
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C. in unincorporated Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. It is one of ten major NASA field centers, named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Dr. Robert H. Goddard. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.

Jon Andrew McBride, , is a retired American naval officer and aviator, fighter pilot, test pilot, aeronautical engineer, and a former NASA astronaut.

Paul William Richards is an American engineer and a former NASA Astronaut. He flew aboard one Space Shuttle mission in 2001.
In software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation (V&V) is the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose. It may also be referred to as software quality control. It is normally the responsibility of software testers as part of the software development lifecycle. In simple terms, software verification is: "Assuming we should build X, does our software achieve its goals without any bugs or gaps?" On the other hand, software validation is: "Was X what we should have built? Does X meet the high level requirements?"
Explorer-1 [Prime], also known as E1P and Electra, was a CubeSat-class picosatellite built by the Space Science and Engineering Laboratory (SSEL) at Montana State University. It was launched aboard a Taurus-XL rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on 4 March 2011, but failed to achieve orbit after the rocket malfunctioned.

Launch Services Program (LSP) is responsible for NASA oversight of launch operations and countdown management, providing added quality and mission assurance in lieu of the requirement for the launch service provider to obtain a commercial launch license. It operates under the Human Exploration and Operations (HEO) Mission Directorate of NASA.
The Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) program is a series of CubeSats built by San Jose State University and University of Idaho students in partnership with NASA's Ames Research Center. These satellites have tested communication technology for smallsats, and have contributed to the development of the Small Payload Quick Return (SPQR) concept.

Exploration Mission-1 or EM-1 is the uncrewed first planned flight of the Space Launch System and the second flight of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. The launch is planned for June 2020 from Launch Complex 39B at the Kennedy Space Center. The Orion spacecraft will spend approximately 3 weeks in space, including 6 days in a retrograde orbit around the Moon. It is planned to be followed by Exploration Mission-2 in 2022.

NanoRacks LLC is a private company that develops products and offers services for the commercial utilization of space.
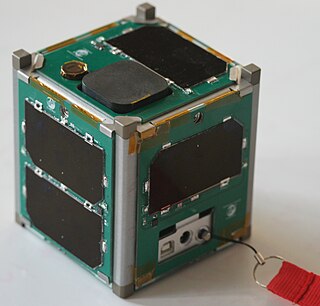
The Vermont Lunar CubeSat is a CubeSat satellite by Vermont Technical College and funded in part by grants from NASA, Vermont Space Grant Consortium and in part by voluntary donations. The satellite, costing about 50,000 US Dollars to build - with NASA offering a free launch as part of the ELaNa program - served as a testing model for guidance and navigation pending future launches. The eventual goal of the project is to build a CubeSat capable of orbiting the Moon.

Mars Cube One was a Mars flyby mission launched on 5 May 2018 alongside NASA's InSight Mars lander mission. It consisted of two nanospacecraft, MarCO-A and MarCO-B, that provided a real-time communications link to Earth for InSight during its entry, descent, and landing (EDL) on 26 November 2018 - when InSight was out of line of sight from the Earth. Both spacecraft were 6U CubeSats, and the mission was a test of new miniaturized communications and navigation technologies. These were the first CubeSats to operate beyond Earth orbit, and aside from telecommunications they also tested CubeSats' endurance in deep space. On 5 February 2019, NASA reported that the CubeSats went silent, and are unlikely to be heard from again.

Lunar IceCube is a planned NASA nanosatellite mission to prospect, locate, and estimate size and composition of water ice deposits on the Moon for future exploitation by robots or humans. It will fly as a secondary payload mission on the first flight of the Space Launch System, Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1) scheduled to launch in 2020.

The Miniature X-ray Solar Spectrometer (MinXSS) CubeSat was the first launched National Aeronautics and Space Administration Science Mission Directorate CubeSat with a science mission. It was designed, built, and operated primarily by students at the University of Colorado Boulder with professional mentorship and involvement from professors, scientists, and engineers in the Aerospace Engineering Sciences department and the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, as well as Southwest Research Institute, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Center for Atmospheric Research's High Altitude Observatory. The mission principal investigator is Dr. Thomas N. Woods and co-investigators are Dr. Amir Caspi, Dr. Phil Chamberlin, Dr. Andrew Jones, Rick Kohnert, Professor Xinlin Li, Professor Scott Palo, and Dr. Stanley Solomon. The student lead was Dr. James Paul Mason, who has since become a Co-I for the second flight model of MinXSS.
ArgoMoon is a nanosatellite that will fly on board NASA's Space Launch System during its first mission scheduled for 2019. The satellite has the dimensions of a shoe box in CubeSat terms, it is a 6U.

Irvine CubeSat STEM Program (ICSP) is a joint educational endeavor to teach, train and inspire the next generation of STEM professionals. ICSP involves students from six high schools from Irvine, California, and its main objective is to assemble, test, and launch a CubeSat into low Earth orbit.
Team Miles is a type of nanosatellite called 6-Unit CubeSat that will demonstrate navigation in deep space using innovative plasma thrusters. It will also test a software-defined radio operating in the S band for communications from about 4 million kilometers from Earth.
Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) is an initiative created by NASA to attract and retain students in the science, technology, engineering and mathematics disciplines. The program is managed by the Launch Services Program (LSP) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Mars Micro Orbiter (MMO) is a spacecraft mission concept that would place a small and inexpensive satellite in orbit around the planet Mars to study some aspects of the Mars atmosphere in visible and infrared wavelengths.
IRVINE01 is a 1U CubeSat built by the Irvine CubeSat STEM Program (ICSP), a team of six high schools from Irvine, California. IRVINE01 is an educational mission that gives high school students the experience of building, testing, and controlling a nano-satellite, with the aim of developing interest and talent in the science and engineering fields..

Simulation-to-Flight 1 (STF-1) is a microsatellite built by the Katherine Johnson Independent Verification and Validation Facility (IV&V) in Fairmont, West Virginia with the collaboration of the West Virginia Space Grants Consortium and West Virginia University.














