| Kiritimatiellota | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Superphylum: | PVC superphylum |
| Phylum: | Kiritimatiellota Spring et al. 2021 [1] |
| Classes [2] | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
| Kiritimatiellota | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Superphylum: | PVC superphylum |
| Phylum: | Kiritimatiellota Spring et al. 2021 [1] |
| Classes [2] | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |

Pseudomonadota is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of several prokaryote phyla in 2021, including Pseudomonadota, remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier name Proteobacteria, of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as Escherichia, Salmonella, Vibrio, Yersinia, Legionella, and many others. Others are free-living (non-parasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation.

A spirochaete or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota, which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm.

The Bacillota are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature.
The Aquificota phylum is a diverse collection of bacteria that live in harsh environmental settings. The name Aquificota was given to this phylum based on an early genus identified within this group, Aquifex, which is able to produce water by oxidizing hydrogen. They have been found in springs, pools, and oceans. They are autotrophs, and are the primary carbon fixers in their environments. These bacteria are Gram-negative, non-spore-forming rods. They are true bacteria as opposed to the other inhabitants of extreme environments, the Archaea.
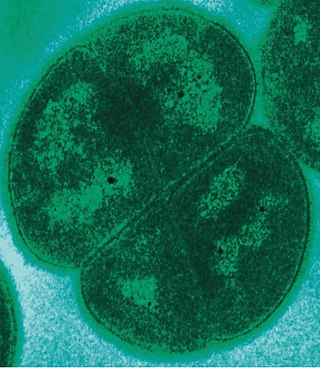
Deinococcota is a phylum of bacteria with a single class, Deinococci, that are highly resistant to environmental hazards, also known as extremophiles. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them gram-positive stains, but they include a second membrane and so are closer in structure to those of gram-negative bacteria.

Acidobacteriota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. Its members are physiologically diverse and ubiquitous, especially in soils, but are under-represented in culture.
The Thermotogota are a phylum of the domain Bacteria. The phylum Thermotogota is composed of Gram-negative staining, anaerobic, and mostly thermophilic and hyperthermophilic bacteria.
Fibrobacterota is a small bacterial phylum which includes many of the major rumen bacteria, allowing for the degradation of plant-based cellulose in ruminant animals. Members of this phylum were categorized in other phyla. The genus Fibrobacter was removed from the genus Bacteroides in 1988.
The Gemmatimonadota are a phylum of bacteria established in 2003. The phylum contains two classes Gemmatimonadetes and Longimicrobia.

The PVC superphylum is a superphylum of bacteria named after its three important members, Planctomycetota, Verrucomicrobiota, and Chlamydiota. Cavalier-Smith postulated that the PVC bacteria probably lost or reduced their peptidoglycan cell wall twice. It has been hypothesised that a member of the PVC clade might have been the host cell in the endosymbiotic event that gave rise to the first proto-eukaryotic cell.
The Synergistota is a phylum of anaerobic bacteria that show Gram-negative staining and have rod/vibrioid cell shape. Although Synergistota have a diderm cell envelope, the genes for various proteins involved in lipopolysaccharides biosynthesis have not yet been detected in Synergistota, indicating that they may have an atypical outer cell envelope. The Synergistota inhabit a majority of anaerobic environments including animal gastrointestinal tracts, soil, oil wells, and wastewater treatment plants and they are also present in sites of human diseases such as cysts, abscesses, and areas of periodontal disease. Due to their presence at illness related sites, the Synergistota are suggested to be opportunistic pathogens but they can also be found in healthy individuals in the microbiome of the umbilicus and in normal vaginal flora. Species within this phylum have also been implicated in periodontal disease, gastrointestinal infections and soft tissue infections. Other species from this phylum have been identified as significant contributors in the degradation of sludge for production of biogas in anaerobic digesters and are potential candidates for use in renewable energy production through their production of hydrogen gas. All of the known Synergistota species and genera are presently part of a single class (Synergistia), order (Synergistiales), and family (Synergistaceae).
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photosynthesis ; and anaerobic halorespirers, which uses halogenated organics as electron acceptors.
In biology, a phylum is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta.
Lentisphaerota is a phylum of bacteria closely related to Chlamydiota and Verrucomicrobiota.

The FCB group is a superphylum of bacteria named after the main member phyla Fibrobacterota, Chlorobiota, and Bacteroidota. The members are considered to form a clade due to a number of conserved signature indels.
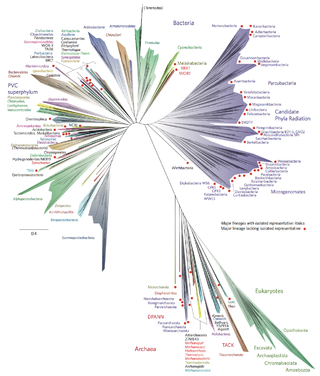
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.

Xenacoelomorpha is a small phylum of bilaterian invertebrate animals, consisting of two sister groups: xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs. This new phylum was named in February 2011 and suggested based on morphological synapomorphies, which was then confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of molecular data.

Tactopoda or Arthropodoidea is a proposed clade of protostome animals that includes the phyla Tardigrada and Euarthropoda, supported by various morphological observations. The cladogram below shows the relationships implied by this hypothesis.
The Coriobacteriia are a class of Gram-positive bacteria within the Actinomycetota phylum. Species within this group are nonsporulating, strict or facultative anaerobes that are capable of thriving in a diverse set of ecological niches. Gordonibacter species are the only members capable of motility by means of flagella within the class. Several species within the Coriobacteriia class have been implicated with human diseases that range in severity. Atopobium, Olsenella, and Cryptobacterium species have responsible for human oral infections including periodontitis, halitosis, and other endodontic infections. Eggerthella species have been associated with severe blood bacteraemia and ulcerative colitis.
Asgard or Asgardarchaeota is a proposed superphylum consisting of a group of archaea that contain eukaryotic signature proteins. It appears that the eukaryotes, the domain that contains the animals, plants, and fungi, emerged within the Asgard, in a branch containing the Heimdallarchaeota. This supports the two-domain system of classification over the three-domain system.