The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula.

The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum.

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.

An ear is the organ that enables hearing and body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most animals, the word "ear" often refers to the external part alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ear canal is cleaned via earwax, which naturally migrates to the auricle. The ears of vertebrates are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head, an arrangement that aids sound localization.

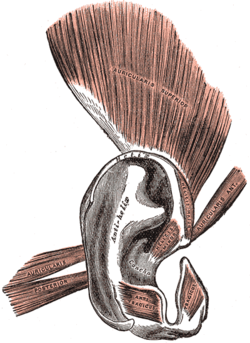
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna, a term that is used more in zoology.
Otoplasty is a procedure for correcting the deformities and defects of the auricle, whether these defects are congenital conditions or caused by trauma. Otoplastic surgeons may reshape, move, or augment the cartilaginous support framework of the auricle to correct these defects.
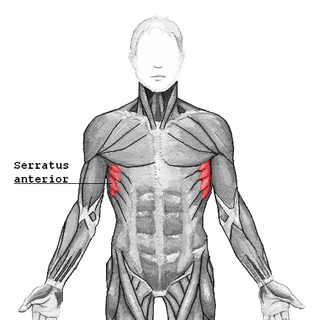
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thoracic nerve from the brachial plexus. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax.
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.

The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.

The antitragus is a feature of mammalian ear anatomy.

The antitragicus is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The tragicus, also called the tragus muscle or Valsalva muscle, is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The transverse muscle of auricle is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear.

The Helicis minor is a small skeletal muscle. The helicis minor is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear. The muscle runs obliques and covers the helical crus, part of the helix located just above the tragus.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The anterior auricular muscle, the smallest of the three auricular muscles, is thin and fan-shaped, and its fibers are pale and indistinct. It arises from the lateral edge of the epicranial aponeurosis, and its fibers converge to be inserted into a projection on the front of the helix.

The pelvis is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.