Same-sex marriage has been legal in Denmark since 15 June 2012. A bill for the legalization of same-sex marriages was introduced by the Thorning-Schmidt I Cabinet, and approved by the Folketing on 7 June 2012. It received royal assent by Queen Margrethe II on 12 June and took effect three days later. Polling indicates that a significant majority of Danes support the legal recognition of same-sex marriage. Denmark was the fourth Nordic country, after Norway, Sweden and Iceland, the eighth in Europe and the eleventh in the world to legalize same-sex marriage. It was the first country in the world to enact registered partnerships, which provided same-sex couples with almost all of the rights and benefits of marriage, in 1989.
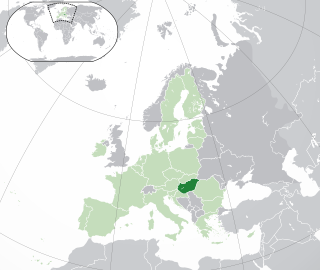
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Hungary face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Homosexuality is legal in Hungary for both men and women. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and sex is banned in the country. However, households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for all of the same legal rights available to heterosexual married couples. Registered partnership for same-sex couples was legalised in 2009, but same-sex marriage remains banned. The Hungarian government has passed legislation that restricts the civil rights of LGBT Hungarians – such as ending legal recognition of transgender Hungarians and banning LGBT content and displays for minors. This trend continues under the Fidesz government of Viktor Orbán. In June 2021, Hungary passed an anti-LGBT law on banning "homosexual and transexual propaganda" effective since 1 July. The law has been condemned by seventeen member states of the European Union. In July 2020, the European Commission started legal action against Hungary and Poland for violations of fundamental rights of LGBTQI people, stating: "Europe will never allow parts of our society to be stigmatized."

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Bulgaria face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex relationships are legal in Bulgaria, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2004, with discrimination based on "gender change" being outlawed since 2015. In July 2019, a Bulgarian court recognized a same-sex marriage performed in France in a landmark ruling. For 2020, Bulgaria was ranked 37 of 49 European countries for LGBT rights protection by ILGA-Europe. Like most countries in Central and Eastern Europe, post-Communist Bulgaria holds socially conservative attitudes when it comes to such matters as homosexuality and transgender people.
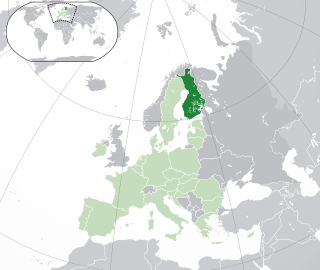
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Finland are among the most advanced in the world. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity have been legal in Finland since 1971 with "promotion" thereof decriminalized and the age of consent equalized in 1999. Homosexuality was declassified as an illness in 1981. Discrimination based on sexual orientation in areas such as employment, the provision of goods and services, etc., was criminalized in 1995 and discrimination based on gender identity in 2005.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) rights in Iceland rank among the highest in the world. Icelandic culture is generally tolerant towards homosexuality and transgender individuals, and Reykjavík has a visible LGBT community. Iceland ranked first on the Equaldex Equality Index in 2023, and second after Malta according to ILGA-Europe's 2024 LGBT rights ranking, indicating it is one of the safest nations for LGBT people in Europe. Conversion therapy in Iceland has been illegal since 2023.
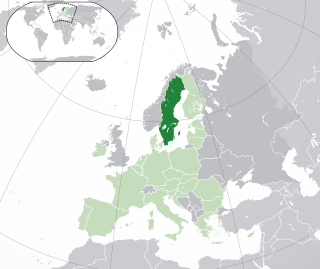
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Sweden are regarded as some of the most progressive in Europe and the world. Same-sex sexual activity was legalized in 1944 and the age of consent was equalized to that of heterosexual activity in 1972. Sweden also became the first country in the world to allow transgender people to change their legal gender post-sex reassignment surgery in 1972, whilst transvestism was declassified as an illness in 2009. Legislation allowing legal gender changes without hormone replacement therapy and sex reassignment surgery was passed in 2013.
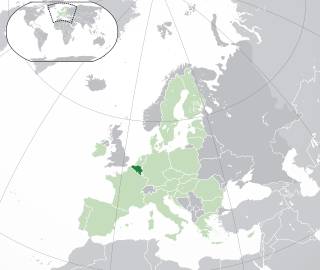
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Belgium are regarded as some of the most progressive in Europe and the world. In 2023, ILGA-Europe ranked Belgium as second in the European Union for LGBT rights protection, behind Malta. In 2024, ILGA-Europe ranked Belgium the third highest after Malta and Iceland.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Cyprus have evolved in recent years, but LGBTQ people still face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity were decriminalised in 1998, and civil unions which grant several of the rights and benefits of marriage have been legal since December 2015. Conversion therapy was banned in Cyprus in May 2023. However, adoption rights in Cyprus are reserved for heterosexual couples only.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Luxembourg have the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. Partnerships, which grant many of the benefits of marriage, have been recognised since 2004. In June 2014, the Luxembourgish Parliament passed a law enabling same-sex marriage and adoption rights, which took effect on 1 January 2015. Additionally, discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and "change of sex" in employment, healthcare and the provision of goods and services is outlawed, and transgender people are allowed to change their legal gender on the basis of self-determination.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Malta rank among the highest in the world. Throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the rights of the LGBTQ community received more awareness and same-sex sexual activity was legalized on 29 January 1973. The prohibition was already dormant by the 1890s.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Moldova face legal and social challenges and discrimination not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as households headed by opposite-sex couples. Same-sex unions are not recognized in the country, so consequently same-sex couples have little to no legal protection. Nevertheless, Moldova bans discrimination based on sexual orientation in the workplace, and same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1995.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Norway have the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. In 1981, Norway became one of the first countries in the world to enact an anti-discrimination law explicitly including sexual orientation. Same-sex marriage, adoption, and assisted insemination treatments for lesbian couples have been legal since 2009. In 2016, Norway became the fourth country in Europe to pass a law allowing the change of legal sex for transgender people based on self-determination. On 1 January 2024, conversion therapy became legally banned within Norway.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Portugal are among the most advanced in the world; having improved substantially in the 21st century. After a long period of oppression during the Estado Novo, Portuguese society has become increasingly accepting of homosexuality, which was decriminalized in 1982, eight years after the Carnation Revolution. Portugal has wide-ranging anti-discrimination laws and is one of the few countries in the world to contain a ban on discrimination based on sexual orientation in its Constitution. On 5 June 2010, the state became the eighth in the world to recognize same-sex marriage. On 1 March 2011, a gender identity law, said to be one of the most advanced in the world, was passed to simplify the process of sex and name change for transgender people. Same-sex couples have been permitted to adopt since 1 March 2016.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Slovenia have significantly evolved over time, and are considered among the most advanced of the former communist countries. Slovenia was the first post-communist country to have legalised same-sex marriage, and anti-discrimination laws regarding sexual orientation and gender identity have existed nationwide since 2016.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in the Faroe Islands are relatively similar to that of Denmark. The progress of LGBT rights has been slower, however. While same-sex sexual activity has been legal in the Faroe Islands since the 1930s, same-sex couples never had a right to a registered partnership. In April 2016, the Løgting passed legislation legalizing civil same-sex marriage on the Faroes, recognizing same-sex marriages established in Denmark and abroad and allowing same-sex adoption. This was ratified by the Folketing in April 2017. The law went into effect on 1 July 2017.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Kosovo have improved in recent years, most notably with the adoption of the new Constitution, banning discrimination based on sexual orientation. Kosovo remains one of the few Muslim-majority countries that hold regular pride parades.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Greenland are some of the most extensive in the Americas and the world, relatively similar to those in Denmark proper in Europe. Same-sex sexual activity is legal, with an equal age of consent, and there are some anti-discrimination laws protecting LGBT people. Same-sex couples had access to registered partnerships, which provided them with nearly all of the rights provided to married opposite-sex couples, from 1996 to 2016. On 1 April 2016, a law repealing the registered partnership act and allowing for same-sex marriages to be performed came into effect.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in North Macedonia face discrimination and some legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity have been legal in North Macedonia since 1996, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

LGBT rights in the European Union are protected under the European Union's (EU) treaties and law. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in all EU member states and discrimination in employment has been banned since 2000. However, EU states have different laws when it comes to any greater protection, same-sex civil union, same-sex marriage, and adoption by same-sex couples.

Adoption by LGBT people in Europe differs in legal recognition from country to country. Full joint adoption or step-child adoption or both is legal in 23 of the 56 European countries, and in all dependent territories.
























