This is a comparison of chipsets, manufactured by ATI Technologies.
This is a comparison of chipsets, manufactured by ATI Technologies.
| Codename | Model | Release date | Processors supported | Fabrication process(nm) | FSB/HT Frequency (MHz) | CrossFire Enabled | Features | Southbridge | NB-SB Interface | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATI A3 | IGP 320 | 2002 | Athlon, Duron | 180 | 266/200 (FSB) | No | Radeon VE IGP (Radeon 7000)160 MHz, AGP 4x | ATI IXP200/IXP250, | A-Link/PCI | HydraVision, Video Immersion, TV-out |
| ATI U1 | IGP 320M | Athlon 4 Mobile, Athlon XP-M, Mobile Duron | ATI PowerPlay, HydraVision, Video Immersion, TV-out | |||||||
| RS380 | ATI Radeon 380 IGP | Athlon 64, Sempron (Socket 754) | 150 | 800? BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | Radeon 9000 IGP, AGP 8x | SB300C, SB380, SB210 (IXP200/250) | |||
| RX380 | Athlon 64, Sempron (Socket 754) | 150 | 800? BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | AGP 8x | SB300C, SB380, SB210 (IXP200/250) | ||||
| RS380M | ATI Radeon 380M IGP | Mobile Athlon 64, Mobile Sempron, Turion 64 | 150 | 800 BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | Radeon 9000 IGP, AGP 8x | Mobile chipset PowerPlay 4.0 support | |||
| RS480 | ATI Radeon Xpress 200 | November 8, 2004 | Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron | 130 | 1000 BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | Radeon X300 graphics core 300 MHz | SB400, SB450, SB460, ULi M1573 | A-Link Express [a] | |
| RX480 | ATI Radeon Xpress 200P | Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron | 130 | 1000 BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | SB400, SB450, SB460, ULi M1573 | A-Link Express [a] | |||
| RS480M | ATI Radeon Xpress 200M (1100/1150) | Mobile Athlon 64, Mobile Sempron, Turion 64, Athlon 64 | 130 | 800 BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | Radeon X300 IGP (Xpress 1100, 300 MHz/ Xpress 1150, 400 MHz) | Mobile chipset PowerPlay 5.0 support | |||
| RS482 | ATI Radeon Xpress 1100 (ATI Radeon Xpress 200) | 2005 | Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron | 110 | 1000 BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | Radeon X300 IGP, 300 MHz | SB450, SB460, ULi M1575 | A-Link Express II [a] | No sideport memory |
| RS485 | ATI Radeon Xpress 1150 (ATI Radeon Xpress 200) | May 23, 2006 | Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron | 110 | 1000 BI-DIRECTIONAL | No | Radeon X300 IGP, 400 MHz | SB450, SB460, SB600, ULi M1575 | A-Link Express II [a] | |
| RD480 | ATI CrossFire Xpress 1600 (ATI Radeon Xpress 200 CrossFire Edition) | September 27, 2005 | Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron | 110 | 1000 BI-DIRECTIONAL | Yes, x8 | SB600, ULi M1575 | A-Link Express II [a] | ||
| RD580 | ATI Radeon Xpress 3200 | March 1, 2006 | Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron | 110 | 1000 BI-DIRECTIONAL | Yes, x16 | SB600 | A-Link Express II [a] |
| Codename | Model | Year | Fabrication process (nm) | SATA Ports | USB Ports | Audio | IDE Channels (2 Devices/Channel) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IXP200 | Radeon 320(M)/330/34x(M)/350M/360 IGP | 2002 | 0 | 6 USB2 | AC'97 | 2 ATA100 | A-Link, 3Com 10/100 Ethernet | |
| IXP250 | A-Link, 3Com 10/100 Ethernet, DMI, MBA, ASF, WOL | |||||||
| SB300C | 2003 | 1 (SATA 150 Mbit/s) | 6 | AC'97 | 2 (ATA133) | 10/100 Ethernet, APM | ||
| IXP380/SB380 | 2003 | 1 (SATA 150 Mbit/s) | 6 (USB 2.0) | AC'97 | 2 (ATA 133) | 10/100 Ethernet, APM, 8-bit HyperTransport links | ||
| IXP400/SB400 | Radeon Xpress 200 Radeon Xpress 1150 | 2004 | 4 | 8 | HD | 2 | ||
| IXP450/SB450 | Radeon Xpress 200 Radeon Xpress 1150 | 2004 | 4 | 8 | HD | 2 (UDMA 100/133) | RAID 0 and 1 | |
| IXP460/SB460 | Radeon Xpress 1600 Radeon Xpress 1150 | 2004 | 4 | 8 | HD | 1 | ||
| SB600 | AMD 480/570/580 CrossFire Chipset | 2006 | 130 | 4 | 10 | HD | 1 (ATA 133) | RAID 0, 1, 10 eSATA, ASF 2.0 |
| Codename | Model | Year | Processors Supported | Fabrication process (nm) | FSB/QDR Frequency (MHz) | Crossfire Enabled | Features | Southbridge | NB-SB Interface | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS200L | IGP 330 | 2002 | Pentium 4 (Northwood, Prescott) | 180 | 400 | No | Radeon VE (7000) IGP 150 MHz, AGP 4x, up to 1GiB of DDR-200 or 266 | ATI IXP200/IXP250, VIA VT82C686B, ALI M1535D+ | A-Link/PCI | HydraVision, Video Immersion, TV-out |
| RS200 | IGP 340 | 533/400 | Radeon VE (7000) IGP 183 MHz, AGP 4x, up to 1GiB of DDR-200 or 266 | |||||||
| RS200M revA | IGP 340M | Pentium 4-M | ATI PowerPlay, HydraVision, Video Immersion, TV-out | |||||||
| RS200M+ | IGP 345M | |||||||||
| RS200M revB | IGP 350M | 2003 | Pentium M | |||||||
| RS250M | IGP 7000 (IGP 360) | 2003 | Pentium 4-M HT, Pentium 4, Pentium M | Radeon VE (7000) IGP 183 MHz, AGP 4x, up to 4GiB of DDR-200, 266 or 333 | ATI PowerPlay 2.0, HydraVision, Video Immersion, TV-out | |||||
| RS350 | ATI Radeon 9100 PRO IGP | 2004 | 800 | No, AGP 8x | Radeon 9100 IGP | IXP150, IXP200, IXP300 | Dual Channel Memory | |||
| RC350 | ATI Radeon 9000 PRO IGP | 2004 | 800 | No, AGP 8x | Radeon 9000 IGP | IXP150, IXP200, IXP300 | Single Channel Memory | |||
| RX330 | 800 | No, AGP 8x | As RS350 without IGP | IXP150, IXP200, IXP300 | ||||||
| RX320M | Mobile chipset, PowerPlay | |||||||||
| RS400 RS415 RC400 RC410 | ATI Radeon Xpress 1150 (originally named ATI Radeon Xpress 200 for Intel) Intel Essential Series D101GCC/D102GCC (Grand Country) | Mar 11 2005 | Pentium 4, Core 2 | 1066 | No | Radeon X300 IGP | ||||
| RS600 | ATI Radeon Xpress 1250 | Aug 29 2006 | Pentium 4, Core 2 | 80 | 1066 | No | Radeon X700 IGP, 500 MHz | AVIVO, HDMI with HDCP, Dual Channel Memory | ||
| RD600 | ATI Radeon CrossFire Xpress 3200 | Sep 27 2006 | Pentium 4, Core 2 | 1066 | Yes, Dual x8 | Dual Channel Memory | ||||
| Codename | Model | Year | Processors Supported | Fabrication process (nm) | FSB/QDR Frequency (MHz) | Crossfire Enabled | Features | Southbridge | NB-SB Interface | Notes |
| Codename | Model | Year | Fabrication process (nm) | SATA Ports | USB Ports | Audio | IDE Channels (2 Devices/Channel) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IXP150 | Radeon 9100 IGP | 0 | 6 | AC'97 | 2 (UDMA33/66) | 3Com 10/100 Ethernet | ||
| IXP210 | 1 (SATA 150 Mbit/s) | 6 | AC'97 | 1 (UDMA 33/66/100/133) | 3Com 10/100 Ethernet, APM, ALink/ALink II | |||
| IXP250 | Radeon 330 IGP | 0 | 6 | AC'97 | 1 (UDMA 100) | 3Com 10/100 Ethernet, DMI, MBA, and ASF | ||
| IXP300/SB300 | Radeon 340 IGP | 2 (SATA 150 Mbit/s) | 6 | AC'97 | 1 (UDMA 33/66/100/133) | 3Com 10/100 Ethernet, APM, ALink/ALink II | ||
| IXP320/SB320 | 2 (SATA 150 Mbit/s) | 8 | AC'97 | 1 (UDMA 33/66/100/133) | 3Com 10/100 Ethernet, RAID 0 and 1, APM, ALink/ALink II | |||
| IXP400/SB400 | Radeon Xpress 200 Radeon Xpress 1150 | 2004 | 4 (SATA 150 Mbit/s) | 8 | AC'97 | 2 (UDMA 100/133) | ||
| IXP450/SB450 | Radeon Xpress 200 Radeon Xpress 1150 | 2004 | 4 | 8 | HD | 2 | ||
| IXP460/SB460 | Radeon Xpress 1600 Radeon Xpress 1150 | 2004 | 4 | 8 | HD | 1 | ||
| SB600 | AMD 480/570/580 CrossFire Chipset | 2006 | 130 | 4 | 10 | HD | 1 (ATA 133) | RAID 0, 1, 10 eSATA, ASF 2.0 |

A graphics card is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to erroneously refer to the graphics card as a whole.

ATI Technologies Inc. was a Canadian semiconductor technology corporation based in Markham, Ontario, that specialized in the development of graphics processing units and chipsets. Founded in 1985, the company listed publicly in 1993 and was acquired by AMD in 2006. As a major fabless semiconductor company, ATI conducted research and development in-house and outsourced the manufacturing and assembly of its products. With the decline and eventual bankruptcy of 3dfx in 2000, ATI and its chief rival Nvidia emerged as the two dominant players in the graphics processors industry, eventually forcing other manufacturers into niche roles.

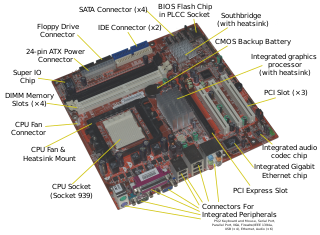
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance. Sometimes the term "chipset" is used to describe a system on chip (SoC) used in a mobile phone.

A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit initially designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. After their initial design, GPUs were found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. Other non-graphical uses include the training of neural networks and cryptocurrency mining.

In computing, a northbridge is a microchip that comprises the core logic chipset architecture on motherboards to handle high-performance tasks, especially for older personal computers. It is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB), and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard.

The nForce4 is a motherboard chipset released by Nvidia in October 2004. The chipset supports AMD 64-bit processors and Intel Pentium 4 LGA 775 processors.

Scalable Link Interface (SLI) is the brand name for a now discontinued multi-GPU technology developed by Nvidia for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output. SLI is a parallel processing algorithm for computer graphics, meant to increase the available processing power.

AMD CrossFire is a brand name for the multi-GPU technology by Advanced Micro Devices, originally developed by ATI Technologies. The technology allows up to four GPUs to be used in a single computer to improve graphics performance.
The nForce 500 is a motherboard chipset series and the successor to the nForce4 series. It was revealed by NVIDIA on 2006-03-07 and released on May 23, 2006. The nForce 500 series supports AMD's Socket AM2 and support for Intel's LGA 775 has also been added.
The Xpress 3200 is a revision of the Xpress 200 computer chipset released by ATI. The chipset supports AMD64 processors for Socket 939 and Socket AM2.

ALi Corporation is a major designer and manufacturer of embedded systems integrated circuits, and a former manufacturer of personal computer integrated circuits. It is based in Taiwan, and is a subsidiary of the Acer group.
AMD 580 chipset series is a computer chipset series designed by the AMD Graphics Product Group, for the AMD processors. It was designed for usage with ATI's CrossFire Multi GPU Technology, with both PCI Express slots running at x16 lanes each.
The nForce 600 chipset was released in the first half of November 2006, coinciding with the GeForce 8 series launch on November 8, 2006. The nForce 600 supports Intel's LGA 775 socket and AMD's Quad FX platform and replaces the nForce 500 series.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.
The AMD 690 chipset series is an integrated graphics chipset family which was developed and manufactured by AMD subsidiary ATI for both AMD and Intel platforms focusing on both desktop and mobile computing markets. The corresponding chipset for the Intel platform has a marketing name of Radeon Xpress 1200 series.

The nForce 700 is a chipset series designed by Nvidia first released in December 2007. The series supports both Intel Core 2 and AMD Phenom processors, and replaces the nForce 600 series chipsets. Several members were spotted, including the codenamed MCP72 for AMD processors and the C72 for Intel processors, launched with the name "nForce 780a" and "nForce 780i" chipsets respectively. Currently, the released variants are the 750i, 780i, 790i, and 790i Ultra.
This is a comparison of chipsets designed by Nvidia. Nvidia stopped producing chipsets in 2009. Nvidia codenames its chipsets MCPs.
GPU switching is a mechanism used on computers with multiple graphic controllers. This mechanism allows the user to either maximize the graphic performance or prolong battery life by switching between the graphic cards. It is mostly used on gaming laptops which usually have an integrated graphic device and a discrete video card.

The AMD 900 chipset series is identical to the AMD 800 chipset series except for the fact that it is only found on Socket AM3+ mainboards, whereas its predecessor is only found on Socket AM3 mainboards. It was released in 2011.

On June 26, 2007, Dell released the new Inspiron desktop series, under the Dell Inspiron branding, as a replacement to the Dell Dimension desktop computers.