the Aleutians.
Achromatorida is an order of non-pigmented intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates belonging to the subclass Haemosporidiasina. The order was created by Jacques Euzéby in 1988.
Dactylosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia.
Lycodes is a genus of zoarcid fish in the subfamily Lycodinae. It is the most species-rich genus in its taxonomic family as well as in the Arctic Ocean and adjacent waters. They occupy both shallow waters and deeper waters down to 3000 meters. A few species can occur in brackish waters.

Eusarcana is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Eusarcana have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from the Early Silurian to the Early Devonian. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, the genus contains three species, E. acrocephalus, E. obesus and E. scorpionis, from the Silurian-Devonian of Scotland, the Czech Republic and the United States respectively.
Microcotyle pacifica is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was first described an illustrated based on 31 specimens from the gills of the blackbelly eelpout Lycodes pacificus off California.











